3. Post Processors¶
A Post Processor defines how robot programs should be generated for a specific robot controller. This allows you to execute a simulation from RoboDK on a real robot. A Post Processor is a key component of simulation and offline programming of industrial robots.
- More information regarding post processors is available in the following two links:
RoboDK documentation about Post Processors: https://robodk.com/doc/en/Post-Processors.html
List of officially available Post Processors with the RoboDK installer: https://robodk.com/posts
When you install RoboDK you’ll have access to many Post Processors, providing support for many robot brands (such as ABB, Fanuc, KUKA, Motoman, UR, …). Post Processors are located in the folder: C:/RoboDK/Posts/. Each Post Processor is a .py file. You must place the py Post Processor file in C:/RoboDK/Posts/ to use a Post Processor that has been provided to you. To remove an existing Post Processor you can simply delete the corresponding py file located in C:/RoboDK/Posts/.
- For example, for KUKA robots you can find the following Post Processors:
KUKA_KRC2: Generates SRC program files compatible with KUKA KRC2 controllers.
KUKA_KRC4: Generates SRC program files compatible with KUKA KRC4 controllers.
KUKA_IIWA: Generates JAVA programs using the KUKA.Sunrise platform, required by KUKA IIWA robots.
Python should be installed and working with RoboDK to properly use Post Processors (How to install).
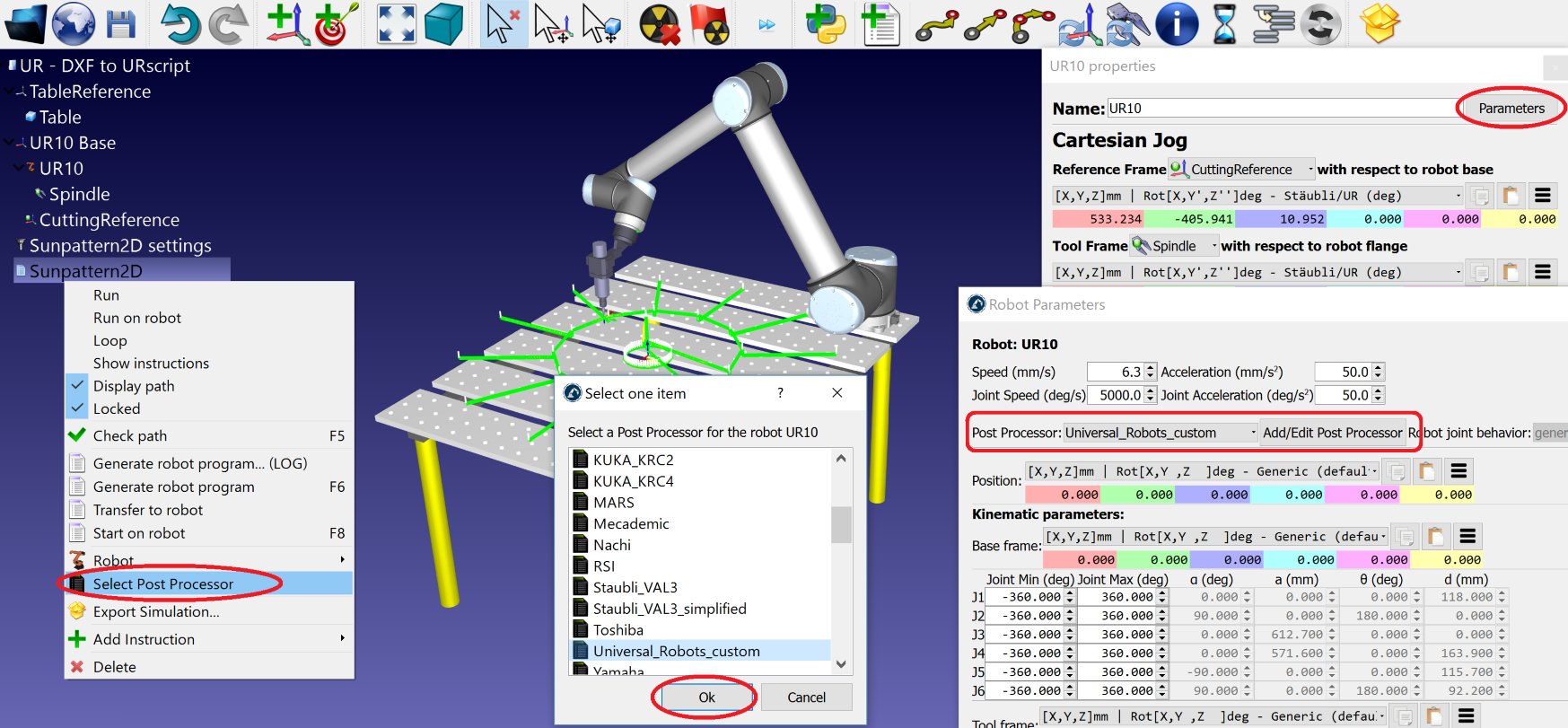
- Follow these steps in RoboDK to link a robot to a specific Post Processor:
Open the robot panel by double clicking a robot.
Select
Parametersat the top right.Select
Select Post Processor.
Alternatively, you can right click a program, then select Select Post Processor.
- To modify or create a Post Processor:
Select
Program-Add/Edit Post Processor.Select an existing Post Processor or create a new one. A template like the example provided in this section will be provided if you decide to create a new Post Processor.
You can edit a Post Processor using a text editor or a Python editor.
A Python editor such as VSCode/VSCodium or Python IDLE allows you to quickly test the Post Processor with a sample program at the end of the module. You can also run a Post Processor file to see a sample of the output that it will generate (double click the py file, or right click the py file, then select Open).
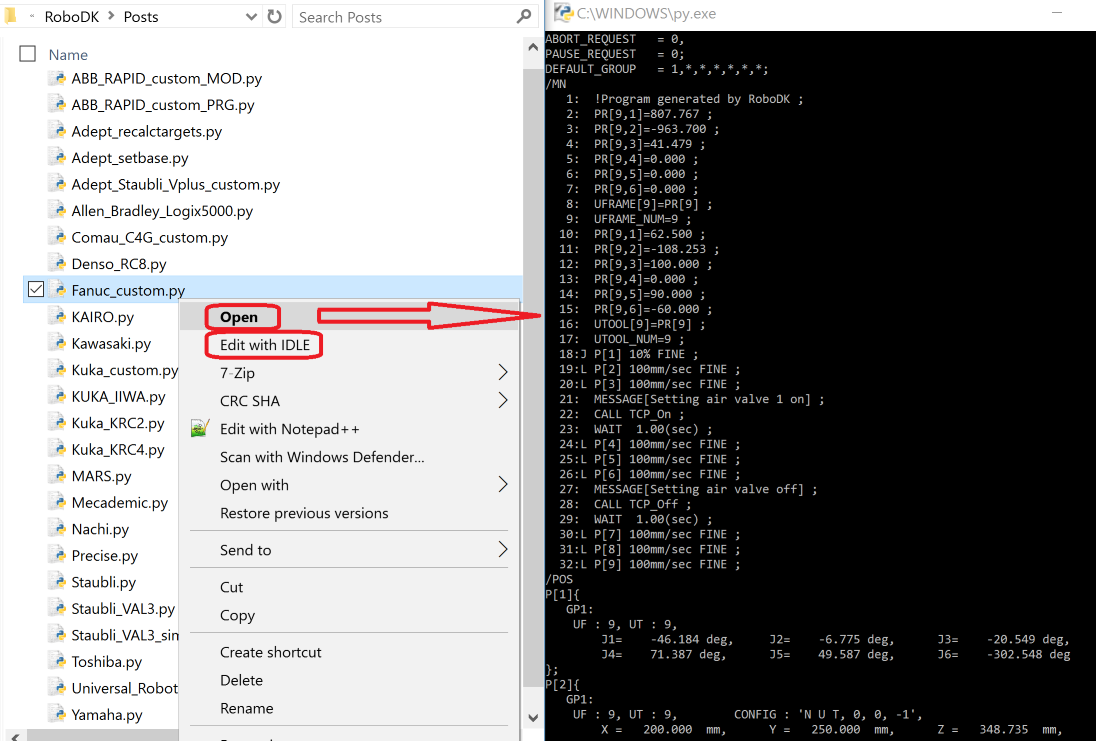
- You can also manually edit a Post Processor without using RoboDK:
Go to the folder
C:/RoboDK/Posts/and open the correspondingpyfile with a text editor such as VSCode/VSCodium, Notepad or Python IDLE (for example, right click thepyfile, then, selectEdit with IDLE)Make any required modifications.
Test the result: Run the Post Processor by double clicking the
pyfile (or right click, then, selectOpen, as shown in the following image).
Alternatively, you can run and preview the result sing a Python editor such as Python IDLE.
You can customize Post Processors by changing the variables ready for customization (either if the post is compiled or not) or you can edit the source code of a post processor. If you would like to make major changes to a post processor you can request the source code by contacting us. You can also use the Post Processor Editor Add-in to easily customize an existing post processor: https://robodk.com/addin/com.robodk.plugin.postprocessoreditor
If you customize a Post Processor, make sure to create a copy using a different and unique name so that if you reinstall RoboDK your edits are not lost or overridden.
3.1. Post Processor Methods¶
This section shows the procedures that every Post Processor should define to properly generate programs from RoboDK simulations. This step is transparent to the end user of RoboDK because the program is automatically generated once a Post Processor has been defined. You do not need to understand what is going on behind the scenes unless you are willing to create or modify a Post Processor.
Once a robot program is ready to be generated, RoboDK creates a generic Python file (pre processed) in %TEMP% that is linked to a Post Processor. The pre-processed file is executed using the selected Post Processor and the desired program is obtained.
- General tips when creating a post processor:
Avoid using instances of
Robolinkand/orItemin the post processor unless absolutely necessary.Add a log using
addlogfor incompatible, unavailable or incomplete features (for example, a robot that does not support I/O or FTP).Use editable variables in the class header for added flexibility. More information here: https://robodk.com/doc/en/Post-Processors.html#EditPost
Watch for unit conversion. Some controllers use percent (%) for speed, while RoboDK outputs mm/s.
