2. RoboDK API (robodk package)¶
Warning
The RoboDK API was refactored with version 5.4.0.
These changes are backward compatible, but not forward compatible. Effectively, the robolink.py module is now a sub-module of the robodk package (robodk.robolink), and robodk.py is now split into different sub-modules (robodk.robomath, robodk.robodialogs, robodk.robofileio).
Before 5.4.0
Most of our examples used the import method below:
from robolink import *
from robodk import *
RDK = Robolink()
pose = eye()
ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT
After 5.4.0
You can use any of the following import methods:
from robodk import robolink, robomath
RDK = robolink.Robolink()
pose = robomath.eye()
robolink.ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT
from robodk.robolink import Robolink, ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT
from robodk.robomath import eye
RDK = Robolink()
pose = eye()
ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT
from robodk.robolink import *
from robodk.robomath import *
RDK = Robolink()
pose = eye()
ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT
The robodk package is the distributed entry point of the Python API. It is the common parent of all sub-packages and modules that constitute the Python API.
- Overview of the RoboDK API:
2.1. robolink.py¶
The robolink sub-module is the bridge between RoboDK and Python. Every object in the RoboDK item tree can be retrieved and it is represented by the object Item. An item can be a robot, a reference frame, a tool, an object or any other item visible in the station tree.
- Overview of the RoboDK API:
The following example uses the robodk and robolink libraries to move a robot.
from robodk.robolink import * # import the robolink library (bridge with RoboDK)
RDK = Robolink() # establish a link with the simulator
robot = RDK.Item('ABB IRB120') # retrieve the robot by name
robot.setJoints([0,0,0,0,0,0]) # set all robot axes to zero
target = RDK.Item('Target') # retrieve the Target item
robot.MoveJ(target) # move the robot to the target
# calculate a new approach position 100 mm along the Z axis of the tool with respect to the target
from robodk.robomath import * # import the robotics toolbox
approach = target.Pose()*transl(0,0,-100)
robot.MoveL(approach) # linear move to the approach position
The following macro shows a basic example to move a robot along a hexagonal path:
/RoboDK/Library/SampleOfflineProgramming.py.
- Examples are available in the Examples section and the RoboDK API GitHub repository:
The robolink module is the bridge between RoboDK and Python. Every object in the RoboDK item tree can be retrieved using a Robolink() object and it is represented by the Item object.
Among others, this module defines the following two classes:
Robolink()
Item()
An item is an object in the RoboDK tree (it can be either a robot, an object, a tool, a frame, a program, …). Items can be retrieved from the RoboDK station using the Robolink() object (such as Robolink.Item() method)
More information about the RoboDK API for Python here:
- robodk.robolink.INS_TYPE_INVALID = -1¶
Invalid instruction type of a
ITEM_TYPE_INSTRUCTION
- robodk.robolink.INS_TYPE_MOVE = 0¶
Move (except MoveC) instruction type of a
ITEM_TYPE_INSTRUCTION
- robodk.robolink.INS_TYPE_MOVEC = 1¶
MoveC instruction type of a
ITEM_TYPE_INSTRUCTION
- robodk.robolink.INS_TYPE_CHANGESPEED = 2¶
Set Speed instruction type of a
ITEM_TYPE_INSTRUCTION
- robodk.robolink.INS_TYPE_CHANGEFRAME = 3¶
Set Frame instruction type of a
ITEM_TYPE_INSTRUCTION
- robodk.robolink.INS_TYPE_CHANGETOOL = 4¶
Set Tool instruction type of a
ITEM_TYPE_INSTRUCTION
- robodk.robolink.INS_TYPE_CHANGEROBOT = 5¶
Set Robot instruction type of a
ITEM_TYPE_INSTRUCTION
- robodk.robolink.INS_TYPE_PAUSE = 6¶
Pause instruction type of a
ITEM_TYPE_INSTRUCTION
- robodk.robolink.INS_TYPE_EVENT = 7¶
Simulation Event instruction type of a
ITEM_TYPE_INSTRUCTION
- robodk.robolink.INS_TYPE_CODE = 8¶
Code instruction type of a
ITEM_TYPE_INSTRUCTION
- robodk.robolink.INS_TYPE_PRINT = 9¶
Show Message instruction type of a
ITEM_TYPE_INSTRUCTION
- robodk.robolink.INS_TYPE_ROUNDING = 10¶
Rounding instruction type of a
ITEM_TYPE_INSTRUCTION
- robodk.robolink.INS_TYPE_IO = 11¶
Set or Wait I/O instruction type of a
ITEM_TYPE_INSTRUCTION
- robodk.robolink.INS_TYPE_CUSTOM = 12¶
Custom instruction type of a
ITEM_TYPE_INSTRUCTION
- robodk.robolink.MOVE_TYPE_INVALID = -1¶
Invalid move type of a
ITEM_TYPE_INSTRUCTION
- robodk.robolink.MOVE_TYPE_JOINT = 1¶
Joint move (MoveJ) type of a
ITEM_TYPE_INSTRUCTION
- robodk.robolink.MOVE_TYPE_LINEAR = 2¶
Linear move (MoveL) type of a
ITEM_TYPE_INSTRUCTION
- robodk.robolink.MOVE_TYPE_CIRCULAR = 3¶
Circular move (MoveC) type of a
ITEM_TYPE_INSTRUCTION
- robodk.robolink.MOVE_TYPE_LINEARSEARCH = 5¶
Linear search move (SearchL) type of a
ITEM_TYPE_INSTRUCTION
- robodk.robolink.PATH_OPENSTATION = 'PATH_OPENSTATION'¶
Full path of the current station (.rdk file) request flag
- robodk.robolink.FILE_OPENSTATION = 'FILE_OPENSTATION'¶
File name of the current station (name of the .rdk file) request flag
- robodk.robolink.PATH_DESKTOP = 'PATH_DESKTOP'¶
Full path to the desktop folder request flag
- robodk.robolink.PATH_LIBRARY = 'PATH_LIBRARY'¶
Full path to the RoboDK local library folder request flag
- robodk.robolink.RUNMODE_SIMULATE = 1¶
Performs the simulation moving the robot (default)
- robodk.robolink.RUNMODE_QUICKVALIDATE = 2¶
Performs a quick check to validate the robot movements
- robodk.robolink.RUNMODE_MAKE_ROBOTPROG = 3¶
Makes the robot program
- robodk.robolink.RUNMODE_MAKE_ROBOTPROG_AND_UPLOAD = 4¶
Makes the robot program and updates it to the robot
- robodk.robolink.RUNMODE_MAKE_ROBOTPROG_AND_START = 5¶
Makes the robot program and starts it on the robot (independently from the PC)
- robodk.robolink.RUNMODE_RUN_ROBOT = 6¶
Moves the real robot from the PC (PC is the client, the robot behaves like a server)
- robodk.robolink.PROGRAM_RUN_ON_SIMULATOR = 1¶
Run on the simulator program flag
- robodk.robolink.PROGRAM_RUN_ON_ROBOT = 2¶
Run on the robot program flag
- robodk.robolink.ROBOTCOM_PROBLEMS = -3¶
Problems connection status
- robodk.robolink.ROBOTCOM_DISCONNECTED = -2¶
Disconnected connection status
- robodk.robolink.ROBOTCOM_NOT_CONNECTED = -1¶
Not connected connection status
- robodk.robolink.ROBOTCOM_READY = 0¶
Ready connection status
- robodk.robolink.ROBOTCOM_WORKING = 1¶
Working connection status
- robodk.robolink.ROBOTCOM_WAITING = 2¶
Problems connection status
- robodk.robolink.ROBOTCOM_UNKNOWN = -1000¶
Problems connection status
- robodk.robolink.CALIBRATE_TCP_BY_POINT = 0¶
Calibrate TCP by point flag
- robodk.robolink.CALIBRATE_TCP_BY_PLANE = 1¶
Calibrate TCP by plane flag
- robodk.robolink.CALIBRATE_TCP_BY_PLANE_SCARA = 4¶
Calibrate TCP by plane (SCARA) flag
- robodk.robolink.CALIBRATE_FRAME_3P_P1_ON_X = 0¶
Calibrate frame by 3 points: [X, X+, Y+] (p1 on X axis) flag
- robodk.robolink.CALIBRATE_FRAME_3P_P1_ORIGIN = 1¶
Calibrate frame by 3 points: [Origin, X+, XY+] (p1 is origin) flag
- robodk.robolink.CALIBRATE_FRAME_6P = 2¶
Calibrate frame by 6 points flag
- robodk.robolink.CALIBRATE_TURNTABLE = 3¶
Calibrate turntable flag
- robodk.robolink.CALIBRATE_TURNTABLE_2X = 4¶
Calibrate a 2 axis turntable flag
- robodk.robolink.PROJECTION_NONE = 0¶
No curve/point projection
- robodk.robolink.PROJECTION_CLOSEST = 1¶
The projection will be the closest point on the surface
- robodk.robolink.PROJECTION_ALONG_NORMAL = 2¶
The projection will be done along the normal
- robodk.robolink.PROJECTION_ALONG_NORMAL_RECALC = 3¶
The projection will be done along the normal. Furthermore, the normal will be recalculated according to the surface normal
- robodk.robolink.PROJECTION_CLOSEST_RECALC = 4¶
The projection will be the closest point on the surface and the normals will be recalculated
- robodk.robolink.PROJECTION_RECALC = 5¶
The normals are recalculated according to the surface normal of the closest projection. The points are not changed.
- robodk.robolink.JOINT_FORMAT = -1¶
Joints (not poses) Euler format flag
- robodk.robolink.EULER_RX_RYp_RZpp = 0¶
RX:RYp:RZpp (generic) Euler format flag
- robodk.robolink.EULER_RZ_RYp_RXpp = 1¶
RZ:RYp:RXpp (ABB RobotStudio) Euler format flag
- robodk.robolink.EULER_RZ_RYp_RZpp = 2¶
RZ:RYp:RZpp (Kawasaki, Adept, Staubli) Euler format flag
- robodk.robolink.EULER_RZ_RXp_RZpp = 3¶
RZ:RXp:RZpp (CATIA, SolidWorks) Euler format flag
- robodk.robolink.EULER_RZ_RY_RX = 5¶
RZ:RY:RX (CRS) Euler format flag
- robodk.robolink.EULER_QUEATERNION = 6¶
Quaternion (ABB Rapid) Euler format flag
- robodk.robolink.WINDOWSTATE_HIDDEN = -1¶
Hidden RoboDK window state
- robodk.robolink.WINDOWSTATE_SHOW = 0¶
Show RoboDK window state
- robodk.robolink.WINDOWSTATE_MINIMIZED = 1¶
Minimized RoboDK window state
- robodk.robolink.WINDOWSTATE_NORMAL = 2¶
Normal RoboDK window state
- robodk.robolink.WINDOWSTATE_MAXIMIZED = 3¶
Maximized RoboDK window state
- robodk.robolink.WINDOWSTATE_FULLSCREEN = 4¶
Fullscreen RoboDK window state
- robodk.robolink.WINDOWSTATE_CINEMA = 5¶
Cinema RoboDK window state
- robodk.robolink.WINDOWSTATE_FULLSCREEN_CINEMA = 6¶
Fullscreen and cinema RoboDK window state
- robodk.robolink.WINDOWSTATE_VIDEO = 7¶
Video RoboDK window state
- robodk.robolink.INSTRUCTION_CALL_PROGRAM = 0¶
Program call instruction type of a Program call
- robodk.robolink.INSTRUCTION_INSERT_CODE = 1¶
Insert code instruction type of a Program call
- robodk.robolink.INSTRUCTION_START_THREAD = 2¶
Start a new process instruction type of a Program call
- robodk.robolink.INSTRUCTION_COMMENT = 3¶
Insert comment instruction type of a Program call
- robodk.robolink.INSTRUCTION_SHOW_MESSAGE = 4¶
Show message instruction type of a Program call
- robodk.robolink.FEATURE_NONE = 0¶
None feature type flag
- robodk.robolink.FEATURE_SURFACE = 1¶
Surface (under the mouse cursor) feature type flag
- robodk.robolink.FEATURE_CURVE = 2¶
Curve feature type flag
- robodk.robolink.FEATURE_POINT = 3¶
Point feature type flag
- robodk.robolink.FEATURE_OBJECT_MESH = 7¶
Object mesh (using ID) feature type flag
- robodk.robolink.FEATURE_SURFACE_PREVIEW = 8¶
Surface preview feature type flag
- robodk.robolink.FEATURE_MESH = 9¶
Mesh (under the mouse cursor) feature flag
- robodk.robolink.FEATURE_HOVER_OBJECT_MESH = 10¶
Object mesh (under the mouse cursor) feature type flag
- robodk.robolink.FEATURE_HOVER_OBJECT = 11¶
Object feature (under the mouse cursor) feature type flag
- robodk.robolink.SPRAY_OFF = 0¶
Spray OFF flag
- robodk.robolink.SPRAY_ON = 1¶
Spray ON flag
- robodk.robolink.COLLISION_OFF = 0¶
Collision OFF flag
- robodk.robolink.COLLISION_ON = 1¶
Collision ON flag
- robodk.robolink.FLAG_ROBODK_TREE_ACTIVE = 1¶
RoboDK tree active flag
- robodk.robolink.FLAG_ROBODK_3DVIEW_ACTIVE = 2¶
RoboDK 3D view (3D mouse navigation) active flag
- robodk.robolink.FLAG_ROBODK_LEFT_CLICK = 4¶
RoboDK left click active flag
- robodk.robolink.FLAG_ROBODK_RIGHT_CLICK = 8¶
RoboDK right click active flag
- robodk.robolink.FLAG_ROBODK_DOUBLE_CLICK = 16¶
RoboDK double clicks active flag
- robodk.robolink.FLAG_ROBODK_MENU_ACTIVE = 32¶
RoboDK main menu (complete menu) active flag
- robodk.robolink.FLAG_ROBODK_MENUFILE_ACTIVE = 64¶
RoboDK File menu active flag
- robodk.robolink.FLAG_ROBODK_MENUEDIT_ACTIVE = 128¶
RoboDK Edit menu active flag
- robodk.robolink.FLAG_ROBODK_MENUPROGRAM_ACTIVE = 256¶
RoboDK Program menu active flag
- robodk.robolink.FLAG_ROBODK_MENUTOOLS_ACTIVE = 512¶
RoboDK Tools menu active flag
- robodk.robolink.FLAG_ROBODK_MENUUTILITIES_ACTIVE = 1024¶
RoboDK Utilities menu active flag
- robodk.robolink.FLAG_ROBODK_MENUCONNECT_ACTIVE = 2048¶
RoboDK Connect menu active flag
- robodk.robolink.FLAG_ROBODK_WINDOWKEYS_ACTIVE = 4096¶
RoboDK keystrokes active flag
- robodk.robolink.FLAG_ROBODK_TREE_VISIBLE = 8192¶
RoboDK tree visible flag
- robodk.robolink.FLAG_ROBODK_REFERENCES_VISIBLE = 16384¶
RoboDK reference frames visible flag
- robodk.robolink.FLAG_ROBODK_STATUSBAR_VISIBLE = 32768¶
RoboDK status bar visible flag
- robodk.robolink.FLAG_ROBODK_NONE = 0¶
RoboDK disable all flag
- robodk.robolink.FLAG_ROBODK_ALL = 65535¶
RoboDK enable all flag
- robodk.robolink.FLAG_ROBODK_MENU_ACTIVE_ALL = 4064¶
RoboDK enable menu only flag
- robodk.robolink.FLAG_ITEM_SELECTABLE = 1¶
Allow selecting the item flag
- robodk.robolink.FLAG_ITEM_EDITABLE = 2¶
Allow editing the item flag
- robodk.robolink.FLAG_ITEM_DRAGALLOWED = 4¶
Allow dragging the item flag
- robodk.robolink.FLAG_ITEM_DROPALLOWED = 8¶
Allow dropping nested items flag
- robodk.robolink.FLAG_ITEM_ENABLED = 32¶
Enable this item in the tree flag
- robodk.robolink.FLAG_ITEM_NONE = 0¶
Disable everything item flag
- robodk.robolink.FLAG_ITEM_ALL = 111¶
Enable everything item flag
- robodk.robolink.MAKE_ROBOT_1R = 1¶
1R model type flag
- robodk.robolink.MAKE_ROBOT_2R = 2¶
2R model type flag
- robodk.robolink.MAKE_ROBOT_3R = 3¶
3R model type flag
- robodk.robolink.MAKE_ROBOT_1T = 4¶
1T model type flag
- robodk.robolink.MAKE_ROBOT_2T = 5¶
2T model type flag
- robodk.robolink.MAKE_ROBOT_3T = 6¶
3T model type flag
- robodk.robolink.MAKE_ROBOT_6DOF = 7¶
6 DOF robot model type flag
- robodk.robolink.MAKE_ROBOT_7DOF = 8¶
7 DOF robot model type flag
- robodk.robolink.MAKE_ROBOT_SCARA = 9¶
SCARA robot model type flag
- robodk.robolink.MAKE_ROBOT_GRIPPER = 10¶
Gripper model type flag
- robodk.robolink.MAKE_ROBOT_6COBOT = 11¶
6 DOF cobot model type flag
- robodk.robolink.MAKE_ROBOT_1T1R = 12¶
1T1R model type flag
- robodk.robolink.MAKE_ROBOT_5XCNC = 13¶
5 axis CNC model type flag
- robodk.robolink.MAKE_ROBOT_3T1R = 15¶
3T1R model type flag
- robodk.robolink.MAKE_ROBOT_GENERIC = 16¶
Generic model type flag
- robodk.robolink.ERROR_KINEMATIC = 1¶
One or more points is not reachable path error flag
- robodk.robolink.ERROR_PATH_LIMIT = 2¶
The path reaches the limit of joint axes path error flag
- robodk.robolink.ERROR_PATH_SINGULARITY = 4¶
The robot reached a singularity point path error flag
- robodk.robolink.ERROR_PATH_NEARSINGULARITY = 8¶
The robot is too close to a singularity path error flag
- robodk.robolink.ERROR_COLLISION = 32¶
Collision detected path error flag
- robodk.robolink.SELECT_RESET = -1¶
Reset selection flag
- robodk.robolink.SELECT_NONE = 0¶
Reset selection flag
- robodk.robolink.SELECT_RECTANGLE = 1¶
Rectangle selection flag
- robodk.robolink.SELECT_ROTATE = 2¶
Rotate selection flag
- robodk.robolink.SELECT_ZOOM = 3¶
Zoom selection flag
- robodk.robolink.SELECT_PAN = 4¶
Pan selection flag
- robodk.robolink.SELECT_MOVE = 5¶
Move selection flag
- robodk.robolink.SELECT_MOVE_SHIFT = 6¶
Move Shift selection flag
- robodk.robolink.SELECT_MOVE_CLEAR = 7¶
Move Clear selection flag
- robodk.robolink.DISPLAY_REF_DEFAULT = -1¶
Default reference frame visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.DISPLAY_REF_NONE = 0¶
None reference frame visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.DISPLAY_REF_TX = 1¶
TX reference frame visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.DISPLAY_REF_TY = 2¶
TY reference frame visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.DISPLAY_REF_TZ = 4¶
TZ reference frame visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.DISPLAY_REF_RX = 8¶
RX reference frame visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.DISPLAY_REF_RY = 16¶
RY reference frame visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.DISPLAY_REF_RZ = 32¶
RZ reference frame visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.DISPLAY_REF_PXY = 64¶
Plane XY reference frame visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.DISPLAY_REF_PXZ = 128¶
Plane XZ reference frame visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.DISPLAY_REF_PYZ = 256¶
Plane YZ reference frame visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.VISIBLE_REFERENCE_DEFAULT = -1¶
Default Item visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.VISIBLE_REFERENCE_ON = 1¶
Visible (ON) Item visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.VISIBLE_REFERENCE_OFF = 0¶
Hidden (OFF) Item visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.VISIBLE_ROBOT_NONE = 0¶
None Robot visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.VISIBLE_ROBOT_FLANGE = 1¶
Flange robot visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_Base_3D = 2¶
Axis base 3D robot visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_Base_REF = 4¶
Axis base reference robot visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_1_3D = 8¶
Axis 1 3D robot visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_1_REF = 16¶
Axis 1 reference robot visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_2_3D = 32¶
Axis 2 3D robot visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_2_REF = 64¶
Axis 2 reference robot visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_3_3D = 128¶
Axis 3 3D robot visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_3_REF = 256¶
Axis 3 reference robot visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_4_3D = 512¶
Axis 4 3D robot visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_4_REF = 1024¶
Axis 4 reference robot visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_5_3D = 2048¶
Axis 5 3D robot visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_5_REF = 4096¶
Axis 5 reference robot visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_6_3D = 8192¶
Axis 6 3D robot visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_6_REF = 16384¶
Axis 6 reference robot visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_7_3D = 32768¶
Axis 7 3D robot visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_7_REF = 131072¶
Axis 7 reference robot visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.VISIBLE_ROBOT_DEFAULT = 715827883¶
Default robot visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.VISIBLE_ROBOT_ALL = 2147483647¶
All robot visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.VISIBLE_ROBOT_ALL_REFS = 357913941¶
All references robot visibility flag
- robodk.robolink.SEQUENCE_DISPLAY_DEFAULT = -1¶
Default sequence display flag
- robodk.robolink.SEQUENCE_DISPLAY_TOOL_POSES = 0¶
Using tool poses (argument type) sequence display flag
- robodk.robolink.SEQUENCE_DISPLAY_ROBOT_POSES = 256¶
Using robot poses (argument type) sequence display flag
- robodk.robolink.SEQUENCE_DISPLAY_ROBOT_JOINTS = 2048¶
Using robot joints (argument type) sequence display flag
- robodk.robolink.SEQUENCE_DISPLAY_COLOR_SELECTED = 1¶
Selected color sequence display flag
- robodk.robolink.SEQUENCE_DISPLAY_COLOR_TRANSPARENT = 2¶
Transparent color sequence display flag
- robodk.robolink.SEQUENCE_DISPLAY_COLOR_GOOD = 3¶
Good (green) color sequence display flag
- robodk.robolink.SEQUENCE_DISPLAY_COLOR_BAD = 4¶
Bad (red) color sequence display flag
- robodk.robolink.SEQUENCE_DISPLAY_OPTION_RESET = 1024¶
Reset previous sequences (force timeout) sequence display flag
- class robodk.robolink.InstructionListJointsFlags(value)¶
InstructionListJoints output flags
- Position = 1¶
- Speed = 2¶
- SpeedAndAcceleration = 3¶
- TimeBased = 4¶
- TimeBasedFast = 5¶
- class robodk.robolink.PathErrorFlags(value)¶
Error flags returned by InstructionListJoints
- NoError = 0¶
- Kinematic = 1¶
- PathLimit = 2¶
- InnacurateDueToLargeAxisMove = 2048¶
- PathSingularity = 4¶
- PathNearSingularity = 8¶
- PathFlipAxis = 16¶
- Collision = 32¶
- WristSingularity = 64¶
- ElbowSingularity = 128¶
- ShoulderSingularity = 256¶
- PathInvalidTarget = 512¶
- InvalidArcMove = 1024¶
- robodk.robolink.ConvertErrorCodeToJointErrorType(evalue)¶
Convert error number returned by InstructionListJoints() to PathErrorFlags
- exception robodk.robolink.TargetReachError¶
Unable to reach desired target or destination error.
