IsaacSim Bridge Functions
This section shows basic IsaacSim Bridge Add-In functions in IsaacSim.
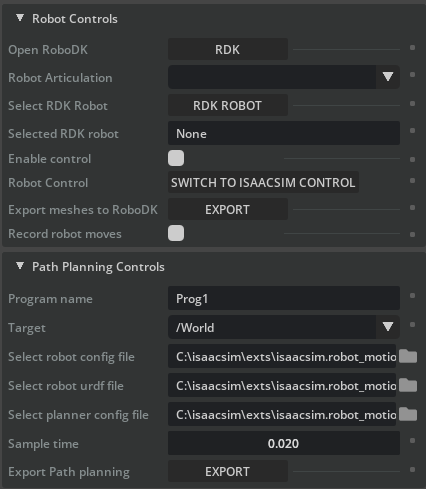
The IsaacSim Bridge Extension window contains following functional elements:
1.Robot Controls
a.Open RoboDK: Opens RoboDK if it is not open or connects to the currently running instance of RoboDK if it is. This is required for the extension to function.
b.Robot Articulation: Select the articulation within IsaacSim to be used.
c.Select RDK Robot: Select the robot within the RoboDK station to be used.
d.Selected RDK Robot: Prints out the name of the selected robot.
e.Enable Control: Enables robot communication between IsaacSim scene and RoboDK station.
f.Robot Control: Select the reference robot that should be used as the robot to be matched. If the option displays Switch to IsaacSim Control, then RoboDK acts as the master and the robot articulation within IsaacSim will follow the pose of the selected RoboDK robot.
g.Export meshes to RoboDK: Convert Mesh objects in the IsaacSim scene to 3D mesh files and load them in the RoboDK station. The converted object’s origin will be at base of the station but will be offset so that the current location matches its location in the IsaacSim scene. Each of the Mesh objects from IsaacSim will be its own object in the RoboDK station and can be moved around.
h.Record robot moves: Records all the moves done by the IsaacSim robot and adds them to a program within RoboDK. This is useful if you have a program within IsaacSim that you want to export to RoboDK.
2.Path Planning Controls
a.Program name: Program name to use when exporting to RDK.
b.Target: Drop down menu of XForms to be used as target for the RRT path planner.
c.Select robot config file: Select the robot config file to be used for the path planning. File format must be yaml.
d.Select robot urdf file: Select the robot definition file to be used for the path planning. File format must be urdf.
e.Select planner config file: Select the planner config file to be used for the path planning. File format must be yaml.
f.Sample time: Select the sample time to be used when generating the path. A shorter sample time will lead to more MoveJ instructions in the program with smaller steps in between them.
g.Export Path planning: Uses RRT to calculate a path between current robot pose and selected target and create a robot program with a list of instructions completing the path.