- class samplepost.RobotPost(robotpost='', robotname='', robot_axes=6, *args, **kwargs)¶
RoboDK Post Processor class. Define variables that can be edited by the user to customize the behavior of the post processor.
Post Processors can be compiled (.pyc, .pyd or .so). However, object variables can be exposed to the user for further customization.
More information on how users can modify variables of a RoboDK Post Processor here:
class RobotPost(object): # Public: define variables that can be edited by the user below MY_PUBLIC_VAR = TRUE # ---------------------------------------------------- # Private: define internal variables that cannot be edited by the user below (note the "# ---------..." splitter) MY_PRIVATE_VAR = False
- __init__(robotpost='', robotname='', robot_axes=6, *args, **kwargs)¶
Create a new post processor.
Tip: Avoid using instances of
robodk.robolink.Robolink()and/orrobodk.robolink.Item()in the post processor unless absolutely necessary.- Parameters
robotpost (str) – Name of the post processor
robotname (str) – Name of the robot
robot_axes (int) – Number of axes of the robot, including synchronized axes
axes_type (list of str, optional) – Type of each axes of the robot (‘R’: Robot rotative, ‘T’: Robot translation, ‘J’: Ext. axis rotative, ‘L’: Ext. axis linear)
native_name (str, optional) – Native name of the robot (before any rename)
ip_com (str, optional) – IP address of the robot (“Connect” tab in RoboDK)
api_port (int, optional) – RoboDK API port to the RoboDK instance
prog_ptr (int, optional) – RoboDK Item pointer to the program generated
robot_ptr (int, optional) – RoboDK Item pointer to the robot associated with the program generated
pose_turntable (
robodk.robomath.PosePP(), optional) – Pose of the synchronized turn tablepose_rail (
robodk.robomath.PosePP(), optional) – Pose of the synchronized linear raillines_x_prog (int, optional) – Maximum number of lines per program (to generate multiple files). This setting can be overridden by in RoboDK (Tools-Options-Program)
pulses_x_deg (list of int, optional) – Pulses per degree (provided in the robot parameters of RoboDK)
Example for a program using the KUKA KRC2 post processor and a KUKA KR 500 3 robot with synchronized linear rail and turn table:
RobotPost(r"""KUKA_KRC2""",r"""KUKA KR 500 3""",9, axes_type=['R','R','R','R','R','R','T','J','J'], native_name=r"""KUKA KR 500 3""", ip_com=r"""192.168.241.127""", api_port=20500, prog_ptr=2109546424992, robot_ptr=2109347059584, pose_turntable=p(1890.627070,1670.706012,-504.767930,-0.060103,0.046410,-0.246888), pose_rail=p(0.000000,0.000000,0.000000,90.000000,0.000000,0.000000))
- ProgStart(progname, *args, **kwargs)¶
Start a new program given a name. Multiple programs can be generated at the same time.
Tip: ProgStart is triggered every time a new program must be generated.
- Parameters
progname (str) – Name of the program
- ProgFinish(progname, *args, **kwargs)¶
This method is executed to define the end of a program or procedure. One module may have more than one program. No other instructions will be executed before another
samplepost.RobotPost.ProgStart()is executed.Tip: ProgFinish is triggered after all the instructions of the program.
- Parameters
progname (str) – Name of the program
- ProgSave(folder, progname, ask_user=False, show_result=False, *args, **kwargs)¶
Saves the program. This method is executed after all programs have been processed.
Tip: ProgSave is triggered after all the programs and instructions have been executed.
- Parameters
folder (str) – Folder hint to save the program
progname (str) – Program name as a hint to save the program
ask_user (bool, str) – True if the default settings in RoboDK are set to prompt the user to select the folder
show_result (bool, str) – False if the default settings in RoboDK are set to not show the program once it has been saved. Otherwise, a string is provided with the path of the preferred text editor
- ProgSendRobot(robot_ip, remote_path, ftp_user, ftp_pass, *args, **kwargs)¶
Send a program to the robot using the provided parameters. This method is executed right after ProgSave if we selected the option “Send Program to Robot”. The connection parameters must be provided in the robot connection menu of RoboDK.
- Parameters
robot_ip (str) – IP address of the robot
remote_path (str) – Remote path of the robot
ftp_user (str) – FTP user credential
ftp_pass (str) – FTP user password
- MoveJ(pose, joints, conf_RLF, *args, **kwargs)¶
Defines a joint movement.
Tip: MoveJ is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Move Joint Instruction.
- Parameters
pose (
robodk.robomath.Mat(), None) – Pose target of the tool with respect to the reference frame. Pose can be None if the target is defined as a joint targetjoints (float list) – Robot joints as a list
conf_RLF (int list, None) – Robot configuration as a list of 3 ints: [REAR, LOWER-ARM, FLIP]. [0,0,0] means [front, upper arm and non-flip] configuration. Configuration can be None if the target is defined as a joint target
- MoveL(pose, joints, conf_RLF, *args, **kwargs)¶
Defines a linear movement.
Tip: MoveL is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Move Linear Instruction.
- Parameters
pose (
robodk.robomath.Mat(), None) – Pose target of the tool with respect to the reference frame. Pose can be None if the target is defined as a joint targetjoints (float list) – Robot joints as a list
conf_RLF (int list, None) – Robot configuration as a list of 3 ints: [REAR, LOWER-ARM, FLIP]. [0,0,0] means [front, upper arm and non-flip] configuration. Configuration can be None if the target is defined as a joint target
- MoveC(pose1, joints1, pose2, joints2, conf_RLF_1, conf_RLF_2, *args, **kwargs)¶
Defines a circular movement.
Tip: MoveC is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Move Circular Instruction.
- Parameters
pose1 (
robodk.robomath.Mat(), None) – Pose target of a point defining an arc (waypoint). Pose can be None if the target is defined as a joint targetpose2 (
robodk.robomath.Mat(), None) – Pose target of the end of the arc (final point). Pose can be None if the target is defined as a joint targetjoints1 (float list) – Robot joints of the waypoint
joints2 (float list) – Robot joints of the final point
conf_RLF_1 (int list, None) – Robot configuration of the waypoint as a list of 3 ints: [REAR, LOWER-ARM, FLIP]. [0,0,0] means [front, upper arm and non-flip] configuration. Configuration can be None if the target is defined as a joint target
conf_RLF_2 (int list, None) – Robot configuration of the final point as a list of 3 ints: [REAR, LOWER-ARM, FLIP]. [0,0,0] means [front, upper arm and non-flip] configuration. Configuration can be None if the target is defined as a joint target
- setFrame(pose, frame_id, frame_name, *args, **kwargs)¶
Defines a new reference frame with respect to the robot base frame. This reference frame is used for following pose targets used by movement instructions.
Tip: setFrame is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Set Reference Frame Instruction.
- Parameters
pose (
robodk.robomath.Mat()) – Pose of the reference frame with respect to the robot base frameframe_id (int) – Number of the reference frame (if available, else -1)
frame_name (str) – Name of the reference frame as defined in RoboDK
- setTool(pose, tool_id, tool_name, *args, **kwargs)¶
Change the robot TCP (Tool Center Point) with respect to the robot flange. Any movement defined in Cartesian coordinates assumes that it is using the last reference frame and tool frame provided.
Tip: setTool is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Set Tool Frame Instruction.
- Parameters
pose (
robodk.robomath.Mat()) – Pose of the TCP frame with respect to the robot base frametool_id (int, None) – Tool ID (if available, else -1)
tool_name (str) – Name of the tool as defined in RoboDK
- Pause(time_ms, *args, **kwargs)¶
Defines a pause in a program (including movements). time_ms is negative if the pause must provoke the robot to stop until the user desires to continue the program.
Tip: Pause is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Pause Instruction.
- Parameters
time_ms (float) – Time of the pause, in milliseconds
- setSpeed(speed_mms, *args, **kwargs)¶
Changes the robot speed (in mm/s)
Tip: setSpeed is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Set Speed Instruction.
- Parameters
speed_mms (float) – Speed in mm/s
- setAcceleration(accel_mmss, *args, **kwargs)¶
Changes the robot acceleration (in mm/s^2)
Tip: setAcceleration is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Set Speed Instruction. An acceleration value must be provided.
- Parameters
accel_mmss (float) – Speed in mm/s^2
- setSpeedJoints(speed_degs, *args, **kwargs)¶
Changes the robot joint speed (in deg/s)
Tip: setSpeedJoints is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Set Speed Instruction. A joint speed value must be provided.
- Parameters
speed_degs (float) – Speed in deg/s
- setAccelerationJoints(accel_degss, *args, **kwargs)¶
Changes the robot joint acceleration (in deg/s^2)
Tip: setAccelerationJoints is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Set Speed Instruction. A joint acceleration value must be provided.
- Parameters
accel_degss (float) – Speed in deg/s^2
- setZoneData(zone_mm, *args, **kwargs)¶
Changes the smoothing radius (also known as rounding, blending radius, CNT, APO or zone data). If this parameter is higher it helps making the movement smoother
Tip: setZoneData is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Set Rounding Instruction.
- Parameters
zone_mm (float) – Rounding radius in mm
- setDO(io_var, io_value, *args, **kwargs)¶
Sets a variable (usually a digital output) to a given value. This method can also be used to set other variables.
Tip: setDO is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Set or Wait I/O Instruction.
- Parameters
io_var (int, str) – Variable to set, provided as a str or int
io_value (int, float, str) – Value of the variable, provided as a str, float or int
- setAO(io_var, io_value, *args, **kwargs)¶
Sets a an analog variable to a given value.
Tip: setAO is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Set or Wait I/O Instruction.
- Parameters
io_var (int, str) – Variable to set, provided as a str or int
io_value (int, float, str) – Value of the variable, provided as a str, float or int
- waitDI(io_var, io_value, timeout_ms=- 1, *args, **kwargs)¶
Waits for a variable (usually a digital input) to attain a given value io_value. This method can also be used to set other variables.Optionally, a timeout can be provided.