- exception robodk.robolink.StoppedError¶
The user stopped the operation by selecting Escape key or moving the robot
- exception robodk.robolink.InputError¶
Invalid input parameters provided to the API. Provide input as stated in the documentation.
- exception robodk.robolink.LicenseError¶
Invalid RoboDK license to use the requested feature.
- robodk.robolink.RoboDKInstallFound()¶
Check if RoboDK is installed
- Return type
bool
- robodk.robolink.getPathRoboDK()¶
RoboDK’s executable/binary file
- Return type
str
- robodk.robolink.getPathIcon()¶
- Return type
str
- robodk.robolink.import_install(module_name, pip_name=None, rdk=None, upgrade_pip=False)¶
Import a module by first installing it if the corresponding package is not available. If the module name does not match the pip install command, provide the pip_name for install purposes. Optionally, you can pass the RoboDK API Robolink object to see install progress in RoboDK’s status bar.
# If you want to install opencv for Python and pyserial you should use: import_install("opencv", "opencv-python", RDK) import_install("serial", "pyserial", RDK) # If the name of the module matches the package you can just pass the name of the module. # Example: import_install("xlrd", rdk=RDK) # You can also use version specifiers (https://peps.python.org/pep-0440/#version-specifiers): import_install('numpy', 'numpy>=1.23') import_install('pandas', 'pandas~=1.4')
- Parameters
module_name (
str) –pip_name (
Optional[str], default:None) –rdk (
Optional[Robolink], default:None) –upgrade_pip (
bool, default:False) –
- robodk.robolink.EmbedWindow(window_name, docked_name=None, size_w=- 1, size_h=- 1, pid=0, area_add=1, area_allowed=15, timeout=500, port=None, args=[])¶
Embed a window from a separate process in RoboDK as a docked window. Returns True if successful.
- Parameters
window_name (str) – The name of the window currently open. Make sure the window name is unique and it is a top level window
docked_name (str) – Name of the docked tab in RoboDK (optional, if different from the window name)
pid (int) – Process ID (optional)
area_add (int) – Set to 1 (right) or 2 (left) (default is 1)
area_allowed (int) – Areas allowed (default is 15:no constrain)
timeout (int) – Timeout to abort attempting to embed the window
Example to embed a window as a docked RoboDK window¶from tkinter import * from robodk.robolink import * import threading # Create a new window window = tkinter.Tk() # Close the window def onClose(): window.destroy() quit(0) # Trigger Select button # IMPORTANT: We need to run the action on a separate thread because # (otherwise, if we want to interact with RoboDK window it will freeze) def on_btnSelect(): def thread_btnSelect(): # Run button action (example to select an item and display its name) RDK = Robolink() item = RDK.ItemUserPick('Select an item') if item.Valid(): RDK.ShowMessage("You selected the item: " + item.Name()) threading.Thread(target=thread_btnSelect).start() # Set the window title (must be unique for the docking to work, try to be creative!) window_title = 'RoboDK API Docked Window' window.title(window_title) # Delete the window when we close it window.protocol("WM_DELETE_WINDOW", onClose) # Add a button (Select action) btnSelect = Button(window, text='Trigger on_btnSelect', height=5, width=60, command=on_btnSelect) btnSelect.pack(fill=X) # Embed the window EmbedWindow(window_title) # Run the window event loop. This is like an app and will block until we close the window window.mainloop()
- Parameters
size_w (
int, default:-1) –size_h (
int, default:-1) –port (
Optional[int], default:None) –
2.1.1. Robolink¶
- class robodk.robolink.Robolink(robodk_ip='localhost', port=None, args=[], robodk_path=None, close_std_out=False, quit_on_close=False, com_object=None, skipstatus=False)¶
The Robolink class is the link to RoboDK and allows creating macros for Robodk, simulate applications and generate programs offline. Any interaction is made through “items” (Item() objects). An item is an object in the robodk tree (it can be either a robot, an object, a tool, a frame, a program, …).
- Parameters
robodk_ip (str) – IP of the RoboDK API server (default=’localhost’)
port (int) – Port of the RoboDK API server (default=None, it will use the default value)
args (list) –
Command line arguments to pass to RoboDK on startup (for example: ‘/NOSPLASH /NOSHOW’ should be passed as args=[‘/NOSPLASH’,’/NOSHOW’] to not display RoboDK). Arguments have no effect if RoboDK is already running.
For more information: RoboDK list of arguments on startup.
robodk_path (str) – RoboDK installation path. It defaults to RoboDK’s default path (C:/RoboDK/bin/RoboDK.exe on Windows or /Applications/RoboDK.app/Contents/MacOS/RoboDK on Mac)
close_std_out (bool) – Close RoboDK standard output path. No RoboDK console output will be shown.
quit_on_close (bool) – Close RoboDK when this instance of Robolink disconnect. It has no effect if RoboDK is already running.
com_object – Custom communication class (allows using WebSockets or other custom implementations). It defaults to socket communication.
skipstatus (bool) – Skip the status flag for operations that only wait for the command response status and do not return anything (assumes the command always completes successfully).
Example of a RoboDK API initialization¶from robodk.robolink import * # Connect to the RoboDK API RDK = Robolink() # Retrieve all items and print their names list_items = RDK.ItemList() for item in list_items: print(item.Name())
Force starting a new RoboDK hidden instance and output debug information¶from robodk.robolink import * # Connect to the RoboDK API RDK = Robolink(args=["-NEWINSTANCE", "-NOUI", "-SKIPINI", "-EXIT_LAST_COM"]) # Add a reference frame RDK.AddFrame("My reference frame") RDK.setPose(transl(100,200,300) * rotz(pi/2)) # Retrieve all items and print their names (just a reference frame) list_items = RDK.ItemList() for item in list_items: print(item.Name()) # Close RoboDK RDK.CloseRoboDK() # Example command line arguments: # -NEWINSTANCE: Forces using a new instance # -NOUI: Run RoboDK behind the scenes (without OpenGL context) # -SKIPINI: Skip using RoboDK's INI settings (global settings), this provides a faster startup # -EXIT_LAST_COM: Exit RoboDK when the last API client connected closes # -DEBUG: Run in debug mode (outputs information in the console) # # Follow these steps to see an extended list of command line arguments: # 1- Select Tools-Run Script # 2- Select ShowCommands # # More information here: # https://robodk.com/doc/en/RoboDK-API.html#CommandLine
See also
See also
- SAFE_MODE: int = 1¶
- AUTO_UPDATE: int = 0¶
- TIMEOUT: int = 10¶
- CAMERA_AS_ITEM: bool = True¶
- COM = None¶
- PORT: int = -1¶
- BUILD: int = 0¶
- NEW_INSTANCE = None¶
- LAST_STATUS_MESSAGE: str = ''¶
- MoveC(target1, target2, itemrobot, blocking=True)¶
Performs a circular movement. Use
Item.MoveC()instead.See also
- __init__(robodk_ip='localhost', port=None, args=[], robodk_path=None, close_std_out=False, quit_on_close=False, com_object=None, skipstatus=False)¶
A connection is attempted upon creation of the object.
- Parameters
robodk_ip (str) – IP of the RoboDK API server (default=’localhost’)
port (int) – Port of the RoboDK API server (default=None, it will use the default value)
args (list) –
Command line arguments to pass to RoboDK on startup (for example: ‘/NOSPLASH /NOSHOW’ should be passed as args=[‘/NOSPLASH’,’/NOSHOW’] to not display RoboDK). Arguments have no effect if RoboDK is already running.
For more information: RoboDK list of arguments on startup.
robodk_path (str) – RoboDK installation path. It defaults to RoboDK’s default path (C:/RoboDK/bin/RoboDK.exe on Windows or /Applications/RoboDK.app/Contents/MacOS/RoboDK on Mac)
close_std_out (bool) – Close RoboDK standard output path. No RoboDK console output will be shown.
quit_on_close (bool) – Close RoboDK when this instance of Robolink disconnect. It has no effect if RoboDK is already running.
com_object – Custom communication class (allows using WebSockets or other custom implementations). It defaults to socket communication.
skipstatus (bool) – Skip the status flag for operations that only wait for the command response status and do not return anything (assumes the command always completes successfully).
- IP: str = 'localhost'¶
- ARGUMENTS: List[str] = []¶
- CLOSE_STD_OUT: bool = False¶
- QUIT_ON_CLOSE: bool = False¶
- APPLICATION_DIR: str = ''¶
- NODELAY: bool = False¶
- PORT_START: int = 20500¶
- PORT_END: int = 20500¶
- DEBUG: bool = False¶
- Disconnect()¶
Stops the communication with RoboDK. If setRunMode is set to RUNMODE_MAKE_ROBOTPROG for offline programming, any programs pending will be generated.
- Finish()¶
Stops the communication with RoboDK. If setRunMode is set to RUNMODE_MAKE_ROBOTPROG for offline programming, any programs pending will be generated.
See also
- NewLink()¶
Reconnect the API using a different communication link.
- isNewInstance()¶
- Return type
bool
- Connect()¶
Establish a connection with RoboDK. If RoboDK is not running it will attempt to start RoboDK from the default installation path (otherwise APPLICATION_DIR must be set properly). If the connection succeeds it returns 1, otherwise it returns 0
- Return type
int
- Item(name, itemtype=None)¶
Returns an item by its name. If there is no exact match it will return the last closest match. Specify what type of item you are looking for with itemtype. This is useful if 2 items have the same name but different type. (check variables ITEM_TYPE_*)
- Parameters
name (str) – name of the item (name of the item shown in the RoboDK station tree)
itemtype (int) – type of the item to be retrieved (avoids confusion if there are similar name matches). Use ITEM_TYPE_*.
Available Item types¶ITEM_TYPE_STATION=1 # station item (.rdk files) ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT=2 # robot item (.robot files) ITEM_TYPE_FRAME=3 # reference frame item ITEM_TYPE_TOOL=4 # tool item (.tool files or tools without geometry) ITEM_TYPE_OBJECT=5 # object item (.stl, .step, .iges, ...) ITEM_TYPE_TARGET=6 # target item ITEM_TYPE_PROGRAM=8 # program item (made using the GUI) ITEM_TYPE_PROGRAM_PYTHON=10 # Python program or macro
See also
See also
Name(),Pose(),setPose(),setParent(),setJoints(),MoveJ(),MoveL()Example:
from robodk.robolink import * # import the robolink library RDK = Robolink() # connect to the RoboDK API (RoboDK starts if it has not started tool = RDK.Item('Tool') # Retrieve an item named tool robot = RDK.Item('', ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT) # the first available robot
- Return type
- ItemList(filter=None, list_names=False)¶
Returns a list of items (list of name or pointers) of all available items in the currently open station of RoboDK.
- Parameters
filter (int) – (optional) Filter the list by a specific item type (ITEM_TYPE_*). For example: RDK.ItemList(filter = ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT)
list_names (int) – (optional) Set to True to return a list of names instead of a list of
Item
See also
- Return type
Union[List[Item],List[str]]
- ItemUserPick(message='Pick one item', itemtype_or_list=None)¶
Shows a RoboDK popup to select one Item from the open station. An item type (ITEM_TYPE_*) can be specified to filter desired items. If no type is specified, all items are selectable.
Note: If only one Item is available, the Item is selected and return without prompting the user. If a candidate Item is currently selected in the RoboDK tree, the Item is selected and return without prompting the user.
Example:
RDK.ItemUserPick("Pick a robot", ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT) RDK.ItemUserPick("Pick a from a list", [item1, item2, item3])
- Parameters
message (str) – message to display
itemtype_or_list (int) – filter choices by a specific item type (ITEM_TYPE_*) or provide a list of items to choose from
See also
- Return type
- ShowRoboDK()¶
Show or raise the RoboDK window
See also
- HideRoboDK()¶
Hide the RoboDK window. RoboDK will keep running as a process
See also
- CloseRoboDK()¶
Close RoboDK window and finish RoboDK’s execution.
- Version()¶
Return RoboDK’s version as a string
- Return type
str
- setWindowState(windowstate=2)¶
Set the state of the RoboDK window
- Parameters
windowstate (int) – state of the window (WINDOWSTATE_*)
Allowed window states¶WINDOWSTATE_HIDDEN = -1 # Hidden WINDOWSTATE_SHOW = 0 # Visible WINDOWSTATE_MINIMIZED = 1 # Minimize window WINDOWSTATE_NORMAL = 2 # Show normal window (last known state) WINDOWSTATE_MAXIMIZED = 3 # Show maximized window WINDOWSTATE_FULLSCREEN = 4 # Show fulscreen window WINDOWSTATE_CINEMA = 5 # Show maximized window without the toolbar and without the menu WINDOWSTATE_FULLSCREEN_CINEMA= 6 # Show fulscreen window without the toolbar and without the menu
See also
- setFlagsRoboDK(flags=65535)¶
Update the RoboDK flags. RoboDK flags allow defining how much access the user has to RoboDK features. Use a FLAG_ROBODK_* variables to set one or more flags.
- Parameters
flags (int) – state of the window (FLAG_ROBODK_*)
Allowed RoboDK flags¶FLAG_ROBODK_TREE_ACTIVE = 1 # Enable the tree FLAG_ROBODK_3DVIEW_ACTIVE = 2 # Enable the 3D view (3D mouse navigation) FLAG_ROBODK_LEFT_CLICK = 4 # Enable left clicks FLAG_ROBODK_RIGHT_CLICK = 8 # Enable right clicks FLAG_ROBODK_DOUBLE_CLICK = 16 # Enable double clicks FLAG_ROBODK_MENU_ACTIVE = 32 # Enable the main menu (complete menu) FLAG_ROBODK_MENUFILE_ACTIVE = 64 # Enable the File menu FLAG_ROBODK_MENUEDIT_ACTIVE = 128 # Enable the Edit menu FLAG_ROBODK_MENUPROGRAM_ACTIVE = 256 # Enable the Program menu FLAG_ROBODK_MENUTOOLS_ACTIVE = 512 # Enable the Tools menu FLAG_ROBODK_MENUUTILITIES_ACTIVE = 1024 # Enable the Utilities menu FLAG_ROBODK_MENUCONNECT_ACTIVE = 2048 # Enable the Connect menu FLAG_ROBODK_WINDOWKEYS_ACTIVE = 4096 # Enable the keyboard FLAG_ROBODK_TREE_VISIBLE = 8192 # Make the station tree visible FLAG_ROBODK_REFERENCES_VISIBLE = 16384 # Make the reference frames visible FLAG_ROBODK_STATUSBAR_VISIBLE = 32768 # Make the status bar visible FLAG_ROBODK_NONE = 0 # Disable everything FLAG_ROBODK_ALL = 0xFFFF # Enable everything FLAG_ROBODK_MENU_ACTIVE_ALL # Enable the menu only
See also
- setFlagsItem(item, flags=111)¶
Update item flags. Item flags allow defining how much access the user has to item-specific features. Use FLAG_ITEM_* flags to set one or more flags.
- Parameters
item (
Item) – item to set (set to 0 to apply to all items)flags (int) – set the item flags (FLAG_ITEM_*)
See also
- getFlagsItem(item)¶
Retrieve current item flags. Item flags allow defining how much access the user has to item-specific features. Use FLAG_ITEM_* flags to set one or more flags.
- Parameters
item (
Item) – item to get flags
Allowed RoboDK flags¶FLAG_ITEM_SELECTABLE = 1 # Allow selecting the item FLAG_ITEM_EDITABLE = 2 # Allow editing the item FLAG_ITEM_DRAGALLOWED = 4 # Allow dragging the item FLAG_ITEM_DROPALLOWED = 8 # Allow dropping nested items FLAG_ITEM_ENABLED = 32 # Enable this item in the tree FLAG_ITEM_NONE = 0 # Disable everything FLAG_ITEM_ALL = 64+32+8+4+2+1 # Enable everything
See also
- Return type
int
- ShowMessage(message, popup=True)¶
Show a message from the RoboDK window. By default, the message will be a blocking popup. Alternatively, it can be a message displayed at the bottom of RoboDK’s main window.
- Parameters
message (str) – message to display
popup (bool) – Set to False to display the message in the RoboDK’s status bar (not blocking)
- Copy(item, copy_childs=True)¶
Makes a copy of an item (same as Ctrl+C), which can be pasted (Ctrl+V) using Paste().
- Parameters
item (
Item) – Item to copy to the clipboard
See also
Paste(),Item.Copy()Example:
RDK = Robolink() object = RDK.Item('My Object') object.Copy() # same as RDK.Copy(object) also works object_copy1 = RDK.Paste() object_copy1.setName('My Object (copy 1)') object_copy2 = RDK.Paste() object_copy2.setName('My Object (copy 2)')
- Parameters
copy_childs (
bool, default:True) –
- Paste(paste_to=0, paste_times=1)¶
Paste the copied item as a dependency of another item (same as Ctrl+V). Paste should be used after Copy(). It returns the newly created item.
- Parameters
paste_to (
Item) – Item to attach the copied item (optional)paste_times (int) – number of times to paste the item (returns a list if greater than 1)
- Returns
New item created
- Return type
See also
- AddFile(filename, parent=0)¶
Load a file and attach it to parent (if provided). The call returns the newly added
Item. If the new file is an object and it is attached to a robot it will be automatically converted to a tool.- Parameters
filename (str) – any file to load, supported by RoboDK. Supported formats include STL, STEP, IGES, ROBOT, TOOL, RDK,… It is also possible to load supported robot programs, such as SRC (KUKA), SCRIPT (Universal Robots), LS (Fanuc), JBI (Motoman), MOD (ABB), PRG (ABB), …
parent (
Item) – item to attach the newly added object (optional)
Example:
RDK = Robolink() item = RDK.AddFile(r'C:\Users\Name\Desktop\object.step') item.setPose(transl(100,50,500)) # Add a tool to an existing robot: tool = RDK.AddFile(r'C:\Users\Name\Desktop\robot-tool.stl', robot) tool.setPoseTool(transl(100,50,500)) # Add a reference frame, move it and add an object to that reference frame (locally): frame = AddFrame('Reference A') frame.setPose(transl(100,200,300)) new_object = RDK.Addfile('path-to-object.stl', frame)
See also
- Return type
- AddShape(triangle_points, add_to=0, override_shapes=False)¶
Adds a shape provided triangle coordinates. Triangles must be provided as a list of vertices. A vertex normal can be provided optionally.
- Parameters
- Returns
added object/shape (0 if failed)
- Return type
See also
- Parameters
add_to (
Item, default:0) –
- AddCurve(curve_points, reference_object=0, add_to_ref=False, projection_type=3)¶
Adds a curve provided point coordinates. The provided points must be a list of vertices. A vertex normal can be provided optionally.
- Parameters
curve_points (
Mat(3xN matrix, or 6xN to provide curve normals as ijk vectors)) – List of points defining the curvereference_object (
Item) – item to attach the newly added geometry (optional)add_to_ref (bool) – If True, the curve will be added as part of the object in the RoboDK item tree (a reference object must be provided)
projection_type (int) – type of projection. Use the PROJECTION_* flags.
- Returns
added object/shape (0 if failed)
- Return type
Available projection types¶PROJECTION_NONE = 0 # No projection PROJECTION_CLOSEST = 1 # The projection will be the closest point on the surface PROJECTION_ALONG_NORMAL = 2 # The projection will be done along the normal. PROJECTION_ALONG_NORMAL_RECALC = 3 # The projection will be done along the normal. Furthermore, the normal will be recalculated according to the surface normal. PROJECTION_CLOSEST_RECALC = 4 # The projection will be the closest point on the surface and the normals will be recalculated PROJECTION_RECALC = 5 # The normals are recalculated according to the surface normal of the closest projection. The points are not changed.
See also
- AddPoints(points, reference_object=0, add_to_ref=False, projection_type=3)¶
Adds a list of points to an object. The provided points must be a list of vertices. A vertex normal can be provided optionally.
- Parameters
points (
Mat(3xN matrix, or 6xN to provide point normals as ijk vectors)) – list of points or matrixreference_object (
Item) – item to attach the newly added geometry (optional)add_to_ref (bool) – If True, the points will be added as part of the object in the RoboDK item tree (a reference object must be provided)
projection_type (int) – type of projection. Use the PROJECTION_* flags.
- Returns
added object/shape (0 if failed)
- Return type
See also
The difference between ProjectPoints and AddPoints is that ProjectPoints does not add the points to the RoboDK station.
If you provide the points in absolute coordinates and you want to add them relative to an existing object you should pass a reference_object.
If you provide relative point coordinates you should not pass a reference object. You can attach the points to the parent using setParent().
For maximum performance results it is better to provide the points as a 6xN matrix.
Example - Project points to an object relative to a coordinate system
# Project points to the part object projected_points = RDK.ProjectPoints( robomath.Mat(points_list)).tr(), part, projection_type=robolink.PROJECTION_ALONG_NORMAL) # Add them to RoboDK as relative points points_object = RDK.AddPoints(projected_points) # Attach them to the same parent points_object.setParent(part.Parent())
- ProjectPoints(points, object_project, projection_type=3, timeout=30)¶
Project a point or a list of points given its coordinates. The provided points must be a list of [XYZ] coordinates. Optionally, a vertex normal can be provided [XYZijk]. This function returns the projected points as a list of points (empty matrix if failed).
This function wors with relative coordinates. The points must be relative to the coordinate system where the object is attached to. And the returned points are relative to the reference frame of the same object provided.
- Parameters
points (list of points (XYZ or XYZijk list of floats), or
Mat(3xN matrix, or 6xN to provide point normals as ijk vectors)) – list of points to projectobject_project (
Item) – object to project the pointsprojection_type (int) – Type of projection. For example: PROJECTION_ALONG_NORMAL_RECALC will project along the point normal and recalculate the normal vector on the surface projected.
timeout (int) – Max timeout to wait for a reply in seconds (30 seconds by default).
For maximum performance results you should provide the points as a 6xN matrix.
The difference between ProjectPoints and AddPoints is that ProjectPoints does not add the points to the RoboDK station.
- Return type
Union[List[float],Mat]
- CloseStation()¶
Closes the current RoboDK station without suggesting to save
- Delete(item_list)¶
Remove a list of items.
See also
- Save(filename, itemsave=0)¶
Save an item or a station to a file (formats supported include RDK, STL, ROBOT, TOOL, …). If no item is provided, the open station is saved.