Tip: waitDI is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Set or Wait I/O Instruction.
- Parameters
io_var (int, str) – Variable to wait for, provided as a str or int
io_value (int, float, str) – Value of the variable, provided as a str, float or int
timeout_ms (float, int) – Maximum wait time
- RunCode(code, is_function_call=False, *args, **kwargs)¶
Adds code or a function call.
Tip: RunCode is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Function call Instruction.
- Parameters
code (str) – Code or procedure to call
is_function_call (bool) – True if the provided code is a specific function to call
- RunMessage(message, iscomment=False, *args, **kwargs)¶
Display a message in the robot controller screen (teach pendant)
Tip: RunMessage is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Show Message Instruction.
- Parameters
message (str) – Message to display on the teach pendant or as a comment on the code
iscomment (bool) – True if the message does not have to be displayed on the teach pendant but as a comment on the code
- addline(newline)¶
Add a new program line. This is a private method used only by the other methods.
- Parameters
newline (str) – New program line to add
- addlog(newline)¶
Add a message to the log. This is a private method used only by the other methods. The log is displayed when the program is generated to show any issues when the robot program has been generated.
- Parameters
newline (str) – New log line to add
3.2. Post Processor Example¶
This section shows a sample post processor. This sample Post Processor is used as a template when a new Post Processor is created using RoboDK.
# Copyright 2015 - RoboDK - https://robodk.com/
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# ----------------------------------------------------
# This file is a POST PROCESSOR for Robot Offline Programming to generate programs
#
# To edit/test this POST PROCESSOR script file:
# Select "Program"->"Add/Edit Post Processor", then select your post or create a new one.
# You can edit this file using any text editor or Python editor. Using a Python editor allows to quickly evaluate a sample program at the end of this file.
# Python should be automatically installed with RoboDK
#
# You can also edit the POST PROCESSOR manually:
# 1- Open the *.py file with Python IDLE (right click -> Edit with IDLE)
# 2- Make the necessary changes
# 3- Run the file to open Python Shell: Run -> Run module (F5 by default)
# 4- The "test_post()" function is called automatically
# Alternatively, you can edit this file using a text editor and run it with Python
#
# To use a POST PROCESSOR file you must place the *.py file in "C:/RoboDK/Posts/"
# To select one POST PROCESSOR for your robot in RoboDK you must follow these steps:
# 1- Open the robot panel (double click a robot)
# 2- Select "Parameters"
# 3- Select "Unlock advanced options"
# 4- Select your post as the file name in the "Robot brand" box
#
# To delete an existing POST PROCESSOR script, simply delete this file (.py file)
#
# ----------------------------------------------------
# More information about RoboDK Post Processors and Offline Programming here:
# https://robodk.com/help#PostProcessor
# https://robodk.com/doc/en/PythonAPI/postprocessor.html
# ----------------------------------------------------
# ----------------------------------------------------
# Description
#
#
# Supported Controllers
#
# ----------------------------------------------------
# ----------------------------------------------------
# Special commands for RoboDK before post processing
# Use the same commands available with "RDK.Command()"
# Do not use multi-line! RDK_COMMANDS = {} must be a single line!
#
# ProgMoveType requires RoboDK v5.7.3.24263 (Win64) or later
#
# Example:
#
# RDK_COMMANDS = {
# "ProgMoveNames": "1", # Tools->Options->Program->Export target names
# "ProgMoveExtAxesPoses": "1", # Tools->Options->Program->Export external axes poses
# "MoveLSplitMM": "2", # Force-split linear movements into smaller joint movements
# "MoveCSplitMM": "2",
# "MoveCSplitDeg": "90",
# "MoveCSplitMinMM": "0",
# "ProgMoveJType": "0", # Tools->Options->Programs->Output for joint movements (index = dropbox index, eg. 0 -> Default)
# "ProgMoveLType": "1", # Tools->Options->Programs->Output for linear movements (index = dropbox index, eg. 1 -> Joint)
# "ProgMoveCType": "2" # Tools->Options->Programs->Output for circular movements (index = dropbox index, eg. 2 -> Cartesian)
# }
RDK_COMMANDS = {"ProgMoveNames": "1", "ProgMoveExtAxesPoses": "1"}
# Import RoboDK tools
from robodk import robomath
from robodk import robodialogs
from robodk import robofileio
from robodk.robodialogs import mbox
# ----------------------------------------------------
def pose_2_str(pose):
"""Converts a robot pose target to a string according to the syntax/format of the controller.
**Tip**: Change the output of this function according to your controller.
:param pose: 4x4 pose matrix
:type pose: :meth:`robodk.robomath.Mat`
:return: postion as a XYZWPR string
:rtype: str
"""
[x, y, z, r, p, w] = robomath.pose_2_xyzrpw(pose)
return ('X%.3f Y%.3f Z%.3f R%.3f P%.3f W%.3f' % (x, y, z, r, p, w))
def joints_2_str(joints):
"""Converts a robot joint target to a string according to the syntax/format of the controller.
**Tip**: Change the output of this function according to your controller.
:param joints: robot joints as a list
:type joints: float list
:return: joint format as a J1-Jn string
:rtype: str
"""
str = ''
data = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K', 'L']
for i in range(min(len(joints), len(data))):
str = str + ('%s%.6f ' % (data[i], joints[i]))
str = str[:-1]
return str
def str_2_type(s):
"""Converts a string containing a numerical or true/false (case insensitive) to a basic data type (bool/int/float).
:param s: The string to process
:type s: str
:return: The basic data type (bool/int/float), or str if it fails
:rtype: str or bool or int or float
"""
if type(s) != str:
return s
if s.lower() in ['true', 'false']:
return bool(s)
try:
f = float(s)
if int(f) == f:
return int(f)
return f
except:
pass
return s
# ----------------------------------------------------
# Object class that handles the robot instructions/syntax
class RobotPost(object):
"""RoboDK Post Processor class. Define variables that can be edited by the user to customize the behavior of the post processor.
Post Processors can be compiled (.pyc, .pyd or .so). However, object variables can be exposed to the user for further customization.
More information on how users can modify variables of a RoboDK Post Processor here:
- https://robodk.com/doc/en/Post-Processors.html#PPEditor
- https://robodk.com/doc/en/Post-Processors.html#EditPost
.. code-block:: python
class RobotPost(object):
# Public: define variables that can be edited by the user below
MY_PUBLIC_VAR = TRUE
# ----------------------------------------------------
# Private: define internal variables that cannot be edited by the user below (note the "# ---------..." splitter)
MY_PRIVATE_VAR = False
"""
# Public: define variables that can be edited by the user below
#
# More information on how users can modify variables of a RoboDK Post Processor here:
# https://robodk.com/doc/en/Post-Processors.html#PPEditor
# https://robodk.com/doc/en/Post-Processors.html#EditPost
# Set the output program extension (for multiple files, handle separately)
PROG_EXT = 'txt'
# Default speed for linear moves in mm/s
DEFAULT_LINEAR_SPEED = 500.0
# Default acceleration for linear moves in mm/s^2
DEFAULT_LINEAR_ACCEL = 2000.0
# Default speed for joint moves in %
DEFAULT_JOINT_SPEED = 100.0
# Default acceleration for joint moves in %
DEFAULT_JOINT_ACCEL = 100.0
# Default blend radius (corners smoothing) in %
DEFAULT_BLENDING = 0.0
# Add the RoboDK frame name as a comment in the output program
ADD_FRAME_NAME = False
# Add the RoboDK tool name as a comment in the output program
ADD_TOOL_NAME = False
# Add the RoboDK target name as a comment in the output program
ADD_TARGET_NAME = False
# ----------------------------------------------------
# Private: define internal variables that cannot be edited by the user below (note the "# ---------..." splitter)
# MY_PRIVATE_VAR = False
def __init__(self, robotpost='', robotname='', robot_axes=6, *args, **kwargs):
"""Create a new post processor.
**Tip**: Avoid using instances of :meth:`robodk.robolink.Robolink` and/or :meth:`robodk.robolink.Item` in the post processor unless absolutely necessary.
:param robotpost: Name of the post processor
:type robotpost: str
:param robotname: Name of the robot
:type robotname: str
:param robot_axes: Number of axes of the robot, including synchronized axes
:type robot_axes: int
:param axes_type: Type of each axes of the robot ('R': Robot rotative, 'T': Robot translation, 'J': Ext. axis rotative, 'L': Ext. axis linear)
:type axes_type: list of str, optional
:param native_name: Native name of the robot (before any rename)
:type native_name: str, optional
:param ip_com: IP address of the robot ("Connect" tab in RoboDK)
:type ip_com: str, optional
:param api_port: RoboDK API port to the RoboDK instance
:type api_port: int, optional
:param prog_ptr: RoboDK Item pointer to the program generated
:type prog_ptr: int, optional
:param robot_ptr: RoboDK Item pointer to the robot associated with the program generated
:type robot_ptr: int, optional
:param pose_turntable: Pose of the synchronized turn table
:type pose_turntable: :meth:`robodk.robomath.PosePP`, optional
:param pose_rail: Pose of the synchronized linear rail
:type pose_rail: :meth:`robodk.robomath.PosePP`, optional
:param lines_x_prog: Maximum number of lines per program (to generate multiple files). This setting can be overridden by in RoboDK (Tools-Options-Program)
:type lines_x_prog: int, optional
:param pulses_x_deg: Pulses per degree (provided in the robot parameters of RoboDK)
:type pulses_x_deg: list of int, optional
Example for a program using the KUKA KRC2 post processor and a KUKA KR 500 3 robot with synchronized linear rail and turn table:
.. code-block:: python
RobotPost(r\"\"\"KUKA_KRC2\"\"\",r\"\"\"KUKA KR 500 3\"\"\",9, axes_type=['R','R','R','R','R','R','T','J','J'], native_name=r\"\"\"KUKA KR 500 3\"\"\", ip_com=r\"\"\"192.168.241.127\"\"\", api_port=20500, prog_ptr=2109546424992, robot_ptr=2109347059584, pose_turntable=p(1890.627070,1670.706012,-504.767930,-0.060103,0.046410,-0.246888), pose_rail=p(0.000000,0.000000,0.000000,90.000000,0.000000,0.000000))
"""
# Constructor parameters (mandatory)
self.ROBOT_POST = robotpost # Name of the robot post processor (provided by RoboDK in the constructor)
self.ROBOT_NAME = robotname # Name of the robot (provided by RoboDK in the constructor)
self.ROBOT_AXES = robot_axes # Number of axes for the robot, including synchronized axes (provided by RoboDK in the constructor)
# Optional constructor parameters (added later, backward compatibility)
self.AXES_TYPE = None # Optional, type of each axes of the robot ('R': Robot rotative, 'T': Robot translation, 'J': Ext. axis rotative, 'L': Ext. axis linear) (provided by RoboDK in the constructor)
self.NATIVE_NAME = robotname # Optional, native/original name of the robot (provided by RoboDK in the constructor)
self.IP_COM = None # Optional, IP address of the robot ("Connect" tab in RoboDK) (provided by RoboDK in the constructor)
self.API_PORT = None # Optional, RoboDK API port to the RoboDK instance (provided by RoboDK in the constructor)
self.PROG_PTR = None # Optional, RoboDK Item pointer to the program generated (provided by RoboDK in the constructor)
self.ROBOT_PTR = None # Optional, RoboDK Item pointer to the robot associated with the program generated (provided by RoboDK in the constructor)
self.POSE_TURNTABLE = None # Optional, offset pose of the synchronized turn table (provided by RoboDK in the constructor)
self.POSE_RAIL = None # Optional, offset pose of the synchronized linear rail (provided by RoboDK in the constructor)
self.MAX_LINES_X_PROG = None # Optional, maximum number of lines per program (to generate multiple files). This setting can be overridden in RoboDK (Tools-Options-Program) (provided by RoboDK in the constructor)
self.PULSES_X_DEG = None # Optional, pulses per degree (provided in the robot parameters of RoboDK) (provided by RoboDK in the constructor)
# Optional constructor parameters, you may or may not use those
for k, v in kwargs.items():
if k == 'axes_type':
self.AXES_TYPE = v
elif k == 'native_name':
self.NATIVE_NAME = v
elif k == 'ip_com':
self.IP_COM = v
elif k == 'api_port':
self.API_PORT = v
elif k == 'prog_ptr':
self.PROG_PTR = v
elif k == 'robot_ptr':
self.ROBOT_PTR = v
elif k == 'pose_turntable':
self.POSE_TURNTABLE = v
elif k == 'pose_rail':
self.POSE_RAIL = v
elif k == 'lines_x_prog':
self.MAX_LINES_X_PROG = v
elif k == 'pulses_x_deg':
self.PULSES_X_DEG = v
# Optional TEMP parameter (depends on RoboDK settings)
self._TargetName = None # Optional, target name (Tools->Options->Program->Export target names) (provided by RoboDK in the TEMP file)
self._TargetNameVia = None # Optional, intermediary target name (MoveC) (Tools->Options->Program->Export target names) (provided by RoboDK in the TEMP file)
self._PoseTrack = None # Optional, current pose of the synchronized linear axis (Tools->Options->Program->Export external axes poses) (provided by RoboDK in the TEMP file)
self._PoseTurntable = None # Optional, current pose of the synchronized turn table (Tools->Options->Program->Export external axes poses) (provided by RoboDK in the TEMP file)
# Initialize internal non-constant variables (caps kept for legacy)
self.PROG = [] # Current program content (list of str)
self.PROG_LIST = [] # List of parsed programs (list of parsed "PROG")
self.PROG_NAMES = [] # List of parsed program names
self.PROG_FILES = [] # Local files generated by the post processor
self.PROG_NAME = '' # Active program name
self.LOG = '' # Current log content (str)
self.ONETAB = ' ' # Tab character(s) (usually white-space or \t)
self.TAB = '' # Current tabulation
# Robot state
self._frame_name = None # Current reference frame name, from setFrame
self._frame_pose = None # Current reference frame pose, from setFrame
self._frame_id = 0 # Current reference frame ID, from setFrame
self._tool_name = None # Current tool name, from setTool
self._tool_pose = None # Current tool pose, from setTool
self._tool_id = 0 # Current tool ID, from setTool
self._target_name = None # Last target name, from MoveL/J/C
self._target_pose = None # Last target pose, from MoveL/J/C
self._target_joints = None # Last target joints, from MoveL/J/C
self._speed = self.DEFAULT_LINEAR_SPEED # Current linear speed, mm/s
self._acceleration = self.DEFAULT_LINEAR_ACCEL # Current linear acceleration, mm/s2
self._speed_joints = self.DEFAULT_JOINT_SPEED # Current joints speed, %
self._acceleration_joints = self.DEFAULT_JOINT_ACCEL # Current joints acceleration, %
self._blending = self.DEFAULT_BLENDING # Current blending, %
def ProgStart(self, progname, *args, **kwargs):
"""Start a new program given a name. Multiple programs can be generated at the same time.
**Tip**:
ProgStart is triggered every time a new program must be generated.
:param progname: Name of the program
:type progname: str
"""
self.PROG_NAME = robofileio.FilterName(progname) # Create a valid program name
self.PROG_NAMES.append(self.PROG_NAME) # Keep track of parsed programs
self.TAB = ''
if len(self.PROG_NAMES) == 1:
self.addline('PROC %s()' % self.PROG_NAME)
else:
# Sub program
self.addline('')
self.addline('SUB %s()' % self.PROG_NAME)
self.TAB = self.ONETAB
def ProgFinish(self, progname, *args, **kwargs):
"""This method is executed to define the end of a program or procedure. One module may have more than one program. No other instructions will be executed before another :meth:`samplepost.RobotPost.ProgStart` is executed.
**Tip**:
ProgFinish is triggered after all the instructions of the program.
:param progname: Name of the program
:type progname: str
"""
self.TAB = ''
if len(self.PROG_NAMES) == 1:
self.addline('ENDPROC %% %s' % self.PROG_NAME)
else:
# Sub program
self.addline('ENDSUB %% %s' % self.PROG_NAME)
self.TAB = self.ONETAB
self.PROG_LIST.append(self.PROG) # Add the program to the list of parsed programs
self.PROG = [] # Reset the program buffer for the next program
def ProgSave(self, folder, progname, ask_user=False, show_result=False, *args, **kwargs):
"""Saves the program. This method is executed after all programs have been processed.
**Tip**:
ProgSave is triggered after all the programs and instructions have been executed.
:param folder: Folder hint to save the program
:type folder: str
:param progname: Program name as a hint to save the program
:type progname: str
:param ask_user: True if the default settings in RoboDK are set to prompt the user to select the folder
:type ask_user: bool, str
:param show_result: False if the default settings in RoboDK are set to not show the program once it has been saved. Otherwise, a string is provided with the path of the preferred text editor
:type show_result: bool, str
"""
if len(self.PROG_NAMES) == 1:
# Save to file
prog_save = self.PROG_NAMES[0] + '.' + self.PROG_EXT
filesave = folder + '/' + prog_save
if ask_user or not robofileio.DirExists(folder):
filesave = robodialogs.getSaveFileName(folder, prog_save)
if not filesave:
return
folder = filesave.replace('\\', '/').rsplit('/', 1)[0]
else:
# Save to folder
if ask_user or not robofileio.DirExists(folder):
folder = robodialogs.getSaveFolder(folder)
if not folder or not robofileio.DirExists(folder):
return
# Here you can create a single file with all programs, or create multiple files for each program
SAVE_AS_ONE_FILE = True
if SAVE_AS_ONE_FILE:
filesave = folder + '/' + self.PROG_NAME + '.' + self.PROG_EXT
with open(filesave, "w", encoding="utf-8") as fid:
for prog_name, prog in zip(self.PROG_NAMES, self.PROG_LIST):
# Japanese controllers need the "shift_jis" codec and "replace" errors to not throw errors on non supported characters
#with open(filesave, "w", encoding="shift_jis", errors="replace") as fid:
for line in prog:
fid.write(line)
fid.write("\n")
print('SAVED: %s\n' % filesave)
self.PROG_FILES.append(filesave)
else:
for prog_name, prog in zip(self.PROG_NAMES, self.PROG_LIST):
filesave = folder + '/' + prog_name + '.' + self.PROG_EXT
# Japanese controllers need the "shift_jis" codec and "replace" errors to not throw errors on non supported characters
#with open(filesave, "w", encoding="shift_jis", errors="replace") as fid:
with open(filesave, "w", encoding="utf-8") as fid:
for line in prog:
fid.write(line)
fid.write("\n")
print('SAVED: %s\n' % filesave)
self.PROG_FILES.append(filesave)
#----------------------
# show result
if show_result:
if type(show_result) is str:
# Open file with provided application
import subprocess
p = subprocess.Popen([show_result] + self.PROG_FILES)
elif type(show_result) is list:
import subprocess
p = subprocess.Popen(show_result + self.PROG_FILES)
else:
# Open file with default application
import os
os.startfile(self.PROG_FILES[0])
if len(self.LOG) > 0:
mbox('Program generation LOG:\n\n' + self.LOG)
def ProgSendRobot(self, robot_ip, remote_path, ftp_user, ftp_pass, *args, **kwargs):
"""Send a program to the robot using the provided parameters. This method is executed right after ProgSave if we selected the option "Send Program to Robot".
The connection parameters must be provided in the robot connection menu of RoboDK.
:param robot_ip: IP address of the robot
:type robot_ip: str
:param remote_path: Remote path of the robot
:type remote_path: str
:param ftp_user: FTP user credential
:type ftp_user: str
:param ftp_pass: FTP user password
:type ftp_pass: str
"""
robofileio.UploadFTP(self.PROG_FILES, robot_ip, remote_path, ftp_user, ftp_pass)
def MoveJ(self, pose, joints, conf_RLF, *args, **kwargs):
"""Defines a joint movement.
**Tip**:
MoveJ is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Move Joint Instruction.