- Parameters
filename (str) – File path to save
itemsave (
Item) – Item to save (leave at 0 to save the current RoboDK station as an RDK file
See also
- AddStation(name='New Station')¶
Add a new empty station. It returns the station
Itemcreated.- Parameters
name (str) – name of the station
See also
- Return type
- AddTarget(name, itemparent=0, itemrobot=0)¶
Add a new target that can be reached with a robot.
- Parameters
- Returns
New target item created
- Return type
See also
- AddFrame(name, itemparent=0)¶
Adds a new reference Frame. It returns the new
Itemcreated.- Parameters
name (str) – name of the new reference frame
itemparent (
Item) – Item to attach the new reference frame (such as another reference frame)
See also
- Return type
- AddProgram(name, itemrobot=0)¶
Add a new program to the RoboDK station. Programs can be used to simulate a specific sequence, to generate vendor specific programs (Offline Programming) or to run programs on the robot (Online Programming). It returns the new
Itemcreated. Tip: Use the MoveRobotThroughLine.py macro to create programs in the RoboDK station (Option 2).- Parameters
name (str) – Name of the program
itemrobot (
Item) – Robot that will be used for this program. It is not required to specify the robot if the station has only one robot or mechanism.
- Returns
New program item
- Return type
See also
AddTarget(),MoveJ(),MoveL(),setDO(),waitDI(),Pause(),RunInstruction(),ShowInstructions(),ShowTargets(),Update()Example 1 - Generic program with movements:
# Turn off rendering (faster) RDK.Render(False) prog = RDK.AddProgram('AutoProgram') # Hide program instructions (optional, but faster) prog.ShowInstructions(False) # Retrieve the current robot position: pose_ref = robot.Pose() # Iterate through a number of points for i in range(len(POINTS)): # add a new target ti = RDK.AddTarget('Auto Target %i' % (i+1)) # use the reference pose and update the XYZ position pose_ref.setPos(POINTS[i]) ti.setPose(pose_ref) # force to use the target as a Cartesian target (default) ti.setAsCartesianTarget() # Add the target as a Linear/Joint move in the new program prog.MoveL(ti) # Hide the target items from the tree: it each movement still keeps its own target. # Right click the movement instruction and select "Select Target" to see the target in the tree program.ShowTargets(False) # Turn rendering ON before starting the simulation (automatic if we are done) RDK.Render(True) #-------------------------------------- # Update the program path to display the yellow path in RoboDK. # Set collision checking ON or OFF check_collisions = COLLISION_OFF # Update the path (can take some time if collision checking is active) update_result = program.Update(check_collisions) # Retrieve the result n_insok = update_result[0] time = update_result[1] distance = update_result[2] percent_ok = update_result[3]*100 str_problems = update_result[4] if percent_ok < 100.0: msg_str = "WARNING! Problems with <strong>%s</strong> (%.1f):<br>%s" % (program_name, percent_ok, str_problems) else: msg_str = "No problems found for program %s" % program_name # Notify the user: print(msg_str) RDK.ShowMessage(msg_str)
Example 2 - Program flow, manage inputs/outputs and program calls:
# Add a pause (in miliseconds) program.Pause(1000) # pause motion 1 second # Stop the program so that it can be resumed # It provokes a STOP (pause until the operator desires to resume) program.Pause() # Add a program call or specific code in the program: program.RunInstruction('ChangeTool(2)',INSTRUCTION_CALL_PROGRAM) program.RunInstruction('ChangeTool(2);',INSTRUCTION_INSERT_CODE) # Set a digital output program.setDO('DO_NAME', 1) # Wait for a digital input: program.waitDI('DI_NAME', 1)
Example 3 - Add movements with external axes:
# Add a new movement involving external axes: # First: create a new target target = RDK.AddTarget("T1", reference) # Set the target as Cartesian (default) target.setAsCartesianTarget() # Specify the position of the external axes: external_axes = [10, 20] # The robot joints are calculated to reach the target # given the position of the external axes target.setJoints([0,0,0,0,0,0] + external_axes) # Specify the pose (position with respect to the reference frame): target.setPose(KUKA_2_Pose([x,y,z,w,p,r])) # Add a new movement instruction linked to that target: program.MoveJ(target)
Example 4 - Add a program call after each movement instruction inside a program:
from robodk.robolink import * # API to communicate with RoboDK from robodk.robodialogs import * # User prompts RDK = Robolink() # Ask the user to select a program: prog = RDK.ItemUserPick("Select a Program to modify", ITEM_TYPE_PROGRAM) if not prog.Valid(): print("Operation cancelled or no programs available") quit() # Ask the user to enter a function call that will be added after each movement: print("Program selected: " + prog.Name()) ins_call = mbox("Enter a program call to add after each movement", entry="SynchRobot") if not ins_call: print("Operation cancelled") quit() # Iterate through all the instructions in a program: ins_id = 0 ins_count = prog.InstructionCount() while ins_id < ins_count: # Retrieve instruction ins_nom, ins_type, move_type, isjointtarget, pose, joints = prog.Instruction(ins_id) if ins_type == INS_TYPE_MOVE: # Select the movement instruction as a reference prog.InstructionSelect(ins_id) # Add a new program call prog.RunInstruction(ins_call, INSTRUCTION_CALL_PROGRAM) # Advance one additional instruction as we just added another instruction ins_id = ins_id + 1 ins_count = ins_count + 1 ins_id = ins_id + 1
More examples to generate programs directly from your script or move the robot directly from your program here: Points to Program. or the macro available in RoboDK/Library/Macros/MoveRobotThroughLine.py
- AddMillingProject(name='Milling settings', itemrobot=0)¶
Deprecated since version 4.0: Obsolete. Use
AddMachiningProject()instead.
- AddMachiningProject(name='Milling settings', itemrobot=0)¶
Add a new robot machining project. Machining projects can also be used for 3D printing, following curves and following points. It returns the newly created
Itemcontaining the project settings. Tip: Use the MoveRobotThroughLine.py macro to see an example that creates a new “curve follow project” given a list of points to follow (Option 4).- Parameters
name (str) – Name of the project settings
itemrobot (
Item) – Robot to use for the project settings (optional). It is not required to specify the robot if only one robot or mechanism is available in the RoboDK station.
See also
- Return type
- RunProgram(fcn_param, wait_for_finished=False)¶
Run a program (start a program). If the program exists in the RoboDK station, it has the same behavior as right clicking and selecting Run (or Run Python script for Python programs). When generating a program offline (Offline Programming), the program call will be generated in the program output (RoboDK will handle the syntax when the code is generated for a specific robot using the post processor).
- Parameters
fcn_param (str) – program name and parameters. Parameters can be provided for Python programs available in the RoboDK station as well.
wait_for_finished (bool) – Set to True to block execution during a simulation until the program finishes (skipped if the program does not exist or when the program is generated)
See also
- Return type
int
- RunCode(code, code_is_fcn_call=False)¶
Generate a program call or a customized instruction output in a program. If code_is_fcn_call is set to True it has the same behavior as RDK.RunProgram(). In this case, when generating a program offline (offline programming), a function/procedure call will be generated in the program output (RoboDK will handle the syntax when the code is generated for a specific robot using the post processor). If the program exists it will also run the program in simulate mode.
- Parameters
code (str) – program name or code to generate
code_is_fcn_call (bool) – Set to True if the provided code corresponds to a function call (same as RunProgram()), if so, RoboDK will handle the syntax when the code is generated for a specific robot.
Example to run an existing program in the RoboDK station:
from robodk.robolink import * # import the robolink library RDK = Robolink() # connect to the RoboDK API (RoboDK starts if it has not started RDK.RunCode("Prog1", True) # Run a program named Prog1 available in the RoboDK station
See also
- Return type
int
- RunMessage(message, message_is_comment=False)¶
Show a message or a comment in the program generated offline (program generation). The message (or code) is displayed on the teach pendant of the robot.
- Parameters
message (str) – message or comment to display.
message_is_comment (bool) – Set to True to generate a comment in the generated code instead of displaying a message on the teach pendant of the robot.
- Render(always_render=False)¶
Display/render the scene: update the display. This function turns default rendering (rendering after any modification of the station unless always_render is set to true). Use Update to update the internal links of the complete station without rendering (when a robot or item has been moved).
- Parameters
always_render (bool) – Set to True to update the screen every time the station is modified (default behavior when Render() is not used).
See also
- Update()¶
Update the screen. This updates the position of all robots and internal links according to previously set values. This function is useful when Render is turned off (Example: “RDK.Render(False)”). Otherwise, by default RoboDK will update all links after any modification of the station (when robots or items are moved).
See also
- IsInside(object_inside, object)¶
Checks if an object is inside another object. The encapsulating object must be closed-form, and both objects must be visible with at least 50% color transparency.
- Parameters
- Returns
1 if object_inside is inside object, else 0.
- Return type
int
See also
- setCollisionActive(check_state=1)¶
Set global collision checking ON or OFF (COLLISION_ON/COLLISION_OFF).
See also
- Parameters
check_state (
int, default:1) –- Return type
int
- setCollisionActivePair(check_state, item1, item2, id1=0, id2=0)¶
Set collision checking ON or OFF (COLLISION_ON/COLLISION_OFF) for a specific pair of objects (
Item). This allows altering the collision map for Collision checking. Specify the link id for robots or moving mechanisms (id 0 is the base) Returns 1 if succeeded. Returns 0 if setting the pair failed (wrong id is provided)See also
- setCollisionActivePairList(list_check_state, list_item1, list_item2, list_id1=None, list_id2=None)¶
Set collision checking ON or OFF (COLLISION_ON/COLLISION_OFF) for a specific list of pairs of objects. This allows altering the collision map for Collision checking. Specify the link id for robots or moving mechanisms (id 0 is the base).
- CollisionActivePairList()¶
Return the list of pairs of items that are being checked for collisions. The list includes the index of a robot joint if the item is a robot.
See also
- Collisions()¶
Return the number of pairs of objects that are currently in a collision state.
- Return type
int
- Collision(item1, item2)¶
Returns 1 if item1 and item2 collided. Otherwise returns 0.
See also
- CollisionItems()¶
Return the list of items that are in a collision state. This function can be used after calling Collisions() to retrieve the items that are in a collision state.
See also
- Return type
List[Item]
- CollisionPairs()¶
Return the list of pairs of items that are in a collision state. The list includes the index of a robot joint if the item is a robot. This function can be used after calling Collisions() to retrieve the items that are in a collision state.
See also
- setSimulationSpeed(speed)¶
Set the simulation speed. A simulation speed of 5 (default) means that 1 second of simulation time equals to 5 seconds in a real application. The slowest speed ratio allowed is 0.001. Set a large simmulation ratio (>100) for fast simulation results.
- Parameters
speed (float) – simulation ratio
See also
- SimulationSpeed()¶
Return the simulation speed. A simulation speed of 1 means real-time simulation. A simulation speed of 5 (default) means that 1 second of simulation time equals to 5 seconds in a real application.
See also
- SimulationTime()¶
Retrieve the simulation time (in seconds). Time of 0 seconds starts with the first time this function is called. The simulation time changes depending on the simulation speed. The simulation time is usually faster than the real time (5 times by default).
See also
- Return type
float
- setRunMode(run_mode=1)¶
Set the run mode (behavior) of the script, for either simulation, offline programming or online programming. By default, robodk shows the path simulation for movement instructions (run_mode=RUNMODE_SIMULATE).
Available run modes¶RUNMODE_SIMULATE=1 # performs the simulation moving the robot (default) RUNMODE_QUICKVALIDATE=2 # performs a quick check to validate the robot movements RUNMODE_MAKE_ROBOTPROG=3 # makes the robot program RUNMODE_MAKE_ROBOTPROG_AND_UPLOAD=4 # makes the robot program and updates it to the robot RUNMODE_MAKE_ROBOTPROG_AND_START=5 # makes the robot program and starts it on the robot (independently from the PC) RUNMODE_RUN_ROBOT=6 # moves the real robot from the PC (PC is the client, the robot behaves like a server)
The following calls will alter the current run mode:
1-
Connect()automatically sets RUNMODE_RUN_ROBOT. So it will use the robot driver together with the simulation.2-
ProgramStart()automatically sets the mode to RUNMODE_MAKE_ROBOTPROG. So it will generate the programSee also
- Parameters
run_mode (
int, default:1) –
- RunMode()¶
Return the current run mode (behavior) of the script. By default, robodk simulates any movements requested from the API (such as prog.MoveL) simulation for movement instructions (run_mode=RUNMODE_SIMULATE).
See also
- Return type
int
- getParams()¶
Get all the user parameters from the open RoboDK station. Station parameters can also be modified manually by right clicking the station item and selecting “Station parameters” :return: list of pairs of strings :rtype: list of str
See also
- getParam(param='PATH_OPENSTATION', str_type=True)¶
Get a global or a station parameter from the open RoboDK station. Station parameters can also be modified manually by right clicking the station item and selecting “Station parameters”
- Parameters
param (str) – name of the parameter
str_type (bool) – True to retrieve a string parameter (False for binary/bytes type)
- Returns
value of the parameter.
- Return type
str, float or None if the parameter is unknown
Available global parameters¶PATH_OPENSTATION # Full path of the current station (.rdk file) FILE_OPENSTATION # File name of the current station (name of the .rdk file) PATH_DESKTOP # Full path to the desktop folder
See also
- setParam(param, value)¶
Set a station parameter. If the parameters exists, it will be updated. Otherwise, it will be added to the station.
- Parameters
param (str) – name of the parameter
value (str) – value of the parameter (value type can be str or bytes)
See also
- Command(cmd, value='', skip_result=False)¶
Send a special command. These commands are meant to have a specific effect in RoboDK, such as changing a specific setting or provoke specific events.
- Parameters
command (str) – Command Name, such as Trace, Threads or Window.
value (str) – Comand value (optional, not all commands require a value)
Select Tools-Run Script-Show Commands to see all available commands.
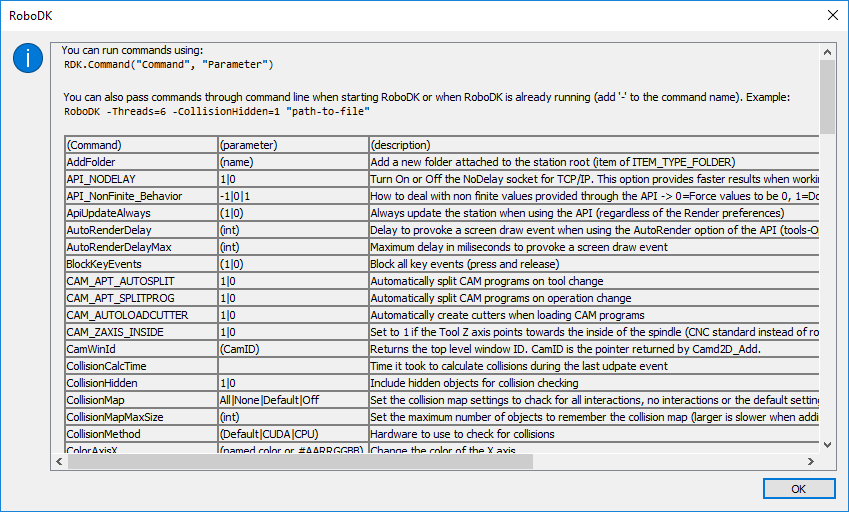 Example commands¶
Example commands¶from robodk.robolink import * RDK = Robolink() # Start the RoboDK API # How to change the number of threads using by the RoboDK application: RDK.Command("Threads", "4") # How to change the default behavior of 3D view using the mouse: RDK.Command("MouseClick_Left", "Select") # Set the left mouse click to select RDK.Command("MouseClick_Mid", "Pan") # Set the mid mouse click to Pan the 3D view RDK.Command("MouseClick_Right", "Rotate") # Set the right mouse click to Rotate the 3D view RDK.Command("MouseClick", "Default") # Set the default mouse 3D navigation settings # Provoke a resize event RDK.Command("Window", "Resize") # Reset the trace RDK.Command("Trace", "Reset")
You can also pass commands through command line when starting RoboDK or when RoboDK is already running (add ‘-‘ to the command name). More information about command line options available in the documentation: https://robodk.com/doc/en/RoboDK-API.html#CommandLine
Example to start RoboDK in Chinese and white background using 6 threads and load a RoboDK project file¶RoboDK -Lang=zh -ColorBgBottom=white -ColorBgTop=white -Threads=6 "path-to-file.rdk"
See also
- Parameters
cmd (
str) –skip_result (
bool, default:False) –
- Return type
Union[str,List[Mat]]
- getOpenStations()¶
Returns the list of open stations in RoboDK
See also
setActiveStation(),getParam(),Childs(),Save(),AddStation()- Return type
List[Item]
- ActiveStation()¶
Returns the active station item (station currently visible)
See also
setActiveStation(),getParam(),Childs(),Save(),AddStation()- Return type
- setActiveStation(stn)¶
Set the active station (project currently visible)
- Parameters
stn (
Item) – station item, it can be previously loaded as an RDK file
See also
ActiveStation(),getOpenStations(),getParam(),Childs(),AddFile(),AddStation()
- ShowSequence(matrix, display_type=- 1, timeout=- 1)¶
Displays a sequence of joints or poses in RoboDK.
- Parameters
matrix (list of list of float, a matrix of joints as a
Mator a list of poses asMat) – list of joints as a matrix or as a list of joint arrays, a list of poses, or a sequence of instructions (same sequence that was supported with RoKiSim).display_type (int, optional) – display options (SEQUENCE_DISPLAY_*). Use -1 to use default.
timeout (int, optional) – display timeout, in milliseconds. Use -1 to use default.
Tip: use
InstructionList()to retrieve the instruction list in RoKiSim format.See also
- LaserTracker_Measure(estimate=[0, 0, 0], search=False)¶
Takes a measurement using the laser tracker with respect to the tracker reference frame. If an estimate point is provided, the laser tracker will first move to those coordinates. If search is True, the tracker will search for a target. Returns the XYZ coordinates of target if it was found. Othewise it retuns None. For trackers that support a 6D measurement, the returned value with be an array of 6 values (list) to include the Euler angles.
- Parameters
estimate (
List[float], default:[0, 0, 0]) –search (
bool, default:False) –
- Return type
List[float]
- MeasurePose(target=- 1, time_avg_ms=0, tip_xyz=None)¶
Takes a measurement with a 6D measurement device. It returns two poses, the base reference frame and the measured object reference frame. Status is negative if the measurement failed. extra data is [error_avg, error_max] in mm, if we are averaging a pose.
- Parameters
time_avg – Take the measurement for a period of time and average the result.
tip_xyz (
Optional[List[float]], default:None) – Offset the measurement to the tip.target (
int, default:-1) –time_avg_ms (
float, default:0) –
- Return type
Tuple[Mat,List]
- Collision_Line(p1, p2, ref=None)¶
Checks the collision between a line and any objects in the station. The line is defined by 2 points.
- Parameters
p1 (list of float) – start point of the line [x,y,z]
p2 (list of float) – end point of the line [x,y,z]
ref (
Mat) – Reference of the two points with respect to the absolute station reference.
- Returns
[collision (True or False), item (collided), point (point of collision with respect to the station)]
- Return type
[bool,
Item, list of float]
- setPoses(items, poses)¶
Sets the relative positions (poses) of a list of items with respect to their parent. For example, the position of an object/frame/target with respect to its parent. Use this function instead of setPose() for faster speed.
See also
- setPosesAbs(items, poses)¶
Set the absolute positions (poses) of a list of items with respect to the station reference. For example, the position of an object/frame/target with respect to its parent. Use this function instead of setPose() for faster speed.
See also
- Joints(robot_item_list)¶
Return the current joints of a list of robots.
See also
Item.setJoints(),Item.Joints() ~robodk.robolink.Item.Joints(),setJoints()
- setJoints(robot_item_list, joints_list)¶
Sets the current robot joints for a list of robot items and a list joints.
See also
- CalibrateTool(poses_xyzwpr, input_format=4, algorithm=0, robot=None, tool=None)¶
Calibrate a TCP given a list of poses/joints and following a specific algorithm/method. Tip: Provide the list of joints instead of poses to maximize accuracy for calibrated robots.
- Parameters
poses_xyzwpr (
Mator a list of list of float) – List of points or a list of robot joints (matrix 3xN or nDOFsxN)input_format (int) – Euler format. Optionally, use JOINT_FORMAT and provide the robot.
algorithm (int) – method/algorithm to use to calculate the new TCP. Tip: use CALIBRATE_TCP …
robot (
Item) – the robot must be provided to calculate the reference frame by jointstool (
Item) – provide a tool item to store the calibration data with that tool (the TCP is not updated, only the calibration joints)
- Return type
Tuple[List[float],List[float],List[float]]- Returns
[TCP, stats, errors]
Out 1 (TCP) - The TCP as a list [x,y,z] with respect to the robot flange
Out 2 (stats) - Statistics as [mean, standard deviation, max] - error stats summary
Out 3 (errors) - List of errors for each pose (array 1xN)
Available Tool Calibration Algorithms¶CALIBRATE_TCP_BY_POINT # Take the same point using different orientations CALIBRATE_TCP_BY_PLANE # Take the same point on a plane
See also
- CalibrateReference(joints_points, method=0, use_joints=False, robot=None)¶
Calibrate a reference frame given a number of points and following a specific algorithm/method. Important: Provide the list of joints to maximize accuracy for calibrated robots.
- Parameters
joints_points (
Mator a list of list of float) – List of points or a list of robot joints (matrix 3xN or nDOFsxN)method (int) – method/algorithm to use to calculate the new TCP. Tip: use CALIBRATE_FRAME …
use_joints (bool) – use points or joint values (bool): Set to True if joints_points is a list of joints
robot (
Item) – the robot must be provided to calculate the reference frame by joints
- Returns
The pose of the reference frame with respect to the robot base frame
- Return type
Available Reference Frame Calibration Algorithms¶CALIBRATE_FRAME_3P_P1_ON_X = 0 # Calibrate by 3 points: [X, X+, Y+] (p1 on X axis) CALIBRATE_FRAME_3P_P1_ORIGIN = 1 # Calibrate by 3 points: [Origin, X+, XY+] (p1 is origin) CALIBRATE_FRAME_6P = 2 # Calibrate by 6 points CALIBRATE_TURNTABLE = 3 # Calibrate turntable CALIBRATE_TURNTABLE = 4 # Calibrate 2-axis turntable
See also
- ProgramStart(programname, folder='', postprocessor='', robot=None)¶
Defines the name of the program when the program is generated (offline programming). It is also possible to specify the name of the post processor as well as the folder to save the program. This method must be called before any program output is generated (before any robot movement or other instruction).