:param pose: Pose target of the tool with respect to the reference frame. Pose can be None if the target is defined as a joint target
:type pose: :meth:`robodk.robomath.Mat`, None
:param joints: Robot joints as a list
:type joints: float list
:param conf_RLF: Robot configuration as a list of 3 ints: [REAR, LOWER-ARM, FLIP]. [0,0,0] means [front, upper arm and non-flip] configuration. Configuration can be None if the target is defined as a joint target
:type conf_RLF: int list, None
"""
# Some post processor might need to specify the speed, reference frame, active tool, blending, on each motion command
# Simply store the data as a member variable
self._target_pose = pose
self._target_joints = joints
# Check self._TargetName for a named target
self._target_name = None
if self._TargetName is not None and type(self._TargetName) is str:
self._target_name = robofileio.FilterName(self._TargetName)
if self.ADD_TARGET_NAME:
self.RunMessage("Target: " + self._TargetName, True)
if pose is None:
# Use absolute joint position
self.addline('MOVJ ' + joints_2_str(joints))
else:
# Check self._PoseTrack and self._PoseTurntable for synchronized external axes poses
# To enable it, Tools->Options->Program->Export external axes poses
if self._PoseTrack or self._PoseTurntable:
if self.POSE_TURNTABLE and self.POSE_RAIL:
# Linear track/rail + turn table/positioner
pose = robomath.invH(self._PoseTrack * self.POSE_RAIL) * self.POSE_TURNTABLE * self._PoseTurntable * self._frame_pose * pose
elif self.POSE_TURNTABLE:
# Turn table/positioner only
pose = self.POSE_TURNTABLE * self._PoseTurntable * self._frame_pose * pose
elif self.POSE_RAIL:
# Linear track/rail
pose = robomath.invH(self._PoseTrack * self.POSE_RAIL) * self._frame_pose * pose
# Optionally, prefer cartesian targets when available
self.addline('MOVJ ' + pose_2_str(pose))
def MoveL(self, pose, joints, conf_RLF, *args, **kwargs):
"""Defines a linear movement.
**Tip**:
MoveL is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Move Linear Instruction.
:param pose: Pose target of the tool with respect to the reference frame. Pose can be None if the target is defined as a joint target
:type pose: :meth:`robodk.robomath.Mat`, None
:param joints: Robot joints as a list
:type joints: float list
:param conf_RLF: Robot configuration as a list of 3 ints: [REAR, LOWER-ARM, FLIP]. [0,0,0] means [front, upper arm and non-flip] configuration. Configuration can be None if the target is defined as a joint target
:type conf_RLF: int list, None
"""
# Some post processor might need to specify the speed, reference frame, active tool, blending, on each motion command
# Simply store the data as a member variable
self._target_pose = pose
self._target_joints = joints
# Check self._TargetName for a named target
self._target_name = None
if self._TargetName is not None and type(self._TargetName) is str:
self._target_name = robofileio.FilterName(self._TargetName)
if self.ADD_TARGET_NAME:
self.RunMessage("Target: " + self._TargetName, True)
# If a MoveL is performed on a joint target, pose will be None
# If your controller supports linear motion with joint targets, fallback to joints
if pose is None:
msg = "Linear movement using joint targets is not supported. Change the target type to cartesian or use a joint movement."
self.addlog(msg)
self.RunMessage(msg, True)
return
# Check self._PoseTrack and self._PoseTurntable for synchronized external axes poses
# To enable it, Tools->Options->Program->Export external axes poses
if self._PoseTrack or self._PoseTurntable:
if self.POSE_TURNTABLE and self.POSE_RAIL:
# Linear track/rail + turn table/positioner
pose = robomath.invH(self._PoseTrack * self.POSE_RAIL) * self.POSE_TURNTABLE * self._PoseTurntable * self._frame_pose * pose
elif self.POSE_TURNTABLE:
# Turn table/positioner only
pose = self.POSE_TURNTABLE * self._PoseTurntable * self._frame_pose * pose
elif self.POSE_RAIL:
# Linear track/rail
pose = robomath.invH(self._PoseTrack * self.POSE_RAIL) * self._frame_pose * pose
self.addline('MOVL ' + pose_2_str(pose))
def MoveC(self, pose1, joints1, pose2, joints2, conf_RLF_1, conf_RLF_2, *args, **kwargs):
"""Defines a circular movement.
**Tip**:
MoveC is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Move Circular Instruction.
:param pose1: Pose target of a point defining an arc (waypoint). Pose can be None if the target is defined as a joint target
:type pose1: :meth:`robodk.robomath.Mat`, None
:param pose2: Pose target of the end of the arc (final point). Pose can be None if the target is defined as a joint target
:type pose2: :meth:`robodk.robomath.Mat`, None
:param joints1: Robot joints of the waypoint
:type joints1: float list
:param joints2: Robot joints of the final point
:type joints2: float list
:param conf_RLF_1: Robot configuration of the waypoint as a list of 3 ints: [REAR, LOWER-ARM, FLIP]. [0,0,0] means [front, upper arm and non-flip] configuration. Configuration can be None if the target is defined as a joint target
:type conf_RLF_1: int list, None
:param conf_RLF_2: Robot configuration of the final point as a list of 3 ints: [REAR, LOWER-ARM, FLIP]. [0,0,0] means [front, upper arm and non-flip] configuration. Configuration can be None if the target is defined as a joint target
:type conf_RLF_2: int list, None
"""
# Some post processor might need to specify the speed, reference frame, active tool, blending, on each motion command
# Simply store the data as a member variable
self._target_pose = pose2 # Keep the last target on a MoveC
self._target_joints = joints2
# Check self._TargetName and self._TargetNameVia for a named target
self._target_name = None
if self._TargetName is not None:
target1 = ""
target2 = ""
if type(self._TargetName) is list and len(self._TargetName) >= 2:
# RoboDK <5.6.9
if self._TargetName[0] is not None:
target1 = self._TargetName[0]
if self._TargetName[1] is not None:
target2 = self._TargetName[0]
elif type(self._TargetName) is str:
# RoboDK >5.6.9
if self._TargetNameVia is not None:
target1 = self._TargetNameVia
if self._TargetName is not None:
target2 = self._TargetName
self._target_name = robofileio.FilterName(target2)
if self.ADD_TARGET_NAME:
self.RunMessage("Target 1: %s" % target1, True)
self.RunMessage("Target 2: %s" % target2, True)
# If a MoveC is performed on a joint target, pose will be None
# If your controller supports linear motion with joint targets, fallback to joints
if pose1 is None or pose2 is None:
msg = "Circular movement using joint targets is not supported. Change the target type to cartesian or use a joint movement."
self.addlog(msg)
self.RunMessage(msg, True)
return
# Check self._PoseTrack and self._PoseTurntable for synchronized external axes poses
# To enable it, Tools->Options->Program->Export external axes poses
if self._PoseTrack or self._PoseTurntable:
if self.POSE_TURNTABLE and self.POSE_RAIL:
# Linear track/rail + turn table/positioner
pose1 = robomath.invH(self._PoseTrack * self.POSE_RAIL) * self.POSE_TURNTABLE * self._PoseTurntable * self._frame_pose * pose1
pose2 = robomath.invH(self._PoseTrack * self.POSE_RAIL) * self.POSE_TURNTABLE * self._PoseTurntable * self._frame_pose * pose2
elif self.POSE_TURNTABLE:
# Turn table/positioner only
pose1 = self.POSE_TURNTABLE * self._PoseTurntable * self._frame_pose * pose1
pose2 = self.POSE_TURNTABLE * self._PoseTurntable * self._frame_pose * pose2
elif self.POSE_RAIL:
# Linear track/rail
pose1 = robomath.invH(self._PoseTrack * self.POSE_RAIL) * self._frame_pose * pose1
pose2 = robomath.invH(self._PoseTrack * self.POSE_RAIL) * self._frame_pose * pose2
self.addline('MOVC ' + pose_2_str(pose1) + ' ' + pose_2_str(pose2))
def setFrame(self, pose, frame_id, frame_name, *args, **kwargs):
"""Defines a new reference frame with respect to the robot base frame. This reference frame is used for following pose targets used by movement instructions.
**Tip**:
setFrame is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Set Reference Frame Instruction.
:param pose: Pose of the reference frame with respect to the robot base frame
:type pose: :meth:`robodk.robomath.Mat`
:param frame_id: Number of the reference frame (if available, else -1)
:type frame_id: int
:param frame_name: Name of the reference frame as defined in RoboDK
:type frame_name: str
"""
self._frame_pose = pose
self._frame_id = frame_id
self._frame_name = robofileio.FilterName(frame_name)
if self.ADD_FRAME_NAME and frame_name:
self.RunMessage("Frame: " + frame_name, True)
self.addline('BASE_FRAME ' + pose_2_str(pose))
def setTool(self, pose, tool_id, tool_name, *args, **kwargs):
"""Change the robot TCP (Tool Center Point) with respect to the robot flange. Any movement defined in Cartesian coordinates assumes that it is using the last reference frame and tool frame provided.
**Tip**:
setTool is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Set Tool Frame Instruction.
:param pose: Pose of the TCP frame with respect to the robot base frame
:type pose: :meth:`robodk.robomath.Mat`
:param tool_id: Tool ID (if available, else -1)
:type tool_id: int, None
:param tool_name: Name of the tool as defined in RoboDK
:type tool_name: str
"""
self._tool_pose = pose
self._tool_id = tool_id
self._tool_name = robofileio.FilterName(tool_name)
if self.ADD_TOOL_NAME:
self.RunMessage("Tool: " + tool_name, True)
self.addline('TOOL_FRAME ' + pose_2_str(pose))
def Pause(self, time_ms, *args, **kwargs):
"""Defines a pause in a program (including movements). time_ms is negative if the pause must provoke the robot to stop until the user desires to continue the program.
**Tip**:
Pause is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Pause Instruction.