- Parameters
progname (str) – Name of the program
folder (str) – Folder to save the program, leave empty to use the default program folder (usually Desktop)
postprocessor (str) – Name of the post processor. For example, to select the post processor C:/RoboDK/Posts/Fanuc_RJ3.py, specify “Fanuc_RJ3.py” or simply “Fanuc_RJ3”.
robot (
Item) – Robot used for program generation
Example:
from robodk.robolink import * # import the robolink library RDK = Robolink() # connect to the RoboDK API (RoboDK starts if it has not started robot = RDK.Item('', ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT) # use the first available robot RDK.ProgramStart('Prog1','C:/MyProgramFolder/', "ABB_RAPID_IRC5", robot) # specify the program name for program generation # RDK.setRunMode(RUNMODE_MAKE_ROBOTPROG) # redundant robot.MoveJ(target) # make a simulation ... RDK.Finish() # Provokes the program generation (disconnects the API)
See also
- Parameters
programname (
str) –- Return type
int
- setViewPose(pose)¶
Set the pose of the world reference frame with respect to the view (camera/screen)
- Parameters
pose (
Mat) – pose of the item with respect to its parent
- ViewPose()¶
Get the pose of the world reference frame with respect to the view (camera/screen)
- Return type
- BuildMechanism(type, list_obj, parameters, joints_build, joints_home, joints_senses, joints_lim_low, joints_lim_high, base=Matrix: (4, 4) Pose(0.000, 0.000, 0.000, 0.000, 0.000, 0.000): [[ 1, 0, 0, 0 ], [ 0, 1, 0, 0 ], [ 0, 0, 1, 0 ], [ 0, 0, 0, 1 ]] , tool=Matrix: (4, 4) Pose(0.000, 0.000, 0.000, 0.000, 0.000, 0.000): [[ 1, 0, 0, 0 ], [ 0, 1, 0, 0 ], [ 0, 0, 1, 0 ], [ 0, 0, 0, 1 ]] , name='New robot', robot=None)¶
Create a new robot or mechanism.
- Parameters
type (int) – Type of the mechanism
list_obj (list) – list of object items that build the robot
parameters (list) – robot parameters in the same order as shown in the RoboDK menu: Utilities-Build Mechanism or robot
list_joints_build – current state of the robot (joint axes) to build the robot
joints_home (list) – joints for the home position (it can be changed later)
robot (
Item) – existing robot in the station to replace it (optional)name (str) – robot name
Example:
# Start the RoboDK API from robodk.robolink import * from robodk.robomath import * RDK = Robolink() # Define your new robot or mechanism # Example to create a Fanuc LR Mate 200iD robot robot_name = 'Fanuc LR Mate 200iD' DOFs = 6 # Define the joints of the robot/mechanism joints_build = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] # Define the home position of the robot/mechanism (default position when you build the mechanism) # This is also the position the robot goes to if you select "Home" joints_home = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] # Define the robot parameters. The parameters must be provided in the same order they appear # in the menu Utilities-Model Mechanism or robot # Some basic mechanisms such as 1 or 2 axis translation/rotation axes don't need any parameters # (translation/rotation will happen around the Z axis) #parameters = [] parameters = [330, 50, 0, 330, 35, 335, 80, 0, -90, 0, 0, 0, 0] # Define the joint sense (set to +1 or -1 for each axis (+1 is used as a reference for the ABB IRB120 robot) joints_senses = [+1, +1, -1, -1, -1, -1] # add -1 as 7th index to account for axis 2 and axis 3 coupling # Joint limits (lower limits for each axis) lower_limits = [-170, -100, -67, -190, -125, -360] # Joint limits (upper limits for each axis) upper_limits = [ 170, 145, 213, 190, 125, 360] # Base frame pose (offset the model by applying a base frame transformation) #base_pose = xyzrpw_2_pose([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]) # Fanuc and Motoman robots have the base frame at the intersection of axes 1 and 2 base_pose = xyzrpw_2_pose([0, 0, -330, 0, 0, 0]) # Tool frame pose (offset the tool flange by applying a tool frame transformation) tool_pose = xyzrpw_2_pose([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]) # Retrieve all your items from RoboDK (they should be previously loaded manually or using the API's command RDK.AddFile()) list_objects = [] for i in range(DOFs + 1): if i == 0: itm = RDK.Item(robot_name + ' Base', ITEM_TYPE_OBJECT) else: itm = RDK.Item(robot_name + ' ' + str(i), ITEM_TYPE_OBJECT) list_objects.append(itm) # Create the robot/mechanism new_robot = RDK.BuildMechanism(MAKE_ROBOT_6DOF, list_objects, parameters, joints_build, joints_home, joints_senses, lower_limits, upper_limits, base_pose, tool_pose, robot_name) if not new_robot.Valid(): print("Failed to create the robot. Check input values.") else: print("Robot/mechanism created: " + new_robot.Name())
- Parameters
joints_build (
List[float]) –joints_senses (
List[int]) –joints_lim_low (
List[float]) –joints_lim_high (
List[float]) –
- Return type
- Cam2D_Add(item_object=None, cam_params='', camera_item=None)¶
Open a simulated 2D camera view. Returns a handle pointer that can be used in case more than one simulated view is used.
- Parameters
Example:
from robodk.robolink import * # API to communicate with RoboDK RDK = Robolink() # Close any open 2D camera views RDK.Cam2D_Close() camref = RDK.ItemUserPick('Select the Camera location (reference, tool or object)') #camref = RDK.Item('Frame 7',ITEM_TYPE_FRAME) # Set parameters in mm and degrees: # FOV: Field of view in degrees (2*atan(0.5*height/distance) of the sensor # FOCAL_LENGTH: focal length in mm # FAR_LENGTH: maximum working distance (in mm) # PIXELSIZE: Size of the pixel in micro meters (square size assumed) # SIZE: size of the window in pixels (fixed) (width x height) # WINDOWFIXED: If we specify the Size, make the size of the window exactly the same size # WINDOWRESIZE: Even if we specify the size # SNAPSHOT: size of the snapshot image in pixels if it should be different from the normal size (width x height). Size can be larger than 4k, depending on graphics card support. # BG_COLOR: background color (rgb color or named color: AARRGGBB) # LIGHT_AMBIENT: ambient color (rgb color or named color: AARRGGBB) # LIGHT_SPECULAR: specular color (rgb color or named color: AARRGGBB) # LIGHT_DIFFUSE: diffuse color (rgb color or named color: AARRGGBB) # DEPTH: Add this flag to create a 32 bit depth map (white=close, black=far) # GRAYSCALE: Add this flag to create a grayscale image # NO_TASKBAR: Don't add the window to the task bar # MINIMIZED: Show the window minimized # ALWAYS_VISIBLE: Keep the window on top of all other windows # DOCKED: Show the view as a docked window (not a separate window) # SHADER_VERTEX: File to a vertex shader (GLSL file) # SHADER_FRAGMENT: File to a fragment shader (GLSL file) # Examples to call Camd2D_Add: # Camera without a fixed window size and 1000 mm length cam_id = RDK.Cam2D_Add(camref, 'FOCAL_LENGTH=6 FOV=32 FAR_LENGTH=1000') # Camera with a fixed window size and 1000 mm length cam_id = RDK.Cam2D_Add(camref, 'FOCAL_LENGTH=6 FOV=32 FAR_LENGTH=1000 SIZE=640x480') # Camera with a black background cam_id = RDK.Cam2D_Add(camref, 'FOCAL_LENGTH=6 FOV=32 FAR_LENGTH=1000 SIZE=640x480 BG_COLOR=black') # Camera without a fixed window size and high resolution snapshot cam_id = RDK.Cam2D_Add(camref, 'FOCAL_LENGTH=6 FOV=32 FAR_LENGTH=1000 SIZE=640x480') # Depth view: 32 bit depth map (white=close, black=far) cam_id = RDK.Cam2D_Add(camref, 'FOCAL_LENGTH=6 FOV=32 FAR_LENGTH=1000 SIZE=640x480 DEPTH') # Minimized camera cam_id = RDK.Cam2D_Add(camref, 'FOCAL_LENGTH=6 FOV=32 FAR_LENGTH=1000 SIZE=640x480 MINIMIZED') # Do not show the camera window in the taskbar cam_id = RDK.Cam2D_Add(camref, 'FOCAL_LENGTH=6 FOV=32 FAR_LENGTH=1000 SIZE=640x480 NO_TASKBAR') # Customize the light cam_id = RDK.Cam2D_Add(camref, 'FOCAL_LENGTH=6 FOV=32 FAR_LENGTH=1000 SIZE=640x480 BG_COLOR=black LIGHT_AMBIENT=red LIGHT_DIFFUSE=#FF00FF00 LIGHT_SPECULAR=black') cam_id = RDK.Cam2D_Add(camref, 'FOCAL_LENGTH=6 FOV=32 FAR_LENGTH=600 SIZE=640x480 BG_COLOR=black LIGHT_AMBIENT=red LIGHT_DIFFUSE=black LIGHT_SPECULAR=white') cam_id = RDK.Cam2D_Add(camref, 'FOCAL_LENGTH=6 FOV=32 FAR_LENGTH=1000 SIZE=640x480 LIGHT_AMBIENT=red') # Provoke a popup and allow the user to enter some parameters cam_id = RDK.Cam2D_Add(camref, 'POPUP') # Example to take a snapshot from the camera RDK.Cam2D_Snapshot(RDK.getParam('PATH_OPENSTATION') + "/sample_image.png", cam_id) # Special command to retrieve the window ID: win_id = RDK.Command("CamWinID", str(cam_id)) # print(str(win_id)) #----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- # Example to use a customized shader to customize the effect of light # Tip: Use the example: C:/RoboDK/Library/Example-Shader-Customized-Light.rdk # Tip: If you need a fixed light source update the variable light_Position in the shader_fragment.glsl file # Get the path to the RoboDK library (usually in C:/RoboDK/Library/) path_library = RDK.getParam("PATH_LIBRARY") file_shader_fragment = path_library + '/Macros/Camera-Shaders/shader_fragment.glsl' file_shader_vertex = path_library + '/Macros/Camera-Shaders/shader_vertex.glsl' cam_id = RDK.Cam2D_Add(camref, 'FOCAL_LENGTH=6 FOV=32 FAR_LENGTH=2500 SHADER_FRAGMENT=' + file_shader_fragment + ' SHADER_VERTEX=' + file_shader_vertex)
See also
- Return type
- Cam2D_Snapshot(file_save_img='', cam_handle=0, params='')¶
Take a snapshot from a simulated camera view and save it to a file. Returns 1 if success, 0 otherwise.
- Parameters
file_save_img (str) – file path to save. Formats supported include PNG, JPEG, TIFF, …
cam_handle (int) – camera handle (item returned by Cam2D_Add). If the camera handle is set to None it will take a snapshot of the full 3D views.
params (str) – additional options (use, “Grayscale”, “Depth” or “Color” to modify the camera snapshot)
See also
- Return type
Union[bool,bytes]
- Cam2D_Close(cam_handle=0)¶
Closes all camera windows or one specific camera if the camera handle is provided. Returns True if success, False otherwise.
- Parameters
cam_handle (int) – camera handle (pointer returned by Cam2D_Add). Leave to 0 to close all simulated views.
See also
- Return type
bool
- Cam2D_SetParams(params, cam_handle=0)¶
Set the parameters of the simulated camera. Returns 1 if success, 0 otherwise.
- Parameters
params (str) – parameter settings according to the parameters supported by Cam2D_Add
See also
- Parameters
cam_handle (
Item, default:0) –- Return type
int
- Spray_Add(item_tool=0, item_object=0, params='', points=None, geometry=None)¶
Add a simulated spray gun that allows projecting particles to a part. This is useful to simulate applications such as: arc welding, spot welding, 3D printing, painting, inspection or robot machining to verify the trace.
The scripts ArcStart, ArcEnd and WeldOn and SpindleOn behave in a similar way, the only difference is the default behavior This behavior simmulates Fanuc Arc Welding and triggers appropriate output when using the customized post processor.
Select ESC to clear the trace manually.
Example scripts that use Spray_Add in Library/Macros:
SpindleOn / SpindleOff: Turn trace On/Off
ArcOn / ArcOff: Turn trace On/Off
SprayOn / SprayOff: Simulate a spray given a workspace volume (for painting)
WeldOn / WeldOff: Support for multiple weld guns
Examples:
SpindleOn(2): Show the trace in blue
SpindleOn(red): Show the trace in red
SpindleOff: Turn off the trace
SpindleOn(green,2.5): Green trace with a sphere of radius 2.5 mm
- Parameters
params (str) – A string specifying the behavior of the simulated particles. The string can contain one or more of the following commands (separated by a space). See the allowed parameter options.
points (
Mat) – provide the volume as a list of points as described in the sample macro SprayOn.pygeometry (
Mat) – (optional) provide a list of points describing triangles to define a specific particle geometry. Use this option instead of the PARTICLE command.
Allowed parameter options¶STEP=AxB: Defines the grid to be projected 1x1 means only one line of particle projection (for example, for welding) PARTICLE: Defines the shape and size of particle (sphere or particle), unless a specific geometry is provided: a- SPHERE(radius, facets) b- SPHERE(radius, facets, scalex, scaley, scalez) b- CUBE(sizex, sizey, sizez) RAND=factor: Defines a random factor factor 0 means that the particles are not deposited randomly ELLYPSE: defines the volume as an ellypse (default) RECTANGLE: defines the volume as a rectangle PROJECT: project the particles to the surface (default) (for welding, painting or scanning) NO_PROJECT: does not project the particles to the surface (for example, for 3D printing)
See also
Example:
tool = 0 # auto detect active tool obj = 0 # auto detect object in active reference frame options_command = "ELLYPSE PROJECT PARTICLE=SPHERE(4,8,1,1,0.5) STEP=8x8 RAND=2" # define the ellypse volume as p0, pA, pB, colorRGBA (close and far), in mm # coordinates must be provided with respect to the TCP close_p0 = [ 0, 0, -200] # xyz in mm: Center of the conical ellypse (side 1) close_pA = [ 5, 0, -200] # xyz in mm: First vertex of the conical ellypse (side 1) close_pB = [ 0, 10, -200] # xyz in mm: Second vertex of the conical ellypse (side 1) close_color = [ 1, 0, 0, 1] # RGBA (0-1) far_p0 = [ 0, 0, 50] # xyz in mm: Center of the conical ellypse (side 2) far_pA = [ 60, 0, 50] # xyz in mm: First vertex of the conical ellypse (side 2) far_pB = [ 0, 120, 50] # xyz in mm: Second vertex of the conical ellypse (side 2) far_color = [ 0, 0, 1, 0.2] # RGBA (0-1) close_param = close_p0 + close_pA + close_pB + close_color far_param = far_p0 + far_pA + far_pB + far_color volume = robomath.Mat([close_param, far_param]).tr() RDK.Spray_Add(tool, obj, options_command, volume) RDK.Spray_SetState(SPRAY_ON)
- Spray_SetState(state=1, id_spray=- 1)¶
Sets the state of a simulated spray gun (ON or OFF)
- Parameters
state (int) – Set to ON or OFF. Use the defined constants: SPRAY_*
id_spray (int) – spray handle (pointer returned by Spray_Add). Leave to -1 to apply to all simulated sprays.
See also
- Return type
int
- Spray_GetStats(id_spray=- 1)¶
Gets statistics from all simulated spray guns or a specific spray gun.
- Parameters
id_spray (int) – spray handle (pointer returned by Spray_Add). Leave to -1 to apply to all simulated sprays.
See also
- Return type
Tuple[str,Mat]
- Spray_Clear(id_spray=- 1)¶
Stops simulating a spray gun. This will clear the simulated particles.
- Parameters
id_spray (int) – spray handle (pointer returned by Spray_Add). Leave the default -1 to apply to all simulated sprays.
See also
- Return type
int
- License()¶
Get the license string
- Return type
Tuple[str,str]
- setSelection(list_items=[])¶
Set the selection in the tree
- Parameters
list_items (list) – List of items to set as selected
- MergeItems(list_items=[])¶
Merge multiple object items as one. A new object is created and returned. Provided objects are deleted.
- Parameters
list_items (list) – List of items to set as selected
- Returns
New object created
- Return type
- Popup_ISO9283_CubeProgram(robot=0)¶
Popup the menu to create the ISO9283 cube program (Utilities-Create Cube ISO)
- setInteractiveMode(mode_type=5, default_ref_flags=- 1, custom_objects=None, custom_ref_flags=None)¶
Set the interactive mode to define the behavior when navigating and selecting items in RoboDK’s 3D view.
- Parameters
mode_type (int) – The mode type defines what accion occurs when the 3D view is selected (Select object, Pan, Rotate, Zoom, Move Objects, …)
default_ref_flags (int) – When a movement is specified, we can provide what motion we allow by default with respect to the coordinate system (set apropriate flags)
custom_objects (list) – Provide a list of optional items to customize the move behavior for these specific items (important: the length of custom_ref_flags must match)
custom_ref_flags (list) – Provide a matching list of flags to customize the movement behavior for specific items
- CursorXYZ(x_coord=- 1, y_coord=- 1)¶
Returns the position of the cursor as XYZ coordinates (by default), or the 3D position of a given set of 2D coordinates of the window (x & y coordinates in pixels from the top left corner) The XYZ coordinates returned are given with respect to the RoboDK station (absolute reference). If no coordinates are provided, the current position of the cursor is retrieved.
- Parameters
x_coord (int) – X coordinate in pixels
y_coord (int) – Y coordinate in pixels
Example to retrieve the 3D point under the mouse cursor¶RDK = Robolink() while True: xyz, item = RDK.CursorXYZ() print(str(item) + " " + str(xyz))
- Return type
Tuple[List[float],Item]
- GetPoints(feature_type=10)¶
Retrieves the object under the mouse cursor.
- Parameters
feature_type (int) – set to FEATURE_HOVER_OBJECT_MESH to retrieve object under the mouse cursor, the selected feature and mesh, or FEATURE_HOVER_OBJECT if you don’t need the mesh (faster).
- Return type
Tuple[Item,int,int,str,List[List[float]]]- Returns
Object under the mouse cursor, selected feature, feature id, list of points and description
# Infinite loop to print the item under the mouse cursor while True: object, feature_type, feature_id, feature_name, points = RDK.GetPoints(FEATURE_HOVER_OBJECT) # Faster if you don't need the mesh #object, feature_type, feature_id, feature_name, points = RDK.GetPoints(FEATURE_HOVER_OBJECT_MESH) if object.Valid(): print("Mouse on: " + object.Name() + ": " + feature_name + " Type/id=" + str(feature_type) + "/" + str(feature_id)) # print(points) # RDK.Selection() # returns selection if object in RDK.Selection(): print("Object is selected!") #RDK.setSelection([]) # Clear selection else: print("Nothing under the mouse cursor") pause(0.1)
See also
- PluginLoad(plugin_name='', load=1)¶
Load or unload the specified plugin (path to DLL, dylib or SO file). If the plugin is already loaded it will unload the plugin and reload it. Pass an empty plugin_name to reload all plugins.
- Parameters
plugin_name (str) – name of the plugin or path (if it is not in the default directory.
load (int) – load the plugin (1/default) or unload (0)
Example to load a plugin¶RDK = Robolink() RDK.PluginLoad("C:/RoboDK/bin/plugin/yourplugin.dll") # or if the Add-in is located in the default folder you can simply do: RDK.PluginLoad("yourplugin") # You can also load the library in RoboDK as you would open any other file: RDK.AddFile("C:/RoboDK/bin/plugin/yourplugin.dll")
- Return type
bool
- PluginCommand(plugin_name, plugin_command='', value='')¶
Send a specific command to a RoboDK plugin. The command and value (optional) must be handled by your plugin. It returns the result as a string.
- Parameters
plugin_name (str) – The plugin name must match the PluginName() implementation in the RoboDK plugin.
command (str) – Specific command handled by your plugin
value (str) – Specific value (optional) handled by your plugin
plugin_command (
str, default:'') –
- Return type
str
- EmbedWindow(window_name, docked_name=None, size_w=- 1, size_h=- 1, pid=0, area_add=1, area_allowed=15, timeout=500)¶
Embed a window from a separate process in RoboDK as a docked window. Returns True if successful.
Note: This function should be called on a seperate thread. Use the static function:
EmbedWindow()instead.- Parameters
window_name (str) – The name of the window currently open. Make sure the window name is unique and it is a top level window
docked_name (str) – Name of the docked tab in RoboDK (optional, if different from the window name)
pid (int) – Process ID (optional)
area_add (int) – Set to 1 (right) or 2 (left) (default is 1)
area_allowed (int) – Areas allowed (default is 15:no constrain)
timeout (int) – Timeout to abort attempting to embed the window
See also
- Parameters
size_w (
int, default:-1) –size_h (
int, default:-1) –
- Return type
bool
2.1.2. Item¶
- class robodk.robolink.Item(link, ptr_item=0, itemtype=- 1)¶
The Item class represents an item in RoboDK station. An item can be a robot, a frame, a tool, an object, a target, … any item visible in the station tree. An item can also be seen as a node where other items can be attached to (child items). Every item has one parent item/node and can have one or more child items/nodes.
RoboDK Items are automatically created and retrieved by generated by
Robolinkmethods such asItem()andItemUserPick()See also
from robodk.robolink import * # Import the robolink library RDK = Robolink() # Connect to the RoboDK API (RoboDK starts if it has not started tool = RDK.Item('Tool') # Get an item named Tool (name in the RoboDK station tree) robot = RDK.Item('', ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT) # Get the first available robot target = RDK.Item('Target 1', ITEM_TYPE_TARGET) # Get a target called "Target 1" frame = RDK.ItemUserPick('Select a reference frame', ITEM_TYPE_FRAME) # Prompt the user to select a reference frame robot.setPoseFrame(frame) robot.setPoseTool(tool) robot.MoveJ(target) # Move the robot to the target using the selected reference frame
- Parameters
link (
Robolink) –ptr_item (
Union[int,str], default:0) –itemtype (
int, default:-1) –
- __init__(link, ptr_item=0, itemtype=- 1)¶
- Parameters
link (
Robolink) –ptr_item (
Union[int,str], default:0) –itemtype (
int, default:-1) –
- equals(item2)¶
Returns True if an item is the same as this item
Item- Parameters
item2 (
Item) – item to compare- Return type
bool
- RDK()¶
Returns the RoboDK link Robolink(). It is important to have different links (Robolink) for multithreaded applications.
See also
- Return type
- Type()¶
Return the type of the item (robot, object, tool, frame, …). Tip: Compare the returned value against ITEM_TYPE_* variables
See also
- Return type
int
- Copy(copy_children=True)¶
Copy the item to the clipboard (same as Ctrl+C). Use together with Paste() to duplicate items.
- Parameters
copy_children (bool) – Set to false to prevent copying all items attached to this item.
- Paste()¶
Paste the copied
Itemfrom the clipboard as a child of this item (same as Ctrl+V) Returns the new item created (pasted)- Return type
- AddFile(filename)¶
Adds an object attached to this object
- Parameters
filename (str) – file path
- Return type
- Save(filename)¶
Save a station or object to a file
- Parameters
filename (str) – file to save. Use *.rdk name for RoboDK stations, *.stl file for objects, *.robot file for robots, etc.