:param time_ms: Time of the pause, in milliseconds
:type time_ms: float
"""
if time_ms < 0:
self.addline('PAUSE')
else:
self.addline('WAIT %.3f' % (time_ms * 0.001))
def setSpeed(self, speed_mms, *args, **kwargs):
"""Changes the robot speed (in mm/s)
**Tip**:
setSpeed is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Set Speed Instruction.
:param speed_mms: Speed in :math:`mm/s`
:type speed_mms: float
"""
self._speed = speed_mms
self.addline('SPEEDL %.2f' % speed_mms)
def setAcceleration(self, accel_mmss, *args, **kwargs):
"""Changes the robot acceleration (in mm/s^2)
**Tip**:
setAcceleration is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Set Speed Instruction. An acceleration value must be provided.
:param accel_mmss: Speed in :math:`mm/s^2`
:type accel_mmss: float
"""
self._acceleration = accel_mmss
self.addline('ACCELL %.2f' % accel_mmss)
def setSpeedJoints(self, speed_degs, *args, **kwargs):
"""Changes the robot joint speed (in deg/s)
**Tip**:
setSpeedJoints is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Set Speed Instruction. A joint speed value must be provided.
:param speed_degs: Speed in :math:`deg/s`
:type speed_degs: float
"""
self._speed_joints = speed_degs
self.addline('SPEEDJ %.2f' % speed_degs)
def setAccelerationJoints(self, accel_degss, *args, **kwargs):
"""Changes the robot joint acceleration (in deg/s^2)
**Tip**:
setAccelerationJoints is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Set Speed Instruction. A joint acceleration value must be provided.
:param accel_degss: Speed in :math:`deg/s^2`
:type accel_degss: float
"""
self._acceleration_joints = accel_degss
self.addline('ACCELJ %.2f' % accel_degss)
def setZoneData(self, zone_mm, *args, **kwargs):
"""Changes the smoothing radius (also known as rounding, blending radius, CNT, APO or zone data). If this parameter is higher it helps making the movement smoother
**Tip**:
setZoneData is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Set Rounding Instruction.
:param zone_mm: Rounding radius in mm
:type zone_mm: float
"""
self._blending = zone_mm
self.addline('BLEND %.2f' % zone_mm)
def setDO(self, io_var, io_value, *args, **kwargs):
"""Sets a variable (usually a digital output) to a given value. This method can also be used to set other variables.
**Tip**:
setDO is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Set or Wait I/O Instruction.
:param io_var: Variable to set, provided as a str or int
:type io_var: int, str
:param io_value: Value of the variable, provided as a str, float or int
:type io_value: int, float, str
"""
if type(io_var) != str:
io_var = 'DO[%s]' % str(io_var)
io_value = str_2_type(io_value)
if type(io_value) != str:
if io_value > 0:
io_value = 'TRUE'
else:
io_value = 'FALSE'
self.addline('%s=%s' % (io_var, io_value))
def setAO(self, io_var, io_value, *args, **kwargs):
"""Sets a an analog variable to a given value.
**Tip**:
setAO is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Set or Wait I/O Instruction.
:param io_var: Variable to set, provided as a str or int
:type io_var: int, str
:param io_value: Value of the variable, provided as a str, float or int
:type io_value: int, float, str
"""
if type(io_var) != str:
io_var = 'AO[%s]' % str(io_var)
io_value = str_2_type(io_value)
if type(io_value) != str:
io_value = '%.3f' % float(io_value)
self.addline('%s=%s' % (io_var, io_value))
def waitDI(self, io_var, io_value, timeout_ms=-1, *args, **kwargs):
"""Waits for a variable (usually a digital input) to attain a given value io_value. This method can also be used to set other variables.Optionally, a timeout can be provided.
**Tip**:
waitDI is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Set or Wait I/O Instruction.
:param io_var: Variable to wait for, provided as a str or int
:type io_var: int, str
:param io_value: Value of the variable, provided as a str, float or int
:type io_value: int, float, str
:param timeout_ms: Maximum wait time
:type timeout_ms: float, int
"""
if type(io_var) != str:
io_var = 'DI[%s]' % str(io_var)
io_value = str_2_type(io_value)
if type(io_value) != str:
if io_value > 0:
io_value = 'TRUE'
else:
io_value = 'FALSE'
if timeout_ms < 0:
self.addline('WAIT FOR %s==%s' % (io_var, io_value))
else:
self.addline('WAIT FOR %s==%s TIMEOUT=%.1f' % (io_var, io_value, timeout_ms))
def RunCode(self, code, is_function_call=False, *args, **kwargs):
"""Adds code or a function call.
**Tip**:
RunCode is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Function call Instruction.
:param code: Code or procedure to call
:param is_function_call: True if the provided code is a specific function to call
:type code: str
:type is_function_call: bool
"""
if is_function_call:
code = robofileio.FilterName(code)
if not code.endswith(')'):
code = code + '()'
self.addline(code)
else:
self.addline(code)
def RunMessage(self, message, iscomment=False, *args, **kwargs):
"""Display a message in the robot controller screen (teach pendant)
**Tip**:
RunMessage is triggered by the RoboDK instruction Program->Show Message Instruction.
:param message: Message to display on the teach pendant or as a comment on the code
:type message: str
:param iscomment: True if the message does not have to be displayed on the teach pendant but as a comment on the code
:type iscomment: bool
"""
if iscomment:
self.addline('% ' + message)
else:
self.addline('TP "%s"' % message)
# ------------------ private ----------------------
def addline(self, newline):
"""Add a new program line. This is a private method used only by the other methods.
:param newline: New program line to add
:type newline: str
"""
self.PROG.append(self.TAB + newline)
def addlog(self, newline):
"""Add a message to the log. This is a private method used only by the other methods. The log is displayed when the program is generated to show any issues when the robot program has been generated.
:param newline: New log line to add
:type newline: str
"""
self.LOG = self.LOG + newline + '\n'
# -------------------------------------------------
# ------------ For testing purposes ---------------
def test_post():
"""Test the post processor with a simple program"""
from robodk.robomath import PosePP as p
r = RobotPost(r"""SamplePost""", r"""RoboDK Industrial""", 6, axes_type=['R', 'R', 'R', 'R', 'R', 'R'], native_name=r"""""", ip_com=r"""127.0.0.1""", api_port=20500, prog_ptr=2465610763008, robot_ptr=2465605812256)
r.ProgStart(r"""MAIN_1""")
r.RunMessage(r"""Program generated by RoboDK using a custom post processor""", True)
r.RunMessage(r"""Using nominal kinematics.""", True)
r._TargetName = r"""Home"""
r.MoveJ(None, [-5.25645e-07, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1.46549e-15], None)
r._TargetName = r"""Target Init 1"""
r.MoveJ(p(1015, 0, 1372, 0, 90, 0), [0, 3.21124, -15.4237, 0, 12.2125, -4.67269e-13], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = r"""Target Init 2"""
r.MoveL(p(1015, 0, 1272, 0, 90, 0), [0, 8.55347, -17.0267, 0, -14.3758, 0], [0, 0, 1])
r.setDO(5, 1)
r.setDO(5, 2)
r.setDO(5, '0.5')
r.setDO(5, 'true')
r.setAO(5, 1)
r.setAO(5, 2)
r.setAO(5, '0.5')
r.setAO(5, 'true')
r.setDO('var', 'val')
r.setAO('var', 'val')
r.waitDI(5, 1, -1)
r.waitDI(5, 2, -1)
r.waitDI(5, '0.5', -1)
r.waitDI(5, 'true', -1)
r.waitDI(5, 1, 100)
r.waitDI('var', 'val', -1)
r.waitDI('var', 'val', 100)
r.RunMessage(r"""Message""")
r.RunCode(r"""REMOTE_PROG_CALL_171""", True)
r.RunCode(r"""CODE_INSERT_172""")
r.RunMessage(r"""Insert Comment""", True)
r.setFrame(p(719.013, -664.003, 0, 0, 0, 0), -1, r"""Frame Pick and Place""")
r.setTool(p(129.073, 0, 85.477, 0, 22.849, 0), 1, r"""Tool 1""")
r.setAccelerationJoints(800.000)
r.setSpeedJoints(500.000)
r.setZoneData(10.000)
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveJ(p(187.264, 125.487, 305.356, 180, 0.184, -180), [-29.3322, 46.677, -0.024523, 26.5456, 25.3957, -51.634], [0, 0, 0])
r.setZoneData(-1.000)
r.setAcceleration(200.000)
r.setSpeed(100.000)
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(187.786, 125.499, 139.112, -179.997, 0.18, 179.996), [-29.3185, 56.1632, -0.458104, 38.9815, 17.7354, -64.9585], [0, 0, 0])
r.setDO(5, 1)
r.RunCode(r"""PICK_PART_111""", True)
r.setZoneData(10.000)
r.setAcceleration(600.000)
r.setSpeed(300.000)
r._TargetName = r"""App_Pick_Jnt"""
r.MoveL(None, [-29.3322, 46.677, -0.0244862, 26.5458, 25.3957, -51.6342], None)
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(187.272, 447.522, 305.347, 179.999, 0.185, -179.998), [-12.7285, 39.1891, 14.3365, 19.7398, 14.7824, -30.877], [0, 0, 0])
r.setZoneData(-1.000)
r.setAcceleration(200.000)
r.setSpeed(100.000)
r._TargetName = None
r.RunMessage(r"""MoveSearch command not implemented""", True)
r.MoveL(p(187.851, 447.517, 126.235, 179.999, 0.185, -179.998), [-12.7213, 50.7452, 13.7281, 58.8071, 5.77865, -70.4133], [0, 0, 0])