- Collision(item_check)¶
Returns True if this item is in a collision state with another
Item, otherwise it returns False.- Parameters
item_check (
Item) – item to check for collisions
See also
- Return type
bool
- IsInside(object)¶
Checks if the Item is inside the provided object. The encapsulating object must be closed-form, and both objects must be visible with at least 50% color transparency.
- Parameters
object (
Item) – Object that encapsulates- Returns
1 if the Item is inside object, else 0.
- Return type
int
See also
- AddGeometry(fromitem, pose)¶
Makes a copy of the geometry fromitem adding it at a given position (pose), relative to this item.
- Delete()¶
Remove this item and all its children from the station.
- Valid(check_deleted=False)¶
Checks if the item is valid. Returns True if the item is valid or False if the item is not valid. An invalid item will be returned by an unsuccessful function call (wrong name or because an item was deleted)
- Parameters
check_deleted (bool) – Check if the item was deleted in RoboDK.
See also
Example:
from robodk.robolink import * # import the robolink library RDK = Robolink() # connect to the RoboDK API (RoboDK starts if it has not started tool = RDK.Item('Tool') # Retrieve an item named tool if not tool.Valid(): print("The tool item does not exist!") quit()
- Return type
bool
- setParent(parent)¶
Attaches the item to a new parent while maintaining the relative position with its parent. The absolute position is changed.
- Parameters
parent (
Item) – parent to attach the item
See also
- Return type
- setParentStatic(parent)¶
Attaches the item to another parent while maintaining the current absolute position in the station. The relationship between this item and its parent is changed to maintain the abosolute position.
- Parameters
parent (
Item) – parent to attach the item
See also
- Return type
- AttachClosest(keyword='', tolerance_mm=- 1, list_objects=[])¶
Attach the closest object to the tool. Returns the item that was attached. Use item.Valid() to check if an object was attached to the tool.
- Parameters
keyword (str) – Keyword needed for an object to be grabbable (leave empty to consider all objects)
tolerance_mm (float) – Distance tolerance to use (at most) to consider grabbing objects. The closest object will be attached. In Tools-Options-General tab you can choose to check object distance between TCP and object shape (instead of the default TCP vs. Object position).
list_objects (list) – List of candidate objects to consider to grab (providing a keyword constrains the choices even more)
See also
- Return type
- DetachClosest(parent=0)¶
Detach the closest object attached to the tool (see also: setParentStatic).
- Parameters
parent (
Item) – New parent item to attach, such as a reference frame (optional). If not provided, the items held by the tool will be placed at the station root.
See also
- Return type
- DetachAll(parent=0)¶
Detaches any object attached to a tool.
- Parameters
parent (
Item) – New parent item to attach, such as a reference frame (optional). If not provided, the items held by the tool will be placed at the station root.
See also
- Childs()¶
Return a list of the childs items (list of
Item) that are attached to this item. Exceptionally, if Childs is called on a program it will return the list of subprograms called by this program.See also
- Return type
List[Item]
- Visible()¶
Returns 1 if the item is visible, otherwise it returns 0.
See also
- Return type
bool
- setVisible(visible, visible_frame=None)¶
Sets the item visiblity.
- Parameters
visible (bool) – Set the object as visible (1/True) or invisible (0/False)
visible_frame (bool) – Set the object reference frame as visible (1/True) or invisible (0/False). It is also possible to provide flags to control the visibility of each robot link (only for robot items). When the item is a robot, this variable can specify robot visibility using suitable flags (as shown in the example).
Note: Use setVisible on a programs to set the “Display path” setting.
Example:
Change robot visibility¶# Retrieve the robot (first robot available) robot = RDK.Item('', ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT) # Show the robot with default settings: robot.setVisible(True, VISIBLE_ROBOT_DEFAULT) # Show the robot and hide all references: robot.setVisible(1, VISIBLE_ROBOT_DEFAULT and not VISIBLE_ROBOT_ALL_REFS) # Show only references (hide the robot): robot.setVisible(1, VISIBLE_ROBOT_ALL_REFS)
Available Frame flags¶# Default values for objects VISIBLE_REFERENCE_DEFAULT = -1 VISIBLE_REFERENCE_ON = 1 # For objects and reference frames only VISIBLE_REFERENCE_OFF = 0 # For objects and reference frames only # Available flags to set robot visiblity VISIBLE_ROBOT_NONE = 0 VISIBLE_ROBOT_FLANGE = 0x01 VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_Base_3D = 0x01 << 1 VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_Base_REF = 0x01 << 2 VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_1_3D = 0x01 << 3 VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_1_REF = 0x01 << 4 VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_2_3D = 0x01 << 5 VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_2_REF = 0x01 << 6 VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_3_3D = 0x01 << 7 VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_3_REF = 0x01 << 8 VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_4_3D = 0x01 << 9 VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_4_REF = 0x01 << 10 VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_5_3D = 0x01 << 11 VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_5_REF = 0x01 << 12 VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_6_3D = 0x01 << 13 VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_6_REF = 0x01 << 14 VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_7_3D = 0x01 << 15 VISIBLE_ROBOT_AXIS_7_REF = 0x02 << 16 VISIBLE_ROBOT_DEFAULT = 0x2AAAAAAB VISIBLE_ROBOT_ALL = 0x7FFFFFFF VISIBLE_ROBOT_ALL_REFS = 0x15555555
See also
- Return type
- Name()¶
Returns the item name. The name of the item is always displayed in the RoboDK station tree. Returns the name as a string (str)
- Returns
New item name
- Return type
str
See also
- setName(name)¶
Set the name of the item. The name of the item will be displayed in the station tree.
- Parameters
name (str) – New item name
See also
- Return type
- setValue(varname, value=None)¶
Set a specific property name to a given value. This is reserved for internal purposes and future compatibility.
- Parameters
varname (str) – property name
value (str) – property value
See also
- setPose(pose)¶
Set the position (pose) of the item with respect to its parent (item it is attached to), for example, the position of an object, frame or target with respect to its parent reference frame.
For robot items, setPose will move the robot joints to reach the pose target using the active tool with respect to the active reference. setPose has no effect on tool items, however, it will modify the pose of the related object with respect to its parent (this is only visible when the tool is converted to an object).
- Parameters
pose (
Mat) – pose of the item with respect to its parent
See also
Pose(),PoseAbs(),setPoseAbs(),setPoseTool(),setPoseFrame(),Item()- Return type
- Pose()¶
Returns the relative pose of an object, target or reference frame. For example, the position of an object, target or reference frame with respect to its parent (the item it is attached to in the tree). For robot items, this function returns the pose of the active tool with respect to the active reference frame.
It returns the pose as
Mat.Tip: Use a Pose_2_* function from the robodk module (such as
robomath.Pose_2_KUKA) to convert the pose to XYZABC (XYZ position in mm and ABC orientation in degrees), specific to a robot brand.Example: Offline Programming
See also
Pose(),setPose(),PoseAbs(),PoseTool(),PoseFrame(),Item()- Return type
- PoseWrt(item)¶
Returns the relative pose of this Item with respect to an another Item.
- setGeometryPose(pose, apply=False)¶
Set the position (pose) the object geometry with respect to its own reference frame. This can be applied to tools and objects. The pose must be a
Mat- Parameters
pose (
Mat) –apply (
bool, default:False) –
- GeometryPose()¶
Returns the position (pose as
Mat) the object geometry with respect to its own reference frame. This procedure works for tools and objects.- Return type
- setPoseAbs(pose)¶
Set the pose (
Mat) of this item with respect to the absolute reference frame (also know as the station reference or world coordinate system -WCS-). For example, the position of an object/frame/target with respect to the origin of the station. If the item is a tool, the joints of the associated robot will be updated to match the absolute pose with the tool (the TCP is not changed). setPoseAbs has no effect on robots.- Parameters
pose (
Mat) – pose of the item with respect to the station reference
- Return type
- PoseAbs()¶
Return the pose (
Mat) of this item with respect to the absolute reference frame (also know as the station reference or world coordinate system -WCS-). For example, the position of an object/frame/target with respect to the origin of the station.For robot items, this returns the pose of the robot base with respect to the origin of the station.
Example:
# Calculate the pose of any object with respect to any reference in RoboDK def CalculatePoseFrame2Object(frame, part): # Get both poses with respect to the station reference (wrt-world coordinate system) framePoseAbs = frame.PoseAbs() partPoseAbs = part.PoseAbs() # Calculate the pose of the object relative to the reference pose = framePoseAbs.inv() * partPoseAbs return pose # Take the object obj = RDK.Item('Sphere') # Retrieve the reference frame = RDK.Item('Frame 2') # Calculate the relationship pose = CalculatePoseFrame2Object(frame,obj) # Display the result print(pose) RDK.ShowMessage("The relative pose is: " + str(pose))
See also
- Return type
- Recolor(tocolor, fromcolor=None, tolerance=None)¶
Changes the color of an
Item(object, tool or robot). Colors must in the format COLOR=[R,G,B,(A=1)] where all values range from 0 to 1. Alpha (A) defaults to 1 (100% opaque). Set A to 0 to make an object transparent.- Parameters
tocolor (list of float) – color to set
fromcolor (list of float) – color to change
tolerance (float (defaults to 0.1)) – tolerance to replace colors (set to 0 for exact match)
See also
- setColor(tocolor)¶
Set the color of an object, tool or robot. A color must in the format COLOR=[R,G,B,(A=1)] where all values range from 0 to 1.
- Parameters
tocolor (list of float) – color to set
- setColorShape(tocolor, shape_id)¶
Set the color of an object shape. It can also be used for tools. A color must in the format COLOR=[R,G,B,(A=1)] where all values range from 0 to 1.
- Parameters
tocolor (list of float) – color to set
shape_id (int) – ID of the shape: the ID is the order in which the shape was added using AddShape()
- setColorCurve(tocolor, curve_id=- 1)¶
Set the color of a curve object. It can also be used for tools. A color must in the format COLOR=[R,G,B,(A=1)] where all values range from 0 to 1.
- Parameters
tocolor (list of float) – color to set
curve_id (int) – ID of the curve: the ID is the order in which the shape was added using AddCurve()
- Color()¶
Return the color of an
Item(object, tool or robot). If the item has multiple colors it returns the first color available). A color is in the format COLOR=[R,G,B,(A=1)] where all values range from 0 to 1.See also
- Return type
List[float]
- Scale(scale, pre_mult=None, post_mult=None)¶
Apply a scale to an object to make it bigger or smaller. The scale can be uniform (if scale is a float value) or per axis (if scale is an array/list [scale_x, scale_y, scale_z]).
- Parameters
- AddShape(triangle_points)¶
Adds a shape to the object provided some triangle coordinates. Triangles must be provided as a list of vertices. A vertex normal can be optionally provided.
See also
- AddCurve(curve_points, add_to_ref=False, projection_type=3)¶
Adds a curve provided point coordinates. The provided points must be a list of vertices. A vertex normal can be provided optionally.
See also
- AddPoints(points, add_to_ref=False, projection_type=3)¶
Adds a list of points to an object. The provided points must be a list of vertices. A vertex normal can be provided optionally.
See also
- ProjectPoints(points, projection_type=3)¶
Projects a point or a list of points to the object given its coordinates. The provided points must be a list of [XYZ] coordinates. Optionally, a vertex normal can be provided [XYZijk].
See also
- SelectedFeature()¶
Retrieve the currently selected feature for this object.
See also
Example:
# Show the point selected object = RDK.Item('Object', ITEM_TYPE_OBJECT) is_selected, feature_type, feature_id = OBJECT.SelectedFeature() points, name_selected = object.GetPoints(feature_type, feature_id) point = None if len(points) > 1: point = points[feature_id] else: point = points[0] RDK.ShowMessage("Selected Point: %s = [%.3f, %.3f, %.3f]" % (name_selected, point[0], point[1], point[2]))
- Return type
Tuple[int,int,int]
- GetPoints(feature_type=1, feature_id=0)¶
Retrieves the point under the mouse cursor, a curve or the 3D points of an object. The points are provided in [XYZijk] format in relative coordinates. The XYZ are the local point coordinate and ijk is the normal of the surface.
- Parameters
feature_type (int) – set to FEATURE_SURFACE to retrieve the point under the mouse cursor, FEATURE_CURVE to retrieve the list of points for that wire, or FEATURE_POINT to retrieve the list of points.
feature_id (int) – used only if FEATURE_CURVE is specified, it allows retrieving the appropriate curve id of an object
- Return type
Tuple[List[List[float]],str]- Returns
List of points
Example 1 - Display the XYZ position of a selected object
from robodk.robolink import * # Import the RoboDK API RDK = Robolink() # Start RoboDK API # Ask the user to select an object OBJECT = RDK.ItemUserPick("Select an object", ITEM_TYPE_OBJECT) while True: is_selected, feature_type, feature_id = OBJECT.SelectedFeature() if is_selected and feature_type == FEATURE_SURFACE: point_mouse, name_feature = OBJECT.GetPoints(FEATURE_SURFACE) print("Selected %i (%i): %s %s" % (feature_id, feature_type, str(point_mouse), name_feature)) else: print("Object Not Selected. Select a point in the object surface...") robomath.pause(0.1)
Example 2 - Display the mesh of a selected object surface
from robolink import * # Import the RoboDK API import time RDK = Robolink() # Start RoboDK API while True: # Check if we have an object under the mouse cursor object, feature_type, feature_id, feature_name, points = RDK.GetPoints(FEATURE_HOVER_OBJECT) if object.Valid() and (object.type == ITEM_TYPE_OBJECT or object.type == ITEM_TYPE_TOOL): # Retrieve the selected feature on the object is_selected, feature_type, feature_id = object.SelectedFeature() if is_selected and feature_type == FEATURE_SURFACE: # Retrieve the mesh related to the surface ID point_mesh, name_feature = object.GetPoints(FEATURE_OBJECT_MESH, feature_id) print("Selected %i (%i): %s" % (feature_id, feature_type, name_feature)) print("Mesh points:") for xyzijk in point_mesh: print(xyzijk) # Clear selection or manipulate as necessary RDK.setSelection([]) else: print("Click the surface to see the mesh") time.sleep(0.1) continue else: print("Object Not Selected. The surface of an object or a tool") time.sleep(0.1)
See also
- GetCurves()¶
Retrieve the curves object. The points are provided in [XYZijk] format in relative coordinates. The XYZ are the local point coordinate and ijk is the normal of the surface.
- Return type
List[Tuple[Mat,str]]- Returns
List of points for each curve as a list
Example - Retrieve all the curves of an object
from robodk.robolink import * # Import the RoboDK API RDK = Robolink() # Start RoboDK API # Ask the user to select an object object = RDK.ItemUserPick("Select an object", ITEM_TYPE_OBJECT) curves = object.GetCurves() print("The object " + object.Name() + " has " + str(len(curves)) + " curves") for c in curves: pts, name = c print("Curve:" + name) print("Number of points: " + str(len(pts[0]))) x,y,z,i,j,k = pts[0,0], pts[1,0], pts[2,0] , pts[3,0], pts[4,0], pts[5,0] print("First point [x,y,z , i,j,k]: %.3f,%.3f,%.3f , %.3f,%.3f,%.3f" % (x,y,z,i,j,k))
See also
- setMillingParameters(ncfile='', part=0, params='')¶
Deprecated since version 4.0: Obsolete. Use
setMachiningParameters()instead.
- setMachiningParameters(ncfile='', part=0, params='')¶
Update the robot milling path input and parameters. Parameter input can be an NC file (G-code or APT file) or an object/part item in RoboDK with curves or points. A curve follow project or a point follow project will be automatically created for the project if the object has curves or points respectively.
Tip: Use getLink(), setPoseTool(), setPoseFrame() to get/set the robot tool, reference frame, robot and program linked to the project. Tip: Use setPose() and setJoints() to update the path to tool orientation or the preferred start joints.
- Parameters
ncfile (str) – path to the NC file (G-code or APT) to be loaded (optional)
part (
Item) – object holding curves or points to automatically set up a curve/point follow project (optional)params (
str, default:'') – Additional options
Example:
object_curve = RDK.AddCurve(POINTS) object_curve.setName('AutoPoints n%i' % NUM_POINTS) path_settings = RDK.AddMachiningProject("AutoCurveFollow settings") # Prepare a curve follow project moving through all the curves in the curve object provided prog, status = path_settings.setMachiningParameters(part=object_curve, params="ReorderAuto=0")
- Return type
Tuple[Item,float]
- setAsCartesianTarget()¶
Sets a target as a cartesian target. A cartesian target moves to cartesian coordinates.
See also
- Return type
- setAsJointTarget()¶
Sets a target as a joint target. A joint target moves to the joint position without taking into account the cartesian coordinates.
See also
- Return type
- isJointTarget()¶
Returns True if a target is a joint target. A joint target moves to the joint position without taking into account the cartesian coordinates.
- Return type
bool
- Joints()¶
Return the current joint position as a
Matof a robot or the joints of a target. If the item is a cartesian target, it returns the preferred joints (configuration) to go to that cartesian position.See also
Example:
from robodk.robolink import * # import the robolink library RDK = Robolink() # connect to the RoboDK API (RoboDK starts if it has not started) tool = RDK.Item('', ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT) # Retrieve the robot joints = robot.Joints().list() # retrieve the current robot joints as a list joints[5] = 0 # set joint 6 to 0 deg robot.MoveJ(joints) # move the robot to the new joint position
- Return type
- SimulatorJoints()¶
Return the current joint position of a robot (only from the simulator, never from the real robot). This should be used only when RoboDK is connected to the real robot and only the simulated robot needs to be retrieved (for example, if we want to move the robot using a spacemouse).
Note: Use robot.Joints() instead to retrieve the simulated and real robot position when connected.
See also
- Return type
List[float]
- JointPoses(joints=None)¶
Returns the positions of the joint links for a provided robot configuration (joints). If no joints are provided it will return the poses for the current robot position. Out 1 : 4x4 x n -> array of 4x4 homogeneous matrices. Index 0 is the base frame reference (it never moves when the joints move).
- JointsHome()¶
Return the home joints of a robot. The home joints can be manually set in the robot “Parameters” menu of the robot panel in RoboDK, then select “Set home position”.
See also
- Return type
- setJointsHome(joints)¶
Set the home position of the robot in the joint space.
- Parameters
joints (list of float or
Mat) – robot joints
See also
- ObjectLink(link_id=0)¶
Returns an item pointer (
Item) to a robot link. This is useful to show/hide certain robot links or alter their geometry.- Parameters
link_id (int) – link index (0 for the robot base, 1 for the first link, …)
- Return type
- getLink(type_linked=2)¶
Returns an item pointer (
Item) to a robot, object, tool or program that is linked to this item. This is useful to retrieve the relationship between programs, robots, tools and other specific projects. This returns the first link found.- Parameters
type_linked (int) – type of the linked item to retrieve (ITEM_TYPE_*)
- Returns
An item that is invalid if no link is found, else the item
- Return type
Example:
prog = machining_proj.getLink(ITEM_TYPE_PROGRAM) # Get the generated program of a machining project robot = prog.getLink(ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT) # Get the robot associated with the program frame = robot.getLink(ITEM_TYPE_FRAME) # Get the active reference frame
See also
- getLinks(type_linked=2)¶
Get all the items of a specific type for which ~robodk.robolink.Item.getLink returns this item.
- Parameters
type_linked (int) – type of the items to check for a link (ITEM_TYPE_*). None means any type.
- Returns
A list of items for which ~robodk.robolink.Item.getLink return the specified item
- Return type
list of
Item
- setLink(item)¶
Sets a link between this item and the specified item. This is useful to set the relationship between programs, robots, tools and other specific projects.
- Parameters
item (
Item) – item to link
See also
- setJoints(joints)¶
Set the current joints of a robot or a target. If robot joints are set, the robot position will be updated on the screen.
- Parameters
joints (list of float or
Mat) – robot joints
See also
- JointLimits()¶
Retrieve the joint limits of a robot. Returns (lower limits, upper limits, joint type).
See also
- setJointLimits(lower_limit, upper_limit)¶
Update the robot joint limits
- Parameters
lower_limit (list of float) – lower joint limits
upper_limit (list of float) – upper joint limits
See also
- setRobot(robot=None)¶
Assigns a specific robot to a program, target or robot machining project.
- Parameters
robot (
Item) – robot to link
- setPoseFrame(frame)¶
Sets the reference frame of a robot (user frame). The frame can be an item or a 4x4 Matrix
See also
- setPoseTool(tool)¶
Set the robot tool pose (TCP) with respect to the robot flange. The tool pose can be an item or a 4x4 Matrix
See also
- PoseTool()¶
Returns the pose (
Mat) of the robot tool (TCP) with respect to the robot flangeSee also
- Return type
- PoseFrame()¶
Returns the pose (
Mat) of the robot reference frame with respect to the robot baseSee also
- Return type
- Htool()¶
Deprecated since version 4.0: Obsolete. Use
PoseTool()instead.Returns the pose (
Mat) of the robot tool (TCP) with respect to the robot flange- Return type
- Tool()¶
Deprecated since version 4.0: Obsolete. Use
PoseTool()instead.Returns the pose (
Mat) of the robot tool (TCP) with respect to the robot flange- Return type
- Frame()¶
Deprecated since version 4.0: Obsolete. Use
PoseFrame()instead.Returns the pose (
Mat) of the robot reference frame with respect to the robot base- Return type
- setHtool(tool)¶
Deprecated since version 4.0: Obsolete.
setPoseTool()instead.Sets the robot tool pose (TCP) with respect to the robot flange. The tool pose can be an item or a 4x4 Matrix
- setTool(tool)¶
Deprecated since version 4.0: Obsolete. Use
setPoseTool()instead.Sets the robot tool pose (TCP) with respect to the robot flange. The tool pose can be an item or a 4x4 Matrix
- setFrame(frame)¶
Deprecated since version 4.0: Obsolete. Use
setPoseFrame()instead.Sets the reference frame of a robot (user frame). The frame can be an item or a 4x4 Matrix
- AddTool(tool_pose, tool_name='New TCP')¶
Add a tool to a robot given the tool pose and the tool name. It returns the tool as an
Item.- Parameters
tool_pose (
Mat) – Tool pose (TCP) of the tool with respect to the robot flangetool_name (str) – name of the tool
See also
- Return type
- SolveFK(joints, tool=None, reference=None)¶
Calculate the forward kinematics of the robot for the provided joints. Returns the pose of the robot flange with respect to the robot base reference (
Mat).- Parameters
joints (list of float or
Mat) – robot jointstool (
Mat) – Optionally provide the tool used to calculate the forward kinematics. If this parameter is ignored it will use the robot flange.reference (
Mat) – Optionally provide the reference frame used to calculate the forward kinematics. If this parameter is ignored it will use the robot base frame.