r.setDO(5, 0)
r.RunCode(r"""PLACE_PART_112""", True)
r.setZoneData(10.000)
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(187.272, 447.522, 305.347, 179.999, 0.185, -179.998), [-12.7285, 39.1891, 14.3365, 19.7398, 14.7824, -30.877], [0, 0, 0])
r.setFrame(p(577.67, 392.25, 0, 38.9595, 0, 0), -1, r"""Frame Circular""")
r.setZoneData(25.000)
r.setAccelerationJoints(800.000)
r.setSpeedJoints(500.000)
r.setAcceleration(200.000)
r.setSpeed(100.000)
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveJ(p(312.208, 292.214, 255.156, -134.549, 11.1813, 178.913), [52.186, 45.6758, 6.92, 66.7342, 19.9323, -92.73], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetNameVia = None
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveC(p(430.047, 43.774, 231.503, -134.549, 11.1813, 178.913), [38.5084, 52.8105, -4.82239, 56.4521, 29.7882, -93.0255], p(109.688, -153.222, 161.073, -134.549, 11.1813, 178.913), [24.802, 41.3257, 29.6032, 87.9704, 29.4626, -142.416], [0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetNameVia = r"""Target 2 Jnt"""
r._TargetName = r"""Target 1 Jnt"""
r.MoveC(None, [38.5084, 52.8104, -4.82235, 56.4523, 29.7882, -93.0257], None, [52.1859, 45.6757, 6.92004, 66.7344, 19.9323, -92.7303], [0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0])
r.setZoneData(-1.000)
r.setAcceleration(200.000)
r.setSpeed(100.000)
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(312.208, 292.214, 255.156, -134.549, 11.1813, 178.913), [52.186, 45.6758, 6.92, 66.7342, 19.9323, -92.73], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = r"""Home"""
r.MoveJ(None, [-5.25645e-07, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1.46549e-15], None)
r.setFrame(p(0, 782.714, 377.61, 0, 0, 0), -1, r"""Frame Inspection""")
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveJ(p(19.898, 201.357, 302.721, -94.9281, -5.42599, -179.533), [88.676, 29.6016, -6.42883, -1.98422, 49.4792, 4.54769], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(19.898, 174.307, 19.008, -94.9281, -5.42599, -179.533), [88.6412, 37.6157, 7.6344, -3.25372, 27.4219, 6.11377], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(378.402, 174.416, 18.997, -94.9281, -5.42599, -179.533), [69.5908, 42.46, -1.04795, 7.90648, 31.8952, -21.7004], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(380.996, 112.363, 34.882, -95.2937, -18.1364, -178.348), [69.0981, 41.4527, 1.28767, -0.293386, 42.3038, -15.9791], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(16.551, 114.359, 34.226, -95.2937, -18.1364, -178.348), [88.801, 36.7217, 9.82069, -2.95529, 38.8939, 5.74175], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(26.434, 54.524, 46.072, -95.4608, 4.34825, 179.585), [87.9395, 25.3303, 24.2482, -5.09867, 13.2949, 8.14809], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(385.448, 48.05, 45.137, -95.5904, 11.1809, 178.913), [65.1172, 28.8227, 18.4513, 48.4598, 15.6087, -63.1988], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(385.448, -1.625, 295.251, -95.5904, 11.1809, 178.913), [63.7612, 15.3737, 13.1682, 23.9712, 31.7352, -37.6981], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = r"""Home"""
r.MoveJ(None, [-5.25645e-07, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1.46549e-15], None)
r.RunCode(r"""EVENT_PROG_START_101""", True)
r.setZoneData(1.000)
r.setSpeed(1000.000)
r.setFrame(p(13.637, -840.08, 0, -90, 0, 0), -1, r"""Frame Inspection""")
r.RunMessage(r"""Show Tool 1""", True)
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveJ(p(-49.939, 252.644, 419.997, -90, 0.353, -179.975), [-68.0903, 24.2019, 26.7855, 38.2134, 36.2017, -98.7964], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.RunCode(r"""EVENT_PATH_APPROACH_102""", True)
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(-49.895, 253.259, 319.999, -90, 0.353, -179.975), [-68.0531, 30.5428, 28.4999, 46.5342, 30.2163, -108.684], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(0, 250, 270, -90, 0.353, -179.975), [-69.4372, 36.478, 24.0662, 48.0716, 29.7098, -111.839], [0, 0, 0])
r.RunCode(r"""EVENT_PATH_START_103""", True)
r._TargetName = None
r.setSpeed(50.000)
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(35.579, 247.455, 270, -90, 0.345, -179.925), [-70.3489, 38.2711, 20.535, 45.6808, 31.1886, -109.993], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(70.433, 239.873, 270, -89.999, 0.330998, -179.876), [-71.4686, 39.9889, 17.146, 43.5315, 32.7489, -108.597], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(103.854, 227.408, 270, -89.999, 0.309997, -179.831), [-72.7633, 41.6047, 13.9532, 41.6289, 34.3488, -107.63], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(135.16, 210.313, 270, -89.999, 0.282996, -179.788), [-74.2041, 43.0922, 11.0104, 39.9679, 35.9473, -107.066], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(163.715, 188.937, 270, -89.999, 0.249996, -179.75), [-75.7653, 44.4258, 8.36962, 38.5347, 37.5045, -106.874], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(188.937, 163.715, 270, -89.999, 0.211995, -179.717), [-77.4239, 45.581, 6.08058, 37.3112, 38.9832, -107.02], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(210.313, 135.16, 270, -89.999, 0.169995, -179.689), [-79.1593, 46.5348, 4.19016, 36.281, 40.3478, -107.477], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(227.408, 103.854, 270, -89.999, 0.123994, -179.668), [-80.9524, 47.2671, 2.73896, 35.4254, 41.5679, -108.213], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(239.873, 70.433, 270, -90, 0.075, -179.654), [-82.7857, 47.7617, 1.76039, 34.7286, 42.6165, -109.203], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(247.455, 35.579, 270, -90, 0.025, -179.647), [-84.6423, 48.0069, 1.27773, 34.1759, 43.4729, -110.421], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(250, 0, 270, -90, -0.025, -179.647), [-86.5062, 47.9966, 1.30332, 33.7555, 44.1209, -111.841], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(247.455, -35.579, 270, -90, -0.075, -179.654), [-88.3612, 47.7315, 1.83611, 33.4564, 44.5527, -113.438], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(239.873, -70.433, 270, -90.001, -0.123994, -179.668), [-90.1913, 47.2177, 2.86315, 33.2711, 44.7653, -115.187], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(227.408, -103.854, 270, -90.001, -0.169995, -179.689), [-91.9795, 46.4674, 4.35991, 33.1942, 44.7621, -117.062], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(210.313, -135.16, 270, -90.001, -0.211995, -179.717), [-93.7081, 45.4974, 6.29208, 33.2231, 44.5515, -119.037], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(188.937, -163.715, 270, -90.001, -0.249996, -179.75), [-95.358, 44.3279, 8.61845, 33.3584, 44.1445, -121.088], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(163.715, -188.937, 270, -90.001, -0.282996, -179.788), [-96.9084, 42.9821, 11.2918, 33.6038, 43.5568, -123.189], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(135.16, -210.313, 270, -90.001, -0.310997, -179.83), [-98.3359, 41.4847, 14.2621, 33.9667, 42.805, -125.317], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(103.854, -227.408, 270, -90.001, -0.331998, -179.876), [-99.6145, 39.8611, 17.4769, 34.4583, 41.9071, -127.446], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(70.433, -239.873, 270, -90, -0.346, -179.925), [-100.715, 38.1376, 20.8827, 35.0938, 40.8826, -129.555], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(35.579, -247.455, 270, -90, -0.353, -179.975), [-101.604, 36.341, 24.425, 35.8921, 39.7503, -131.622], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(0, -250, 270, -90, -0.353, -179.975), [-102.247, 34.4892, 28.0665, 36.9342, 38.491, -133.695], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(0, -250, 270, -90, -0.353, 179.975), [-102.245, 34.4987, 28.0477, 36.877, 38.5317, -133.625], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(-35.579, -247.455, 270, -90, -0.346, 179.925), [-102.596, 32.6395, 31.6928, 38.0753, 37.2477, -135.543], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(-70.433, -239.873, 270, -89.999, -0.330998, 179.876), [-102.611, 30.7935, 35.299, 39.5163, 35.9209, -137.353], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(-103.854, -227.408, 270, -89.999, -0.309997, 179.831), [-102.244, 28.9935, 38.801, 41.2289, 34.5749, -139.031], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(-135.16, -210.313, 270, -89.999, -0.282996, 179.788), [-101.448, 27.2756, 42.1281, 43.2369, 33.234, -140.549], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(-163.715, -188.937, 270, -89.999, -0.249996, 179.75), [-100.183, 25.6792, 45.2042, 45.554, 31.924, -141.876], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(-188.937, -163.715, 270, -89.999, -0.211995, 