See also
Example:
from robodk.robolink import * # import the robolink library RDK = Robolink() # connect to the RoboDK API (RoboDK starts if it has not started robot = RDK.Item('', ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT) # Retrieve the robot # get the current robot joints robot_joints = robot.Joints() # get the robot position from the joints (calculate forward kinematics) robot_position = robot.SolveFK(robot_joints) # get the robot configuration (robot joint state) robot_config = robot.JointsConfig(robot_joints) # calculate the new robot position new_robot_position = transl([x_move,y_move,z_move])*robot_position # calculate the new robot joints new_robot_joints = robot.SolveIK(new_robot_position) if len(new_robot_joints.tolist()) < 6: print("No robot solution!! The new position is too far, out of reach or close to a singularity") continue # calculate the robot configuration for the new joints new_robot_config = robot.JointsConfig(new_robot_joints) if robot_config[0] != new_robot_config[0] or robot_config[1] != new_robot_config[1] or robot_config[2] != new_robot_config[2]: print("Warning! Robot configuration changed: this may lead to unextected movements!") print(robot_config) print(new_robot_config) # move the robot to the new position robot.MoveJ(new_robot_joints) #robot.MoveL(new_robot_joints)
- Return type
- JointsConfig(joints)¶
Returns the robot configuration state for a set of robot joints. The configuration state is defined as: [REAR, LOWERARM, FLIP, turns]. The turns are reserved for future use.
Example:
# Retrieve all solutions for a given pose: all_solutions = robot.SolveIK_All(pose, toolpose, framepose) joints = [] # Iterate through each solution for j in all_solutions: # Retrieve flags as a list for each solution conf_RLF = robot.JointsConfig(j).list() # Breakdown of flags: rear = conf_RLF[0] # 1 if Rear , 0 if Front lower = conf_RLF[1] # 1 if Lower, 0 if Upper (elbow) flip = conf_RLF[2] # 1 if Flip , 0 if Non flip (Flip is usually when Joint 5 is negative) # Look for a solution with Front and Elbow up configuration #if conf_RLF[0:2] == [0,0]: if rear == 0 and lower == 0: print("Solution found!") joints = j break
- Parameters
joints (list of float) – robot joints
- Return type
- SolveIK(pose, joints_approx=None, tool=None, reference=None)¶
Calculates the inverse kinematics for a given specified pose. The pose must be robot flange with respect to the robot base unless you provide the tool and/or reference. SolveIK returns the joints solution as a Mat object (size 1xnDOFs). Use list() on a Mat to convert to a list. If there is no solution it returns an array of size 0. If there is no solution it returns an empty matrix.
Note: For some 6-axis robots, SolveIK returns 2 additional values that can be ignored.
- Parameters
pose (
Mat) – pose of the robot flange with respect to the robot base framejoints_approx (list of float) – Preferred joint solution. Leave blank to return the closest match to the current robot position.
tool (
Mat) – Tool pose with respect to the robot flange (TCP)reference (
Mat) – Reference pose (reference frame with respect to the robot base)
See also
- Return type
- SolveIK_All(pose, tool=None, reference=None)¶
Calculates the inverse kinematics for the specified robot and pose. The function returns all available joint solutions as a 2D matrix. Returns a list of joints as a 2D matrix [N x M], where N is the number of degrees of freedom (robot joints) and M is the number of solutions. For some 6-axis robots, SolveIK returns 2 additional values that can be ignored.
- Parameters
pose (
Mat) – pose of the robot flange with respect to the robot base frame
See also
- FilterTarget(pose, joints_approx=None)¶
Filters a target to improve accuracy. This option requires a calibrated robot. :type pose:
Mat:param pose: pose of the robot TCP with respect to the robot reference frame :type pose:Mat:type joints_approx:Union[Mat,List[float],None], default:None:param joints_approx: approximated desired joints to define the preferred configuration :type joints_approx: list of float orMat
- Connect(robot_ip='', blocking=True)¶
Connect to a real robot and wait for a connection to succeed. Returns 1 if connection succeeded, or 0 if it failed.
- Parameters
robot_ip (str) – Robot IP. Leave blank to use the IP selected in the connection panel of the robot.
See also
- Parameters
blocking (
bool, default:True) –- Return type
int
- ConnectSafe(robot_ip='', max_attempts=5, wait_connection=4, callback_abort=None)¶
Connect to a real robot and wait for a connection to succeed. Returns the connected state returned by ConnectedState() (0 if connection succeeded and the robot is ready).
- Parameters
robot_ip (str) – Robot IP. Leave blank to use the IP selected in the connection panel of the robot.
max_attempts (int) – maximum connection attemps before reporting an unsuccessful connection
wait_connection (float) – time to wait in seconds between connection attempts
callback_abort (function) – function pointer that returns true if we should abort the connection operation
See also
- Return type
int
- ConnectionParams()¶
Returns the robot connection parameters :rtype:
Tuple[str,int,str,str,str] :return: [robotIP (str), port (int), remote_path (str), FTP_user (str), FTP_pass (str)]See also
- setConnectionParams(robot_ip, port, remote_path, ftp_user, ftp_pass)¶
Set the robot connection parameters
- Parameters
robot_ip (str) – robot IP
port (int) – robot communication port
remote_path (str) – path to transfer files on the robot controller
ftp_user (str) – user name for the FTP connection
ftp_pass (str) – password credential for the FTP connection
See also
- ConnectedState()¶
Check connection status with a real robobt Out 1 : status code -> (int) ROBOTCOM_READY if the robot is ready to move, otherwise, status message will provide more information about the issue Out 2 : status message -> Message description of the robot status
See also
Example:
from robodk.robolink import * # import the robolink library robot = RDK.Item('', ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT) # Get the first robot available state = robot.Connect() print(state) # Check the connection status and message state, msg = robot.ConnectedState() print(state) print(msg) if state != ROBOTCOM_READY: print('Problems connecting: ' + robot.Name() + ': ' + msg) quit() # Move the robot (real robot if we are connected) robot.MoveJ(jnts, False)
- Return type
Tuple[int,str]
- Disconnect()¶
Disconnect from a real robot (when the robot driver is used) Returns 1 if it disconnected successfully, 0 if it failed. It can fail if it was previously disconnected manually for example.
See also
- Return type
int
- MoveJ(target, blocking=True)¶
Move a robot to a specific target (“Move Joint” mode). This function waits (blocks) until the robot finishes its movements. If this is used with a program item, a new joint movement instruction will be added to the program. Important note when adding new movement instructions to programs: only target items supported, not poses.
- Parameters
target (
Mat, list of joints orItem) – Target to move to. It can be the robot joints (Nx1 or 1xN), the pose (4x4) or a target (item pointer)blocking (bool) – Set to True to wait until the robot finished the movement (default=True). Set to false to make it a non blocking call. Tip: If set to False, use robot.Busy() to check if the robot is still moving.
See also
- MoveL(target, blocking=True)¶
Moves a robot to a specific target (“Move Linear” mode). This function waits (blocks) until the robot finishes its movements. This function can also be called on Programs and a new movement instruction will be added at the end of the program. If this is used with a program item, a new linear movement instruction will be added to the program. Important note when adding new movement instructions to programs: only target items supported, not poses.
- Parameters
target (
Mat, list of joints orItem) – Target to move to. It can be the robot joints (Nx1 or 1xN), the pose (4x4) or a target (item pointer)blocking (bool) – Set to True to wait until the robot finished the movement (default=True). Set to false to make it a non blocking call. Tip: If set to False, use robot.Busy() to check if the robot is still moving.
See also
- SearchL(target, blocking=True)¶
Moves a robot to a specific target and stops when a specific input switch is detected (“Search Linear” mode). This function waits (blocks) until the robot finishes its movements.
- Parameters
target (
Mat, list of joints orItem) – Target to move to. It can be the robot joints (Nx1 or 1xN), the pose (4x4) or a target (item pointer)blocking (bool) – Set to True to wait until the robot finished the movement (default=True). Set to false to make it a non blocking call. Tip: If set to False, use robot.Busy() to check if the robot is still moving.
See also
Example:
from robodk.robolink import * # import the robolink library RDK = Robolink() # Connect to the RoboDK API r = RDK.Item('', ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT) r.MoveJ(pose_from) # Move to the approach point r.SearchL(pose_to) # Move towards the search location # Retrieve the contact point as joints and pose: targetJoints = r.Joints().list() targetPose = r.Pose() status = r.setParam("Driver", "Status") # Status is "1" a contact was found or "0" if not found (empty string means the driver does not support it) if len(status) > 0: # Important! Not all robot drivers support this "Driver Status" flag # This works in simulation if "1" in status: # Contact found! We already have the robot joints and pose as targetJoints and targetPose respectively pass else: # Nothing found! targetJoints = None targetPose = None else: # When the driver does not support the Driver Status flag, we can use this workaround to check if we found an interference # Check if we are near the end point (for drivers that don't support the first option) if pose_is_similar(r.Pose(), pose_to, 0.1): # The robot was not able to detect any interference targetJoints = None targetPose = None
- Return type
List[float]
- MoveC(target1, target2, blocking=True)¶
Move a robot to a specific target (“Move Circular” mode). By default, this procedure waits (blocks) until the robot finishes the movement.
- Parameters
See also
- MoveJ_Test(j1, j2, minstep_deg=- 1)¶
Checks if a joint movement is feasible and free of collisions (if collision checking is activated). The robot will moved to the collision point if a collision is detected (use Joints to collect the collision joints) or it will be placed at the destination joints if a collision is not detected.
- Parameters
j1 (list of float) – start joints
j2 (list of float) – end joints
minstep_deg (float) – joint step in degrees
- Returns
returns 0 if the movement is free of collision or any other issues. Otherwise it returns the number of pairs of objects that collided if there was a collision.
- Return type
int
See also
- MoveJ_Test_Blend(j1, j2, j3, blend_deg=5, minstep_deg=- 1)¶
Checks if a joint movement with blending is feasible and free of collisions (if collision checking is activated). The robot will move to the collision point if a collision is detected (use Joints to collect the collision joints) or it will be placed at the destination joints if a collision is not detected.
- Parameters
j1 (list of float) – start joints
j2 (list of float) – joints via
j3 (list of float) – joints final destination
blend_deg (float) – blend in degrees
minstep_deg (float) – maximum joint step in degrees
- Returns
returns 0 if the movement is free of collision or any other issues. Otherwise it returns the number of pairs of objects that collided if there was a collision.
- Return type
int
See also
- MoveL_Test(j1, pose, minstep_mm=- 1)¶
Checks if a linear movement is feasible and free of collisions (if collision checking is activated). The robot will moved to the collision point if a collision is detected (use Joints to collect the collision joints) or it will be placed at the destination pose if a collision is not detected.
- Parameters
j1 (list of float) – start joints
pose (
Mat) – end pose (position of the active tool with respect to the active reference frame)minstep_mm (float) – linear step in mm
- Returns
returns 0 if the movement is free of collision or any other issues.
- Return type
int
If the robot can not reach the target pose it returns -2. If the robot can reach the target but it can not make a linear movement it returns -1.
- setSpeed(speed_linear, speed_joints=- 1, accel_linear=- 1, accel_joints=- 1)¶
Sets the linear speed of a robot. Additional arguments can be provided to set linear acceleration or joint speed and acceleration.
- Parameters
speed_linear (float) – linear speed -> speed in mm/s (-1 = no change)
speed_joints (float) – joint speed (optional) -> speed in deg/s (-1 = no change)
accel_linear (float) – linear acceleration (optional) -> acceleration in mm/s^2 (-1 = no change)
accel_joints (float) – joint acceleration (optional) -> acceleration in deg/s^2 (-1 = no change)
- setAcceleration(accel_linear)¶
Sets the linear acceleration of a robot in mm/s2
- Parameters
accel_linear (float) – acceleration in mm/s2
- setSpeedJoints(speed_joints)¶
Sets the joint speed of a robot in deg/s for rotary joints and mm/s for linear joints
- Parameters
speed_joints (float) – speed in deg/s for rotary joints and mm/s for linear joints
- setAccelerationJoints(accel_joints)¶
Sets the joint acceleration of a robot
- Parameters
accel_joints (float) – acceleration in deg/s2 for rotary joints and mm/s2 for linear joints
See also
- setRounding(rounding_mm)¶
Sets the rounding accuracy to smooth the edges of corners. In general, it is recommended to allow a small approximation near the corners to maintain a constant speed. Setting a rounding values greater than 0 helps avoiding jerky movements caused by constant acceleration and decelerations.
- Parameters
rounding_mm (float) – rounding accuracy in mm. Set to -1 (default) for best accuracy and to have point to point movements (might have a jerky behavior)
This rounding parameter is also known as ZoneData (ABB), CNT (Fanuc), C_DIS/ADVANCE (KUKA), cornering (Mecademic) or blending (Universal Robots)
See also
- setZoneData(zonedata)¶
Deprecated since version 4.0: Obsolete. Use
setRounding()instead.- Parameters
zonedata (
float) –
- ShowSequence(matrix, display_type=- 1, timeout=- 1)¶
Displays a sequence of joints or poses in RoboDK.
- Parameters
matrix (list of list of float, a matrix of joints as a
Mator a list of poses asMat) – list of joints as a matrix or as a list of joint arrays, a list of poses, or a sequence of instructions (same sequence that was supported with RoKiSim).display_type (int, optional) – display options (SEQUENCE_DISPLAY_*). Use -1 to use default.
timeout (int, optional) – display timeout, in milliseconds. Use -1 to use default.
Tip: use
InstructionList()to retrieve the instruction list in RoKiSim format.Example:
from robolink import * from robodk import * RDK = Robolink() prog = RDK.ItemUserPick('Select a Program', ITEM_TYPE_PROGRAM) if not prog.Valid(): quit() robot = prog.getLink(ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT) if not robot.Valid(): quit() # Calculate delta time to display robots prog_stats = prog.Update() time_estimate = prog_stats[1] TIME_STEP = max(1, time_estimate / 100) # Define the way we want to output the list of joints status_msg, joint_list, status_code = prog.InstructionListJoints(1, 1, flags=5, time_step=TIME_STEP) # Status code is negative if there are errors in the program print("Status code:" + str(status_code)) print("Status message: " + status_msg) print(joint_list.tr()) print("Size: " + str(len(joint_list))) # Show as ghost robot joints = [] for j in joint_list: joints.append(j) # Display "ghost" robots in RoboDK robot.ShowSequence(joints, SEQUENCE_DISPLAY_OPTION_RESET | SEQUENCE_DISPLAY_ROBOT_JOINTS | SEQUENCE_DISPLAY_TRANSPARENT, 3600*1000)
- Busy()¶
Checks if a robot or program is currently running (busy or moving). Returns a busy status (1=moving, 0=stopped)
See also
Example:
from robodk.robolink import * # import the robolink library from robodk.robomath import * RDK = Robolink() # Connect to the RoboDK API prog = RDK.Item('MainProgram', ITEM_TYPE_PROGRAM) prog.RunCode() while prog.Busy(): pause(0.1) print("Program done")
- Return type
int
- Stop()¶
Stop a program or a robot
- WaitMove(timeout=360000)¶
Waits (blocks) until the robot finishes its movement.
- Parameters
timeout (float) – Maximum time to wait for robot to finish its movement (in seconds)
- ProgramStart(programname, folder='', postprocessor='')¶
Defines the name of the program when a program must be generated. It is possible to specify the name of the post processor as well as the folder to save the program. This method must be called before any program output is generated (before any robot movement or other program instructions).
- Parameters
progname (str) – name of the program
folder (str) – folder to save the program, leave empty to use the default program folder
postprocessor (str) – name of the post processor (for a post processor in C:/RoboDK/Posts/Fanuc_post.py it is possible to provide “Fanuc_post.py” or simply “Fanuc_post”)
See also
- Parameters
programname (
str) –- Return type
int
- setAccuracyActive(accurate=1)¶
Sets the accuracy of the robot active or inactive. A robot must have been calibrated to properly use this option.
- Parameters
accurate (int) – set to 1 to use the accurate model or 0 to use the nominal model
See also
- AccuracyActive()¶
Returns True if the accurate kinematics are being used. Accurate kinematics are available after a robot calibration.
See also
- Return type
bool
- setParamRobotTool(tool_mass=5, tool_cog=None)¶
Sets the tool mass and center of gravity. This is only used with accurate robots to improve accuracy.
- Parameters
tool_mass (float) – tool weigth in Kg
tool_cog (list) – tool center of gravity as [x,y,z] with respect to the robot flange
- FilterProgram(filestr)¶
Filter a program file to improve accuracy for a specific robot. The robot must have been previously calibrated. It returns 0 if the filter succeeded, or a negative value if there are filtering problems. It also returns a summary of the filtering.
- Parameters
filestr (str) – File path of the program. Formats supported include: JBI (Motoman), SRC (KUKA), MOD (ABB), PRG (ABB), LS (FANUC).
- Return type
Tuple[int,str]
- MakeProgram(folder_path='', run_mode=3)¶
Generate the program file. Returns True if the program was successfully generated.
- Parameters
pathstr (str) – Folder to save the program (not including the file name and extension). Make sure the folder ends with a slash. You can use backslashes or forward slashes to define the path. In most cases, the file name is defined by the program name (visible in the RoboDK tree) and the extension is defined by the Post Processor (the file extension must match the extension supported by your robot controller). It can be left empty to use the default action (save to the default programs location)
run_mode (
int, default:3) – RUNMODE_MAKE_ROBOTPROG to generate the program file. Alternatively, Use RUNMODE_MAKE_ROBOTPROG_AND_UPLOAD or RUNMODE_MAKE_ROBOTPROG_AND_START to transfer the program through FTP and execute the program.
- Return type
Tuple[bool,str,bool]- Returns
[success (True or False), log (str), transfer_succeeded (True/False)]
Transfer succeeded is True if there was a successful program transfer (if RUNMODE_MAKE_ROBOTPROG_AND_UPLOAD or RUNMODE_MAKE_ROBOTPROG_AND_START are used)
See also
- Parameters
folder_path (
str, default:'') –
- setRunType(program_run_type)¶
Set the Run Type of a program to specify if a program made using the GUI will be run in simulation mode or on the real robot (“Run on robot” option).
- Parameters
program_run_type (int) – Use “PROGRAM_RUN_ON_SIMULATOR” to set the program to run on the simulator only or “PROGRAM_RUN_ON_ROBOT” to force the program to run on the robot
See also
- RunType()¶
Get the Run Type of a program to specify if a program made using the GUI will be run in simulation mode or on the real robot (“Run on robot” option).
See also
- Return type
int
- RunProgram(prog_parameters=None)¶
Deprecated since version 4.0: Obsolete. Use
RunCode()instead. RunProgram is available for backwards compatibility.- Parameters
prog_parameters (
Optional[List[str]], default:None) –- Return type
int
- RunCode(prog_parameters=None)¶
Run a program. It returns the number of instructions that can be executed successfully (a quick program check is performed before the program starts). This is a non-blocking call. Use program.Busy() to check if the program execution finished, or program.WaitFinished() to wait until the program finishes.
If setRunMode(RUNMODE_SIMULATE) is used: the program will be simulated (default run mode)
If setRunMode(RUNMODE_RUN_ROBOT) is used: the program will run on the robot (default when RUNMODE_RUN_ROBOT is used)
If setRunMode(RUNMODE_RUN_ROBOT) is used together with program.setRunType(PROGRAM_RUN_ON_ROBOT): the program will run sequentially on the robot the same way as if we right clicked the program and selected “Run on robot” in the RoboDK GUI
- Parameters
prog_parameters (list of str) – Program parameters can be provided for Python programs as a string
See also
- Return type
int
- RunCodeCustom(code, run_type=0)¶
Deprecated since version 4.0: Obsolete, use RunInstruction instead.
Adds a program call, code, message or comment to the program. Returns 0 if succeeded.
See also
- Parameters
code (
str) –run_type (
int, default:0) –
- Return type
int
- RunInstruction(code, run_type=0)¶
Adds a program call, code, message or comment to the program. Returns 0 if succeeded.
- Parameters
code (str) – The code to insert, program to run, or comment to add.
run_type (int) – Use INSTRUCTION_* variable to specify if the code is a program call or just a raw code insert. For example, to add a line of customized code use:
Available Instruction Types¶INSTRUCTION_CALL_PROGRAM = 0 # Program call INSTRUCTION_INSERT_CODE = 1 # Insert raw code in the generated program INSTRUCTION_START_THREAD = 2 # Start a new process INSTRUCTION_COMMENT = 3 # Add a comment in the code INSTRUCTION_SHOW_MESSAGE = 4 # Add a message
See also
Example:
program.RunInstruction('Setting the spindle speed', INSTRUCTION_COMMENT) program.RunInstruction('SetRPM(25000)', INSTRUCTION_INSERT_CODE) program.RunInstruction('Done setting the spindle speed. Ready to start!', INSTRUCTION_SHOW_MESSAGE) program.RunInstruction('Program1', INSTRUCTION_CALL_PROGRAM)
- Return type
int
- Pause(time_ms=- 1)¶
Pause instruction for a robot or insert a pause instruction to a program (when generating code offline -offline programming- or when connected to the robot -online programming-).
- Parameters
time_ms (float) – time in miliseconds. Do not provide a value (leave the default -1) to pause until the user desires to resume the execution of a program.
See also
- setDO(io_var, io_value)¶
Set a Digital Output (DO). This command can also be used to set any generic variables to a desired value.
- Parameters
io_var (str or int) – Digital Output (string or number)
io_value (str, int or float) – value
See also
- setAO(io_var, io_value)¶
Set an Analog Output (AO).
- Parameters
io_var (str or int) – Analog Output (string or number)
io_value (str, int or float) – value
See also
- getDI(io_var)¶
Get a Digital Input (DI). This function is only useful when connected to a real robot using the robot driver. It returns a string related to the state of the Digital Input (1=True, 0=False). This function returns an empty string if the script is not executed on the robot.
- Parameters
io_var (str or int) – Digital Input (string or number)
See also
- Return type
str
- getAI(io_var)¶
Get an Analog Input (AI). This function is only useful when connected to a real robot using the robot driver. It returns a string related to the state of the Digital Input (0-1 or other range depending on the robot driver). This function returns an empty string if the script is not executed on the robot.
- Parameters
io_var (str or int) – Analog Input (string or number)
See also
- Return type
str
- waitDI(io_var, io_value, timeout_ms=- 1)¶
Wait for an digital input io_var to attain a given value io_value. Optionally, a timeout can be provided.
- Parameters
io_var (str or int) – digital input (string or number)
io_value (str, int or float) – value
timeout_ms (int or float) – timeout in milliseconds
See also
- customInstruction(name, path_run, path_icon='', blocking=1, cmd_run_on_robot='')¶
Add a custom instruction. This instruction will execute a Python file or an executable file.
- Parameters
name (str or int) – Name of the instruction
path_run (str) – path of the executable or Python script to run (relative to RoboDK/bin/ folder or absolute path)
path_icon (str) – instruction image/icon path (relative to RoboDK/bin/ folder or absolute path)
blocking (int) – 1 if blocking, 0 if it is a non blocking executable trigger
cmd_run_on_robot (str) – Command to send to the driver when connected to the robot
See also
- addMoveJ(itemtarget)¶
Deprecated since version 4.0: Obsolete. Use
MoveJ()instead.Adds a new robot joint move instruction to a program.
- Parameters
itemtarget (
Item) – target item to move to
See also
- addMoveL(itemtarget)¶
Deprecated since version 4.0: Obsolete. Use
MoveL()instead.Adds a new linear move instruction to a program.
- Parameters
itemtarget (
Item) – target item to move to
See also
- addMoveSearch(itemtarget)¶
Deprecated since version 4.0: Obsolete. Use
SearchL()instead.Adds a new linear search move instruction to a program.
- Parameters
itemtarget (
Item) – target item to move to
See also
- addMoveC(itemtarget1, itemtarget2)¶
Deprecated since version 4.0: Obsolete. Use
MoveC()instead.Adds a new circular move instruction to a program.
- Parameters
itemtarget (
Item) – target item to move to
See also
- ShowInstructions(show=True)¶
Show or hide instruction items of a program in the RoboDK tree
- Parameters
show (bool) – Set to True to show the instruction nodes, otherwise, set to False
See also
- ShowTargets(show=True)¶
Show or hide targets of a program in the RoboDK tree
- Parameters
show (bool) – Set to False to remove the target item (the target is not deleted as it remains inside the program), otherwise, set to True to show the targets
See also
- InstructionCount()¶
Return the number of instructions of a program.
See also
- Return type
int
- InstructionSelect(ins_id=- 1)¶
Select an instruction in the program as a reference to add new instructions. New instructions will be added after the selected instruction. If no instruction ID is specified, the active instruction will be selected and returned (if the program is running), otherwise it returns -1.
See also
- Parameters
ins_id (
int, default:-1) –- Return type
int
- InstructionDelete(ins_id=0)¶
Delete an instruction of a program
See also
- Parameters
ins_id (
int, default:0) –- Return type
int
- Instruction(ins_id=- 1)¶
Return the current program instruction or the instruction given the instruction id (if provided). It returns the following information about an instruction:
name: name of the instruction (displayed in the RoboDK tree)
instype: instruction type (INS_TYPE_*). For example, INS_TYPE_MOVE for a movement instruction.
movetype: type of movement for INS_TYPE_MOVE instructions: MOVE_TYPE_JOINT for joint moves, or MOVE_TYPE_LINEAR for linear moves
isjointtarget: 1 if the target is specified in the joint space, otherwise, the target is specified in the cartesian space (by the pose)
target: pose of the target as
Itemjoints: robot joints for that target
- Parameters
ins_id (int) – instruction id to return
See also
- setInstruction(ins_id, name, instype, movetype, isjointtarget, target, joints)¶
Update a program instruction.
- Parameters
ins_id (int) – index of the instruction (0 for the first instruction, 1 for the second, and so on)
name (str) – Name of the instruction (displayed in the RoboDK tree)
instype (int) – Type of instruction. INS_TYPE_*
movetype (int) – Type of movement if the instruction is a movement (MOVE_TYPE_JOINT or MOVE_TYPE_LINEAR)
isjointtarget (int) – 1 if the target is defined in the joint space, otherwise it means it is defined in the cartesian space (by the pose)
target (
Mat) – target posejoints (list of float) – robot joints for the target
See also
- Update(check_collisions=0, timeout_sec=3600, mm_step=- 1, deg_step=- 1)¶
Updates a program and returns the estimated time and the number of valid instructions. An update can also be applied to a robot machining project. The update is performed on the generated program.
- Parameters
check_collisions (int) – Check collisions (COLLISION_ON -yes- or COLLISION_OFF -no-)
timeout_sec (int) – Maximum time to wait for the update to complete (in seconds)
mm_step (float) – Step in mm to split the program (-1 means default, as specified in Tools-Options-Motion)
deg_step (float) – Step in deg to split the program (-1 means default, as specified in Tools-Options-Motion)
- Return type
Tuple[float,float,float,float,str]- Returns
[valid_instructions, program_time, program_distance, valid_ratio, readable_msg]
valid_instructions: The number of valid instructions
program_time: Estimated cycle time (in seconds)
program_distance: Estimated distance that the robot TCP will travel (in mm)
valid_ratio: This is a ratio from [0.00 to 1.00] showing if the path can be fully completed without any problems (1.0 means the path 100% feasible) or valid_ratio is <1.0 if there were problems along the path.
valid_ratio will be < 0 if Update is called on a machining project and the machining project can’t be achieved successfully.
readable_msg: a readable message as a string
See also
- InstructionList()¶
Returns the list of program instructions as an MxN matrix, where N is the number of instructions and M equals to 1 plus the number of robot axes. This is the equivalent sequence that used to be supported by RoKiSim. Tip: Use RDK.ShowSequence(matrix) to dipslay a joint list or a RoKiSim sequence of instructions.
Out 1: Returns the matrix
Out 2: Returns 0 if the program has no issues
See also
- Return type
Tuple[Mat,int]
- InstructionListJoints(mm_step=10, deg_step=5, save_to_file=None, collision_check=0, flags=0, time_step=0.1)¶
Returns a list of joints an MxN matrix, where M is the number of robot axes plus 4 columns. Linear moves are rounded according to the smoothing parameter set inside the program.
- Parameters
mm_step (float) – step in mm to split the linear movements
deg_step (float) – step in deg to split the joint movements
save_to_file (str) – (optional) save the result to a file as Comma Separated Values (CSV). If the file name is not provided it will return the matrix. If step values are very small, the returned matrix can be very large.
collision_check (int) – (optional) check for collisions
flags (int) – (optional) set to 1 to include the timings between movements, set to 2 to also include the joint speeds (deg/s), set to 3 to also include the accelerations, set to 4 to include all previous information and make the splitting time-based.
time_step (float) – (optional) set the time step in seconds for time based calculation
- Return type
Tuple[str,Mat,int]- Returns
[message (str), joint_list (
Mat), status (int)]
Outputs:
message (str): Returns a human readable error message (if any).
joint_list (
Mat): 2D matrix with all the joint information and corresponding information such as step, time stamp and speeds. Each entry is one column.status (int): Status is negative if there are program issues (singularity, axis limit, targets not properly defined or collision if activated). Otherwise it returns the number of instructions that can be successfully executed.
It also returns the list of joints as [J1, J2, …, Jn, ERROR, MM_STEP, DEG_STEP, MOVE_ID, TIME, X,Y,Z] or the file name if a file path is provided to save the result. Default units are MM and DEG. Use list(
Mat) to extract each column in a list. The ERROR is returned as an int but it needs to be interpreted as a binary number.Error bit masks¶# If error is not 0, check the binary error using the following bit masks error_bin = int(str(ERROR),2) ERROR_KINEMATIC = 0b001 # One or more points in the path is not reachable ERROR_PATH_LIMIT = 0b010 # The path reached a joint axis limit ERROR_PATH_NEARSINGULARITY = 0b1000 # The robot is too close to a wrist singularity (J5). Lower the singularity tolerance to allow the robot to continue. ERROR_PATH_SINGULARITY = 0b100 # The robot reached a singularity point ERROR_COLLISION = 0b100000 # Collision detected
See also
- getParam(param)¶
Get custom binary data from this item. Use setParam to set the data.
- Parameters
param (str) – Parameter name
See also
- setParam(param, value='', skip_result=False)¶
Set a specific item parameter.
Select Tools-Run Script-Show Commands to see all available commands for items and the station.
Note: For parameters (commands) that require a JSON string value you can also provide a dict.
- Parameters
param (str) – Parameter/command name
value (str) – Parameter value (optional, not all commands require a value). If value is bytes it will store customized data to an item given the param name.
Example to expand or collapse an item in the tree¶from robodk.robolink import * import time RDK = Robolink() # Start the RoboDK API # How to expand or collapse an item in the tree item = RDK.ItemUserPick("Select an item") item.setParam("Tree", "Expand") time.sleep(2) item.setParam("Tree", "Collapse")
Example to change the post processor¶robot = RDK.ItemUserPick("Select a robot", ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT) # Set the robot post processor (name of the py file in the posts folder) robot.setParam("PostProcessor", "Fanuc_RJ3")
Example to change display style¶# How to change the display style of an object (color as AARRGGBB): obj = RDK.ItemUserPick('Select an object to change the style', ITEM_TYPE_OBJECT) # Display points as simple dots given a certain size (suitable for fast rendering or large point clouds) # Color is defined as AARRGGBB obj.setValue('Display', 'POINTSIZE=4 COLOR=#FF771111') # Display each point as a cube of a given size in mm obj.setValue('Display','PARTICLE=CUBE(0.2,0.2,0.2) COLOR=#FF771111') # Another way to change display style of points to display as a sphere (size,rings): obj.setValue('Display','PARTICLE=SPHERE(4,8) COLOR=red') # Example to change the size of displayed curves: obj.setValue('Display','LINEW=4') # More examples to change the appearance of points and curves available here: https://github.com/RoboDK/Plug-In-Interface/tree/master/PluginAppLoader/Apps/SetStyle
- Parameters
skip_result (
bool, default:False) –- Return type
str
2.1.3. Special Commands¶
The following is the current list of available commands for Robolink’s Command.
(Command) | (parameter) | (description) |
|---|---|---|
AddBallbarValid | (name) | Add a new ballbar validation project |
AddCalibration | (name) | Add a new calibration project |
AddFolder | (name) | Add a new folder attached to the station root (item of ITEM_TYPE_FOLDER) |
AddFrame | (string) | Add a reference frame |
AddItem | (name) | Add a generic item container. You can customize the name and hold custom properties using setParam(‘property’,’value’). You can also customize the icon using the plugin interface. |
AddNotes | (name) | Add notes to the station root |
AddPathValid | (name) | Add a new path validation |
AddStationNested | 1|0 | Add new RDK station files as nested stations (added to the currently open station) |
AddValidation | (name) | Add a new validation project |
AllowExternalAPI | 1|0 | Allow external API |
API_NODELAY | 1|0 | Turn On or Off the NoDelay socket for TCP/IP. This option provides faster results when working with the API from a remote PC |
API_NonFinite_Behavior | -1|0|1 | How to deal with non finite values provided through the API -> 0=Force values to be 0, 1=Do not allow, -1=Ignore |
ApiUpdateAlways | (1|0) | Always update the station when using the API (regardless of the Render preferences) |
AutoRenderDelay | (int) | Delay to provoke a screen draw event when using the AutoRender option of the API (tools-Options-Other-Auto Render Delay) |
AutoRenderDelayMax | (int) | Maximum delay in miliseconds to provoke a screen draw event |
BlockKeyEvents | (1|0) | Block all key events (press and release) |
CAM_APT_AUTOSPLIT | 1|0 | Automatically split CAM programs on tool change |
CAM_APT_SPLITPROG | 1|0 | Automatically split CAM programs on operation change |
CAM_AUTOLOADCUTTER | 1|0 | Automatically create cutters when loading CAM programs |
CAM_ZAXIS_INSIDE | 1|0 | Set to 1 if the Tool Z axis points towards the inside of the spindle (CNC standard instead of robot) |
CamWinId | (CamID) | Returns the top level window ID. CamID is the pointer returned by Camd2D_Add. |
ClearSelection | (ignored) | Clear the selection |
CollisionCalcTime | Time it took to calculate collisions during the last udpate event | |
CollisionCUDAtriangles | (int) | Minimum number of n1*n2 triangles needed for CUDA collision checking |
CollisionHidden | 1|0 | Include hidden objects for collision checking |
CollisionMap | All|None|Default|Uncheck|Off | Set the collision map settings to chack for all interactions, no interactions or the default settings (setting it to Off removes the default collision presets to speed up loading multiple parts) |
CollisionMapMaxSize | (int) | Set the maximum number of objects to remember the collision map (larger is slower when adding new objects) |
CollisionMethod | (Default|CUDA|CPU) | Hardware to use to check for collisions |
ColorAxisX | (named color or #AARRGGBB) | Change the color of the X axis |
ColorAxisY | (named color or #AARRGGBB) | Change the color of the Y axis |
ColorAxisZ | (named color or #AARRGGBB) | Change the color of the Z axis |
ColorBgBottom | (named color or #RRGGBB) | Change the color of the background (bottom gradient) |
ColorBgTop | (named color or #RRGGBB) | Change the color of the background (top gradient) |
ColorPlaneXY | (named color or #AARRGGBB) | Change the color of the XY plane |
ColorPlaneXZ | (named color or #AARRGGBB) | Change the color of the XZ plane |
ColorPlaneYZ | (named color or #AARRGGBB) | Change the color of the YZ plane |
ColorSelected | (named color or #AARRGGBB) | Change the color of selected objects |
CudaDevice | Name of the CUDA harware being used | |
CudaThreads | (int) | Number of threads to use for CUDA GPUs |
DisplayCurveNormalsOnSelect | 1|0 | Show curve normals when selected |
DisplayCurves | 1|0 | Display object curves |
DisplayPoints | 1|0 | Display object points |
DisplayThreshold | (double) | Do not display small object of a given size (size as a percentage of the screen). Set to -1 to always display everything. |
EXIT_LAST_COM | When this command is used, RoboDK will close after the last instance of the API closes | |
FitAll | Fit all objects in the screen (Fit All action). | |
FitIsometric | Set Isometric view. | |
FitSelection | Fit to selection. | |
FrameSizes | (double) | Set the sizes of coordinate systems as a ratio with respect to the default values (1=default) |
FrameSizes-PlaneWidthRatio | (double) | Apply a ratio to the width of the planes |
FrameSizesOther | (double) | Set the size for other coordinate systems in mm (if no value is provided it will return the current size) |
FrameSizesPath | (double) | Set the size of coordinate systems for paths in mm (if no value is provided it will return the current size) |
FrameSizesRef | (double) | Set the size of coordinate systems for reference frames in mm (if no value is provided it will return the current size) |
FrameSizesTarget | (double) | Set the size of coordinate systems for target items in mm (if no value is provided it will return the current size) |
HelixTol | (double) | Tolerance in mm to consider an arc move as a helix |
ImportCurvesAndPointsExtract | 1|0 | Extract surface edges as curves from STEP and IGES files |
ImportCurvesAndPointsRead | 1|0 | Load curves from STEP and IGES files |
ImportCurvesPoints | (double) | Import surface edges (Tools-Options-CAD) |
ImportSurfaceEdges | (double) | Import surface edges (Tools-Options-CAD) |
KeyEvent | (string) | Trigger an action given the key shortcut (such as Ctrl+C) |
Lang | (string) | Set the language as a 2-letter ISO language code |
LastRender | Returns the time of last display update in ms since epoch | |
MAC | Retrieve the MAC address of the computer | |
Machining_DefaultApproach | (double) | Default approach for robot machining projects |
Machining_DefaultFrameShift | (pose script) | Default reference shift pose, as as script string, for robot machining parameters. Example: rotz(0) |
Machining_DefaultToolShift | (pose script) | Default tool shift pose, as as script string, for robot machining parameters. Example: rotx(0)*roty(0) |
MainProcess_ID | RoboDK’s main process ID | |
MainWindow_ID | Top level window ID | |
MaxDecimalsPost | (int) | Maximum decimals used for post processing (intermediate file) |
MouseClickLeft | Select|Rotate|Zoom|Pan|None | Set the default action for the mouse left click |
MouseClickMid | Select|Rotate|Zoom|Pan|None | Set the default action for the mouse mid button click |
MouseClickRight | Select|Rotate|Zoom|Pan|None | Set the default action for the mouse right click |
MouseFeedback | (1|0) | Activate or disable mouse feedback in the 3D view (highlight object on hover). |
MouseNav | (int) | Change the 3D navigation type |
MoveCSplitDeg | (double) | Get/set the default step to generate circular movements in deg |
MoveCSplitMinMM | (double) | Get/set the minimum step to generate circular movements in mm |
MoveCSplitMM | (double) | Get/set the default step to generate circular movements in mm |
MoveJSplitDeg | (double) | Get/set the default step to generate joint movements in deg |
MoveLSplitDeg | (double) | Get/set the default step to generate linear movements in deg |
MoveLSplitMinMM | (double) | Get/set the minimum step to generate linear movements in mm |
MoveLSplitMM | (double) | Get/set the default step to generate linear movements in mm |
PATH_PROGRAMS | (folder) | Set the path to save generated programs |
PathCheckActiveKin | 1|0 | Check paths using active kinematics (accurate or nominal). If the value is set to 0 it will use nominal kinematics |
PathPostProcessor | (string) | Path to post processors |
PathPrograms | (string-folder) | Default path to save programs |
PathStepCollisionDeg | (double) | Get/set the movement step for collision detection, in deg |
PathStepCollisionMM | (double) | Get/set the movement step for collision detection, in mm |
PathStepMM | (double) | Get/set the step for simulation in mm |
PluginApiEvents | (All|) | Allows you to enable feedback for all events while a plugin is loaded |
PluginCommand | (command=value=name) | Send a plugin command, value and name (plugin name is optional) |
PluginLoad | (string) | Load a plugin by name or path to library |
PluginReload | (string) | Reload a plugin |
PluginsList | (string) | List of plugins including pointers |
PluginsLoad | (ignored) | Load plugins |
PluginsUnload | (ignored) | Unload plugins |
Popups | 1|0 | Prevent showing any blocking popup messages |
ProgMaxLines | (int) | Number of lines per program |
ProgMoveCType | (int) | Type of targets for circular movements |
ProgMoveJType | (int) | Type of targets for joint movements |
ProgMoveLType | (int) | Type of targets for linear movements |
ProgMoveNames | 1|0 | Export program names for program generation |
ProgramsShow | (1|0) | Show programs when they are generated (use the command PATH_PROGRAMS to specify the folder and MAKEPROGS to generate all programs). |
ProgRecalc | 1|0 | Recalculate targets before program generation |
ProgressBar | (-1 or 0-100) | Set the status of the progress bar from 0 to 100 (-1 to hide) |
PYTHONPATH | (string) | Get or set the Python path |
PythonRunCode | (string) | Run Python code, new lines can be represented as br HTML tags |
RunProg | (string) | Run program name |
SetSize3D | (w x h) | Set the size of the 3D window as Width x Height (example: 640x480) |
Settings | Load|Save|Defaults | Load, save or reset the computer and user specific settings related to RoboDK |
ShowCoords | 1|0 | Display coordinate systems |
ShowCurveNormals | 1|0 | Show curve normals |
ShowCurvePoints | 1|0 | Show curve points |
ShowHiddenSelected | 1|0 | Show transparent items when the are hidden and selected |
ShowMessage | (str) | Display a message (blocking) |
ShowPointNormals | 1|0 | Show point normals |
ShowRef_NewObjects | 1|0 | Display references by default for newly added objects |
ShowRef_NewReferences | 1|0 | Display references by default for newly added references |
ShowSelectedPointNormals | 1|0 | Show point normals for selected curves |
ShowText | 1|0 | Display text on the screen |
ShowTextObject | 1|0 | Display text on the screen for objects |
SilentMessage | (str) | Display a message in the toolbar |
SimulationSpeed | (double) | Set the simulation speed (> 0) |
SimulationTime | (ms) | Retrieve the time of the simulation (0 ms starts the first time this value is requested) |
SizeCurveArrow | (double) | Curve arrow size |
SizeCurvePoints(double) | Size of curve points | |
SizeNormals | (double) | Normals size |
SizeRatioCurves | (double) | Size of the curves (ratio with respect to the default size). Default value = 1 |
Snapshot | (string/file) | Save a screenshot (PNG, JPG and other formats supported) |
SnapshotWhite | (string/file) | Save a screenshot using a white background (PNG, JPG and other formats supported) |
Threads | (int) | Number of threads used for parallel processing |
Time | (seconds) | Retrieve the time of the computer as seconds since Epoch |
TimeGhostRobot | (int) | Timeout to display ghost robots. Ghost robots are displayed when a target is moved. Set to -1 to disable this feature. |
ToggleWorkspace | (ignored) | Toggle showing workspace |
TolerancePickCurve | (double) | Import surface edges (Tools-Options-Display) |
TolerancePickPoint | (double) | Import surface edges (Tools-Options-Display) |
ToleranceSingularityBack | (double, in mm) | Tolerance to avoid front/back singularity (wrist on axis 1) (Tools-Options-Motion-Tolerance to avoid front/back singularity) |
ToleranceSingularityElbow | (double, in deg) | Tolerance to avoid elbow singularity for (joint 3) (Tools-Options-Motion-Tolernace to avoid elbow singularity |
ToleranceSingularityWrist | (double, in deg) | Tolerance to avoid wrist singularity for (joint 5) (Tools-Options-Motion-Tolerance to avoid wrist singularity |
ToleranceTurn180 | (double) | Tolerance to avoid 180 deg rotations (Tools-Options-Motion) |
ToolbarLayout | (None|Basic|Complete|Viewer) | Set the toolbar layout |
Trace | On|Off|Reset | Turn the trace On, Off or Reset/Clear it |
TrajectoryTime | (ignored|double) | Returns the trajectory time in seconds. The trajectory time is the simulation time used by robots and mechanisms while they are moving. Provide a delta time in seconds to move the simulation by a given simulation time. The returned time is the final trajectory time. |
Tree | (Detach|Visible|Hidden) | Detach/hide/show the tree from the main screen (the tree can’t be attached once detached. Use -SKIPINI command line option on RoboDK startup to ignore user settings) |
TriggerAction | (string) | Trigger an action given the action name (leave empty to retrieve list) |
UseGPU | (int) | Use GPU arrays for rendering |
Version | Return the full string of the RoboDK version | |
ViewPerspective | 0|1 | Set the view in perspective mode (1) or orthographic mode (0) |
ViewPoseVR | (x,y,z,rx,ry,rz) | Get or set the view pose of the VR headset (mm and rad) |
VR | (ignored) | Open Virtual Reality view. |
Window | Resize | Provoke a resize event |
ZoomInvert | 1|0 | Invert the sense of the zoom |
ZoomSpeed | (double)|Auto|Fixed | Set the zoom speed as a ratio, set to Automatic (default) or fixed |
The following is the current list of available commands for an Item’s setParam.