179.717), [-98.4224, 24.2473, 47.9477, 48.1695, 30.6693, -142.971], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(-210.313, -135.16, 270, -89.999, -0.168995, 179.69), [-96.1665, 23.0258, 50.2743, 51.0388, 29.4927, -143.783], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(-227.408, -103.854, 270, -89.999, -0.122994, 179.669), [-93.4513, 22.0607, 52.1014, 54.0696, 28.4134, -144.254], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(-239.873, -70.433, 270, -90, -0.075, 179.654), [-90.3597, 21.3939, 53.3553, 57.1156, 27.4453, -144.315], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(-247.455, -35.579, 270, -90, -0.025, 179.647), [-87.0219, 21.0579, 53.9806, 59.9848, 26.5968, -143.904], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(-250, 0, 270, -90, 0.025, 179.647), [-83.6036, 21.0703, 53.9474, 62.4559, 25.8733, -142.962], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(-247.455, 35.579, 270, -90, 0.075, 179.655), [-80.2832, 21.4306, 53.2574, 64.3165, 25.2806, -141.457], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(-239.873, 70.433, 270, -90.001, 0.122994, 179.669), [-77.224, 22.12, 51.9432, 65.4009, 24.829, -139.389], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(-227.408, 103.854, 270, -90.001, 0.169995, 179.689), [-74.5516, 23.1051, 50.0624, 65.6191, 24.5358, -136.794], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(-210.313, 135.16, 270, -90.001, 0.211995, 179.717), [-72.344, 24.3435, 47.6903, 64.973, 24.4221, -133.759], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(-188.937, 163.715, 270, -90.001, 0.249996, 179.75), [-70.6334, 25.7892, 44.9098, 63.5472, 24.5124, -130.402], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(-163.715, 188.937, 270, -90.001, 0.282996, 179.788), [-69.4163, 27.3965, 41.8051, 61.4929, 24.8267, -126.877], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(-135.16, 210.313, 270, -90.001, 0.309997, 179.831), [-68.6649, 29.1225, 38.4571, 58.9975, 25.3753, -123.345], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(-103.854, 227.408, 270, -90.001, 0.331998, 179.876), [-68.338, 30.9278, 34.9417, 56.2542, 26.1575, -119.965], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(-70.433, 239.873, 270, -90, 0.346, 179.925), [-68.3888, 32.7769, 31.3288, 53.4349, 27.1586, -116.864], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(-35.579, 247.455, 270, -90, 0.353, 179.975), [-68.7701, 34.6371, 27.6833, 50.6754, 28.3536, -114.137], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(0, 250, 270, -90, 0.353, 179.975), [-69.4415, 36.4872, 24.0478, 48.0255, 29.7609, -111.78], [0, 0, 0])
r.setSpeed(1000.000)
r.RunCode(r"""EVENT_PATH_FINISH_105""", True)
r._TargetName = None
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(49.895, 253.258, 319.999, -90, 0.353, 179.975), [-70.3186, 36.0547, 18.426, 41.04, 34.416, -104.418], [0, 0, 0])
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(49.939, 252.642, 419.997, -90, 0.353, 179.975), [-70.3547, 30.4247, 16.7719, 35.1262, 40.174, -97.0327], [0, 0, 0])
r.RunCode(r"""EVENT_PATH_RETRACT_106""", True)
r.RunCode(r"""EVENT_PROG_FINISH_107""", True)
r.setFrame(p(719.013, -664.003, 0, 0, 0, 0), -1, r"""Frame Pick and Place""")
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveJ(p(187.264, 125.487, 305.356, 180, 0.184, -180), [-29.3322, 46.677, -0.024523, 26.5456, 25.3957, -51.634], [0, 0, 0])
r.Pause(1250.0)
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(187.786, 125.499, 139.112, -179.997, 0.18, 179.996), [-29.3185, 56.1632, -0.458104, 38.9815, 17.7354, -64.9585], [0, 0, 0])
r.waitDI(1, 1, -1)
r._TargetName = None
r.MoveL(p(187.264, 125.487, 305.356, 180, 0.184, -180), [-29.3322, 46.677, -0.024523, 26.5456, 25.3957, -51.634], [0, 0, 0])
r.RunCode(r"""PROG 1 _.-[]/\;,><&*:%=+@!#^|?^ with a very long name and special characters""", True)
r.RunCode(r"""ProgSync""", True)
r.ProgFinish(r"""MAIN_1""")
r.ProgStart(r"""PROG 1 _.-[]/\;,><&*:%=+@!#^|?^ with a very long name and special characters""")
r.RunMessage(r"""This is a subprogram call to PROG_1""", True)
r.setFrame(p(0, 1000, 0, 0, 0, 0), 1, r"""Frame 1 _.-[]/\;,><&*:%=+@!#^|?^ with a very long name and special characters""")
r.setTool(p(0, 0, 200, 0, 0, 0), 1, r"""Tool 1 _.-[]/\;,><&*:%=+@!#^|?^ with a very long name and s""")
r._TargetName = r"""Target 1 _.-[]/\;,><&*:%=+@!#^|?^ with a very long name and special characters"""
r.MoveJ(p(1015, -1000, 1237, -5.25645e-07, 90, 0), [-5.25645e-07, 0, 0, 0, 0, -3.50835e-15], [0, 0, 0])
r.ProgFinish(r"""PROG 1 _.-[]/\;,><&*:%=+@!#^|?^ with a very long name and special characters""")
r.ProgStart(r"""ProgSync""")
r.setFrame(p(0, 0, -900, -180, 0, 0), -1, r"""ABB IRBP A250 D1000 Base""")
r.setTool(p(0, 0, 200, 0, 0, 0), 3, r"""Tool 3""")
r._TargetName = r"""Target Ext 1"""
r._PoseTrack = p(530.000000, 0.000000, 408.000000, 0.000000, 0.000000, 0.000000)
r._PoseTurntable = p(0.000000, 0.000000, 900.000000, 180.000000, 0.000000, -0.000000)
r.MoveJ(None, [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], None)
r._TargetName = r"""Target Ext 2"""
r._PoseTrack = p(2516.890000, 0.000000, 408.000000, 0.000000, 0.000000, 0.000000)
r._PoseTurntable = p(0.000000, -67.103148, 920.515491, -55.373835, -29.031918, -18.526568)
r.MoveJ(None, [-9.98, 27.51, 15.86, 26.08, -36.71, -26.4, 1986.89, 34, 119.79], None)
r._TargetName = r"""Target Ext 3"""
r._PoseTrack = p(2516.890000, 0.000000, 408.000000, 0.000000, 0.000000, 0.000000)
r._PoseTurntable = p(0.000000, -67.103148, 920.515491, -55.373835, -29.031918, -18.526568)
r.MoveJ(p(-45.0933, 52.3752, 1053.33, 104.025, 78.1296, -141.161), [-15.1078, 25.9289, 17.2052, 17.9009, -35.0913, -20.6442, 1986.89, 34, 119.79], [0, 0, 1])
r._TargetName = r"""Target Ext 2"""
r._PoseTrack = p(2516.890000, 0.000000, 408.000000, 0.000000, 0.000000, 0.000000)
r._PoseTurntable = p(0.000000, -67.103148, 920.515491, -55.373835, -29.031918, -18.526568)
r.MoveL(None, [-9.98, 27.51, 15.86, 26.08, -36.71, -26.4, 1986.89, 34, 119.79], None)
r._TargetName = r"""Target Ext 3"""
r._PoseTrack = p(2516.890000, 0.000000, 408.000000, 0.000000, 0.000000, 0.000000)
r._PoseTurntable = p(0.000000, -67.103148, 920.515491, -55.373835, -29.031918, -18.526568)
r.MoveL(p(-45.0933, 52.3752, 1053.33, 104.025, 78.1296, -141.161), [-15.1078, 25.9289, 17.2052, 17.9009, -35.0913, -20.6442, 1986.89, 34, 119.79], [0, 0, 1])
r.ProgFinish(r"""ProgSync""")
#r.ProgSave(".", r"""MAIN_1""", False, False)
for prog in r.PROG_LIST:
for line in prog:
print(line)
if len(r.LOG) > 0:
mbox('Program generation LOG:\n\n' + r.LOG)
#input("Press Enter to close...")
if __name__ == "__main__":
"""Procedure to call when the module is executed by itself: test_post()"""
test_post()
3.3. Post Processor Example Output¶
Once a program has been generated using a Post Processor, an output such as the following will be obtained. In this example, the result is meant to be used with an ABB robot using an IRC5 controller.
MODULE MOD_Weld_Hexagon
PERS wobjdata rdkWObj := [FALSE, TRUE, "", [[0,0,0],[1,0,0,0]],[[0,0,0],[1,0,0,0]];
PERS tooldata rdkTool := [TRUE,[[0,0,0],[1,0,0,0]],[3,[0,0,200],[1,0,0,0],0,0,0.005]];
VAR speeddata rdkSpeed := [500,500,500,500];
VAR extjoint rdkExtax := [9E9,9E9,9E9,9E9,9E9,9E9];
PROC Weld_Hexagon()
!Program generated by RoboDK for ABB IRB 1600ID-4/1.5 on 29/11/2014 17:42:31
ConfJ \On;
ConfL \On;
rdkWObj.oframe:=[0,0,0],[1,0,0,0];
rdkWObj.uframe:=[0,0,0],[1,0,0,0];
rdkTool.tframe:=[-4,0,371.3],[0.92387953,0,0.38268343,0];
MoveAbsJ [[-0,-19.143793,-7.978668,0,49.189506,-0]],rdkExtax], rdkSpeed, rdkZone, rdkTool, \WObj:=rdkWObj;
MoveJ [[1010.634,-114.491,662.29],[0,0,1,0],[-1,0,-1,0],rdkExtax], rdkSpeed, rdkZone, rdkTool, \WObj:=rdkWObj;
WeldStart;
MoveL [[810.634,-114.491,662.29],[0,0,1,0],[-1,0,-1,0],rdkExtax], rdkSpeed, rdkZone, rdkTool, \WObj:=rdkWObj;
MoveL [[910.634,58.715,662.29],[0,0,1,0],[0,-1,0,0],rdkExtax], rdkSpeed, rdkZone, rdkTool, \WObj:=rdkWObj;
MoveL [[1110.634,58.715,662.29],[0,0,1,0],[0,-1,0,0],rdkExtax], rdkSpeed, rdkZone, rdkTool, \WObj:=rdkWObj;
MoveL [[1210.634,-114.491,662.29],[0,0,1,0],[-1,0,-1,0],rdkExtax], rdkSpeed, rdkZone, rdkTool, \WObj:=rdkWObj;
MoveL [[1110.634,-287.696,662.29],[0,0,1,0],[-1,0,-1,0],rdkExtax], rdkSpeed, rdkZone, rdkTool, \WObj:=rdkWObj;
MoveL [[910.634,-287.696,662.29],[0,0,1,0],[-1,0,-1,0],rdkExtax], rdkSpeed, rdkZone, rdkTool, \WObj:=rdkWObj;
MoveL [[810.634,-114.491,662.29],[0,0,1,0],[-1,0,-1,0],rdkExtax], rdkSpeed, rdkZone, rdkTool, \WObj:=rdkWObj;
WeldStop;
MoveL [[1010.634,-114.491,662.29],[0,0,1,0],[-1,0,-1,0],rdkExtax], rdkSpeed, rdkZone, rdkTool, \WObj:=rdkWObj;
MoveAbsJ [[-0,-19.143793,-7.978668,0,49.189506,-0]],rdkExtax], rdkSpeed, rdkZone, rdkTool, \WObj:=rdkWObj;
ConfJ \On;
ConfL \On;
ENDPROC
ENDMODULE