See also
(ItemCommand) | (ItemParameter) | (description) |
|---|---|---|
(id) | (dict or JSON string) | For a program, providing the instruction id you can get or set the instruction parameters. |
Add | (dict or JSON string) | Add the new instruction to a program using a dict or JSON format. |
Approach | (Normal|Tangent|Side|XYZ|NTS|ArcN|ArcS A B C) | Set the approach or retract of a robot machining toopath |
ApproachRetractAllCurves | (1|0) | For curve follow projects: Apply approach and retract to each curve section. |
BoundingBox | Returns the bounding box of this object, robot or tool a JSON string, in mm and with respect to station coordinates (absolute) | |
Clear | Point|Curve|Surf | Delete object points, curves or mesh |
ClearanceZ | (ignored) | Get the clearance distance along the positive Z axis (for tools, objects or coordinate systems). |
Close | (ignored) | Close camera view |
Code | (ignored) | Get the code of a script |
Code | (ignored) | Get the Python code |
Convert | (Object|Tool) | Convert a tool or geometry to an object or an object to a tool. If the pointer changes it returns the object pointer as a string, otherwise it returns OK. |
Cutter | (1|0) | Set this tool as a cutter: it is treated accordingly when using a robot machining project. |
FilterMesh | (double double double) | Remove small object triangles given a tolerance [min part size (mm), min triangle surface (mm2), triangle angle (deg)]. |
FitAll | (double) | Fits the screen to the current item and its children. Optionally provide a minimum size to fit. |
Form | (Open|Close) | Open or close a form or camera linked to an item |
HTML | (string) | Get or set the HTML text of a notes item |
IconGet | (ignored) | Get the item icon as a PNG bytearray in hex format |
IconSet | (image file or hex bytearray representing png data) | Set the icon of an item (see command AddItem) |
IsJointTarget | (ignored) | Returns 1 if the target is a joint target. |
IsOpen | (ignored) | Returns 1 if the view is open, 0 otherwise |
JoinCurveTol | (double) | For curve follow projects: Join curve tolerance (in mm). |
Loop | (1|0) | Set program to loop |
Machining | (dict or JSON string) | Get or set the robot machining settings (see also: ProgEvents and OptimAxes) |
NormalApproach | (double) | For robot machining projects: Use a normal approach with a given distance. |
OffsetRail | (double) | For robot machining projects: Offset of the rail when optimized (mm). |
OffsetTurntable | (double) | For robot machining projects: Offset of the turntable when optimized (deg). |
Open | (ignored) | Open camera view |
OperationSpeed | (double) | For curve follow projects: Operation speed (in mm/s). |
OptimAxes | (dict or JSON string) | Get or set the robot optimization settings for external axes (settings linked to a robot machining project or robot) |
OptimRail | (0|1) | For robot machining projects: Use linear rail optimization. |
OptimTurntable | (0|1) | For robot machining projects: Use turntable optimization. |
Orient | (Teach) | Set the teach action for machining/curve follow projects |
PathDisplay | (Estimated|Preferred|Quick|None) | Preview path for robot machining/curve follow projects. Add the Quick flag to display for a brief moment (about 2 seconds). |
PointApproach | (double) | For point follow projects: Point approach (in mm). |
PostProcessor | (string) | Set the post processor (file or name excluding the path). Leave empty to retrieve current post processor. |
ProgEvents | (dict or JSON string) | Get or set the program events of a robot machining project (use a station to change default settings) |
RangeRotZ | (double 0-180) | For robot machining projects: Tool rotation range around the Z axis (deg). |
Reachable | (ignored) | Returns 1 if the target is reachable with the currently active tool and reference frame, 0 otherwise. |
Recalculate | (ignored) | Recalculate a target. |
RecalculateTargets | (string) | Recalculate all targets of a program. |
Reframe | (ignored) | Reframe on this object |
Reset | (Surf|Curves|Points) | Delete the mesh, curves and/or points of an object or tool |
Retract | (Normal|Tangent|Side|XYZ|NTS|ArcN|ArcS A B C) | Set the approach or retract of a robot machining toopath |
SaveTableCalib | (path to csv file) | Save the calibration data as a CSV file. |
SaveTableRail | (path to csv file) | Save the rail data as a CSV file. |
SaveTableValid | (path to csv file) | Save the validation data as a CSV file. |
SelectAlgorithm | (0|1|2) | Select the algorithm (0: minimum tool orientation change, 1: Tool orientation follows path, 3: Robot holds object). |
Settings | (1|0) | Set camera settings |
ShowWorkspace | (0|1|2|3) | Show or hide robot workspace (0: hide, 1: show for wrist center, 2: show for flange, 3: show for active tool). |
SimplifyMesh | (ignored) | Simplify the geometry of an object (it does not change the object appearance). |
Start | (int) | Start a program at a given instruction (0 to start from the beginning) |
StatsAccuracy | (Validation|Calibration) | Robot calibration statistics |
StepRotZ | (double) | For robot machining projects: Tool rotation steps around the Z axis (deg). |
Stop | (ignored) | Stop a program |
Tree | (expand|collapse|isExpanded) | Expand or collapse the item in the tree. |
UpdatePath | (ignored) | Update the operation toolpath (green path). Use this option after changing an approach or retract |
Visible | (1|0) | Get or set visibility of an item. |
VisibleChilds | (1|0) | Get or set visibility of an item including children items. |
2.2. robomath.py¶
The robomath module is a robotics toolbox for Python, based on Peter Corke’s Robotics Toolbox (regarding pose transformations): https://petercorke.com/toolboxes/robotics-toolbox/. The robomath sub-module includes the Mat class to represent transformations in 3D.
The following page provides a brief overview of the RoboDK API for Python: https://www.robodk.com/offline-programming
A summary regarding the RoboDK API is available in the documentation: https://robodk.com/doc/en/RoboDK-API.html
This is a robotics toolbox to facilitate operations with the RoboDK API and matrix (pose) operations. This toolbox includes a simple matrix class for pose transformations (Mat class).
This toolbox has been inspired from Peter Corke’s Robotics Toolbox: https://petercorke.com/toolboxes/robotics-toolbox/
In this module: pose = transformation matrix = homogeneous matrix = 4x4 matrix = Mat class
More information about the RoboDK API for Python here:
- robodk.robomath.pi: float = 3.141592653589793¶
PI
- robodk.robomath.pause(seconds)¶
Pause the execution for a specified duration.
- Parameters
seconds (float) – time in seconds
- robodk.robomath.sqrt(value)¶
Computes the square root of a given value.
- Parameters
value (float) – Value to find the square root of.
- Returns
Square root of the input value.
- Return type
float
- robodk.robomath.sqrtA(value)¶
Computes the square root of a value if it’s positive; returns 0 for non-positive values (differs from IEEE-754).
- Parameters
value (float) – Value to compute the square root of.
- Returns
Square root of the input value if positive, otherwise 0.
- Return type
float
- robodk.robomath.sin(value)¶
Calculates the sine of an angle given in radians.
- Parameters
value (float) – Angle in radians.
- Returns
Sine of the angle.
- Return type
float
- robodk.robomath.cos(value)¶
Calculates the cosine of an angle given in radians.
- Parameters
value (float) – Angle in radians.
- Returns
Cosine of the angle.
- Return type
float
- robodk.robomath.tan(value)¶
Calculates the tangent of an angle given in radians.
- Parameters
value (float) – Angle in radians.
- Returns
Tangent of the angle.
- Return type
float
- robodk.robomath.asin(value)¶
Calculates the arc sine of a value, result in radians.
- Parameters
value (float) – Value to compute the arc sine for.
- Returns
Arc sine of the input value in radians.
- Return type
float
- robodk.robomath.acos(value)¶
Calculates the arc cosine of a value, result in radians.
- Parameters
value (float) – Value to compute the arc cosine for.
- Returns
Arc cosine of the input value in radians.
- Return type
float
- robodk.robomath.atan2(y, x)¶
Calculates the angle of a point from the origin in the XY plane.
- Parameters
y (float) – Y-coordinate of the point.
x (float) – X-coordinate of the point.
- Returns
Angle of the point in radians.
- Return type
float
- robodk.robomath.name_2_id(str_name_id)¶
Extracts the numerical ID from a string containing a named object. For example: “Frame 3”, “Frame3”, “Fram3 3” returns 3.”
- Parameters
str_name_id (str) – String containing the named object and its ID.
- Returns
Numerical ID found in the string, or -1 if none found.
- Return type
float
- robodk.robomath.rotx(rx)¶
Returns a rotation matrix around the X axis (radians)
R_x(\theta) = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & c_\theta & -s_\theta & 0 \\ 0 & s_\theta & c_\theta & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}
- Parameters
rx (float) – rotation around X axis in radians
- Return type
- robodk.robomath.roty(ry)¶
Returns a rotation matrix around the Y axis (radians)
R_y(\theta) = \begin{bmatrix} c_\theta & 0 & s_\theta & 0 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \\ -s_\theta & 0 & c_\theta & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}
- Parameters
ry (float) – rotation around Y axis in radians
- Return type
- robodk.robomath.rotz(rz)¶
Returns a rotation matrix around the Z axis (radians)
R_x(\theta) = \begin{bmatrix} c_\theta & -s_\theta & 0 & 0 \\ s_\theta & c_\theta & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}
- Parameters
rz (float) – rotation around Z axis in radians
- Return type
- robodk.robomath.transl(tx=0, ty=0, tz=0)¶
Returns a translation matrix (mm) given translations in each dimension. Supports passing inputs as a list through the tx argument, but this ignores ty and tz.
T(t_x, t_y, t_z) = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 & t_x \\ 0 & 1 & 0 & t_y \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & t_z \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}
- Parameters
tx (float or list of float, optional) – translation along the X axis (mm) or list of the supported parameters (i.e. [tx, ty, tz])
ty (float, optional) – translation along the Y axis (mm), defaults to 0
tz (float, optional) – translation along the Z axis (mm)
- Return type
- robodk.robomath.RelTool(target_pose, x, y, z, rx=0, ry=0, rz=0)¶
Calculates a relative target with respect to the tool coordinates. This procedure has exactly the same behavior as ABB’s RelTool instruction. X,Y,Z are in mm, RX,RY,RZ are in degrees.
- Parameters
target_pose (
Mat) – Reference posex (float) – translation along the Tool X axis (mm)
y (float) – translation along the Tool Y axis (mm)
z (float) – translation along the Tool Z axis (mm)
rx (float) – rotation around the Tool X axis (deg), optional
ry (float) – rotation around the Tool Y axis (deg), optional
rz (float) – rotation around the Tool Z axis (deg), optional
- Return type
- robodk.robomath.Offset(target_pose, x, y, z, rx=0, ry=0, rz=0)¶
Calculates a relative target with respect to the reference frame coordinates. X,Y,Z are in mm, RX,RY,RZ are in degrees.
- Parameters
target_pose (
Mat) – Reference posex (float) – translation along the Reference X axis (mm)
y (float) – translation along the Reference Y axis (mm)
z (float) – translation along the Reference Z axis (mm)
rx (float) – rotation around the Reference X axis (deg), optional
ry (float) – rotation around the Reference Y axis (deg), optional
rz (float) – rotation around the Reference Z axis (deg), optional
- Return type
- robodk.robomath.point_Xaxis_2_pose(point, xaxis, zaxis_hint1=[0, 0, - 1], zaxis_hint2=[0, - 1, 0])¶
Returns a pose given the origin as a point, a X axis and a preferred orientation for the Z axis
- Parameters
point (
List[float]) –xaxis (
List[float]) –zaxis_hint1 (
List[float], default:[0, 0, -1]) –zaxis_hint2 (
List[float], default:[0, -1, 0]) –
- Return type
- robodk.robomath.point_Yaxis_2_pose(point, yaxis, zaxis_hint1=[0, 0, - 1], zaxis_hint2=[- 1, 0, 0])¶
Returns a pose given the origin as a point, a Y axis and a preferred orientation for the Z axis
- Parameters
point (
List[float]) –yaxis (
List[float]) –zaxis_hint1 (
List[float], default:[0, 0, -1]) –zaxis_hint2 (
List[float], default:[-1, 0, 0]) –
- Return type
- robodk.robomath.point_Zaxis_2_pose(point, zaxis, yaxis_hint1=[0, 0, 1], yaxis_hint2=[0, 1, 1])¶
Returns a pose given the origin as a point, a Z axis and a preferred orientation for the Y axis
- Parameters
point (
List[float]) –zaxis (
List[float]) –yaxis_hint1 (
List[float], default:[0, 0, 1]) –yaxis_hint2 (
List[float], default:[0, 1, 1]) –
- Return type
- robodk.robomath.eye(size=4)¶
Returns the identity matrix
T(t_x, t_y, t_z) = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}
- Parameters
size (int) – square matrix size (4x4 Identity matrix by default, otherwise it is initialized to 0)
- Return type
- robodk.robomath.size(matrix, dim=None)¶
Returns the size of a matrix (m,n). Dim can be set to 0 to return m (rows) or 1 to return n (columns)
- Parameters
matrix (
Mat) – posedim (int) – dimension
- Return type
Union[Tuple[int,int],int]
- robodk.robomath.tr(matrix)¶
Returns the transpose of the matrix
- robodk.robomath.invH(matrix)¶
Returns the inverse of a homogeneous matrix
- Parameters
matrix (
Mat) – pose
- Return type
- robodk.robomath.catV(mat1, mat2)¶
Concatenate 2 matrices (vertical concatenation)
- robodk.robomath.catH(mat1, mat2)¶
Concatenate 2 matrices (horizontal concatenation)
- robodk.robomath.tic()¶
Start a stopwatch timer
- robodk.robomath.toc()¶
Read the stopwatch timer
- robodk.robomath.PosePP(x, y, z, r, p, w)¶
Create a pose from XYZRPW coordinates. The pose format is the one used by KUKA (XYZABC coordinates). This is function is the same as KUKA_2_Pose (with the difference that the input values are not a list). This function is used as “p” by the intermediate file when generating a robot program.
See also
KUKA_2_Pose(),Mat,TxyzRxyz_2_Pose(),Pose_2_TxyzRxyz(),Pose_2_ABB(),Pose_2_Adept(),Pose_2_Comau(),Pose_2_Fanuc(),Pose_2_KUKA(),Pose_2_Motoman(),Pose_2_Nachi(),Pose_2_Staubli(),Pose_2_UR(),quaternion_2_pose()- Parameters
x (
float) –y (
float) –z (
float) –r (
float) –p (
float) –w (
float) –
- Return type
- robodk.robomath.pose_2_xyzrpw(H)¶
Calculates the equivalent position (mm) and Euler angles (deg) as an [x,y,z,r,p,w] array, given a pose. It returns the values that correspond to the following operation: transl(x,y,z)*rotz(w*pi/180)*roty(p*pi/180)*rotx(r*pi/180)
- Parameters
H (
Mat) – pose- Return type
List[float]- Returns
[x,y,z,r,p,w] in mm and deg
- robodk.robomath.xyzrpw_2_pose(xyzrpw)¶
Calculates the pose from the position (mm) and Euler angles (deg), given a [x,y,z,r,p,w] array. The result is the same as calling: H = transl(x,y,z)*rotz(w*pi/180)*roty(p*pi/180)*rotx(r*pi/180)
See also
Mat,TxyzRxyz_2_Pose(),Pose_2_TxyzRxyz(),Pose_2_ABB(),Pose_2_Adept(),Pose_2_Comau(),Pose_2_Fanuc(),Pose_2_KUKA(),Pose_2_Motoman(),Pose_2_Nachi(),Pose_2_Staubli(),Pose_2_UR(),quaternion_2_pose()- Parameters
xyzrpw (
List[float]) –- Return type
- robodk.robomath.Pose(x, y, z, rxd, ryd, rzd)¶
Returns the pose (
Mat) given the position (mm) and Euler angles (deg) as an array [x,y,z,rx,ry,rz]. The result is the same as calling: H = transl(x,y,z)*rotx(rx*pi/180)*roty(ry*pi/180)*rotz(rz*pi/180) This pose format is printed for homogeneous poses automatically. This Pose is the same representation used by Mecademic or Staubli robot controllers.- Parameters
tx (float) – position (X coordinate)
ty (float) – position (Y coordinate)
tz (float) – position (Z coordinate)
rxd (float) – first rotation in deg (X coordinate)
ryd (float) – first rotation in deg (Y coordinate)
rzd (float) – first rotation in deg (Z coordinate)
See also
- Parameters
x (
float) –y (
float) –z (
float) –
- Return type
- robodk.robomath.TxyzRxyz_2_Pose(xyzrpw)¶
Returns the pose given the position (mm) and Euler angles (rad) as an array [x,y,z,rx,ry,rz]. The result is the same as calling: H = transl(x,y,z)*rotx(rx)*roty(ry)*rotz(rz)
- Parameters
xyzrpw (list of float) – [x,y,z,rx,ry,rz] in mm and radians
See also
Mat,TxyzRxyz_2_Pose(),Pose_2_TxyzRxyz(),Pose_2_ABB(),Pose_2_Adept(),Pose_2_Comau(),Pose_2_Fanuc(),Pose_2_KUKA(),Pose_2_Motoman(),Pose_2_Nachi(),Pose_2_Staubli(),Pose_2_UR(),quaternion_2_pose()- Return type
- robodk.robomath.Pose_2_TxyzRxyz(H)¶
Retrieve the position (mm) and Euler angles (rad) as an array [x,y,z,rx,ry,rz] given a pose. It returns the values that correspond to the following operation: H = transl(x,y,z)*rotx(rx)*roty(ry)*rotz(rz).
- Parameters
H (
Mat) – pose
See also
Mat,TxyzRxyz_2_Pose(),Pose_2_TxyzRxyz(),Pose_2_ABB(),Pose_2_Adept(),Pose_2_Comau(),Pose_2_Fanuc(),Pose_2_KUKA(),Pose_2_Motoman(),Pose_2_Nachi(),Pose_2_Staubli(),Pose_2_UR(),quaternion_2_pose()- Return type
List[float]
- robodk.robomath.Pose_2_Staubli(H)¶
Converts a pose (4x4 matrix) to a Staubli XYZWPR target
- Parameters
H (
Mat) – pose
See also
Mat,TxyzRxyz_2_Pose(),Pose_2_TxyzRxyz(),Pose_2_ABB(),Pose_2_Adept(),Pose_2_Comau(),Pose_2_Fanuc(),Pose_2_KUKA(),Pose_2_Motoman(),Pose_2_Nachi(),Staubli_2_Pose(),Pose_2_UR(),quaternion_2_pose()- Return type
List[float]
- robodk.robomath.Staubli_2_Pose(xyzwpr)¶
Converts a Staubli XYZWPR target to a pose (4x4 matrix)
- Parameters
H (
Mat) – pose
See also
Mat,TxyzRxyz_2_Pose(),Pose_2_TxyzRxyz(),Pose_2_ABB(),Pose_2_Adept(),Pose_2_Comau(),Pose_2_Fanuc(),Pose_2_KUKA(),Pose_2_Motoman(),Pose_2_Nachi(),Pose_2_Staubli(),Pose_2_UR(),quaternion_2_pose()- Parameters
xyzwpr (
List[float]) –- Return type
- robodk.robomath.Pose_2_Motoman(H)¶
Converts a pose (4x4 matrix) to a Motoman XYZWPR target (mm and deg)
- Parameters
H (
Mat) – pose
See also
Mat,TxyzRxyz_2_Pose(),Pose_2_TxyzRxyz(),Pose_2_ABB(),Pose_2_Adept(),Pose_2_Comau(),Pose_2_Fanuc(),Pose_2_KUKA(),Pose_2_Motoman(),Pose_2_Nachi(),Pose_2_Staubli(),Pose_2_UR(),quaternion_2_pose()- Return type
List[float]
- robodk.robomath.Pose_2_Fanuc(H)¶
Converts a pose (4x4 matrix) to a Fanuc XYZWPR target (mm and deg)
- Parameters
H (
Mat) – pose
See also
Mat,TxyzRxyz_2_Pose(),Pose_2_TxyzRxyz(),Pose_2_ABB(),Pose_2_Adept(),Pose_2_Comau(),Pose_2_Fanuc(),Pose_2_KUKA(),Pose_2_Motoman(),Pose_2_Nachi(),Pose_2_Staubli(),Pose_2_UR(),quaternion_2_pose()- Return type
List[float]
- robodk.robomath.Pose_2_Techman(H)¶
Converts a pose (4x4 matrix) to a Techman XYZWPR target (mm and deg)
- Parameters
H (
Mat) – pose
See also
Mat,TxyzRxyz_2_Pose(),Pose_2_TxyzRxyz(),Pose_2_ABB(),Pose_2_Adept(),Pose_2_Comau(),Pose_2_Fanuc(),Pose_2_KUKA(),Pose_2_Motoman(),Pose_2_Nachi(),Pose_2_Staubli(),Pose_2_UR(),quaternion_2_pose()- Return type
List[float]
- robodk.robomath.Motoman_2_Pose(xyzwpr)¶
Converts a Motoman target to a pose (4x4 matrix)
See also
Mat,TxyzRxyz_2_Pose(),Pose_2_TxyzRxyz(),Pose_2_ABB(),Pose_2_Adept(),Pose_2_Comau(),Pose_2_Fanuc(),Pose_2_KUKA(),Pose_2_Motoman(),Pose_2_Nachi(),Pose_2_Staubli(),Pose_2_UR(),quaternion_2_pose()- Parameters
xyzwpr (
List[float]) –- Return type
- robodk.robomath.Fanuc_2_Pose(xyzwpr)¶
Converts a Fanuc target to a pose (4x4 matrix)
See also
Mat,TxyzRxyz_2_Pose(),Pose_2_TxyzRxyz(),Pose_2_ABB(),Pose_2_Adept(),Pose_2_Comau(),Pose_2_Fanuc(),Pose_2_KUKA(),Pose_2_Motoman(),Pose_2_Nachi(),Pose_2_Staubli(),Pose_2_UR(),quaternion_2_pose()- Parameters
xyzwpr (
List[float]) –- Return type
- robodk.robomath.Techman_2_Pose(xyzwpr)¶
Converts a Techman target to a pose (4x4 matrix)
See also
Mat,TxyzRxyz_2_Pose(),Pose_2_TxyzRxyz(),Pose_2_ABB(),Pose_2_Adept(),Pose_2_Comau(),Pose_2_Fanuc(),Pose_2_KUKA(),Pose_2_Motoman(),Pose_2_Nachi(),Pose_2_Staubli(),Pose_2_UR(),quaternion_2_pose()- Parameters
xyzwpr (
List[float]) –- Return type
- robodk.robomath.Pose_2_KUKA(H)¶
Converts a pose (4x4 matrix) to an XYZABC KUKA target (Euler angles), required by KUKA KRC controllers.
- Parameters
H (
Mat) – pose
See also
Mat,TxyzRxyz_2_Pose(),Pose_2_TxyzRxyz(),Pose_2_ABB(),Pose_2_Adept(),Pose_2_Comau(),Pose_2_Fanuc(),Pose_2_KUKA(),Pose_2_Motoman(),Pose_2_Nachi(),Pose_2_Staubli(),Pose_2_UR(),quaternion_2_pose()- Return type
List[float]
- robodk.robomath.KUKA_2_Pose(xyzrpw)¶
Converts a KUKA XYZABC target to a pose (4x4 matrix), required by KUKA KRC controllers.
See also
Mat,TxyzRxyz_2_Pose(),Pose_2_TxyzRxyz(),Pose_2_ABB(),Pose_2_Adept(),Pose_2_Comau(),Pose_2_Fanuc(),Pose_2_KUKA(),Pose_2_Motoman(),Pose_2_Nachi(),Pose_2_Staubli(),Pose_2_UR(),quaternion_2_pose()- Parameters
xyzrpw (
List[float]) –- Return type
- robodk.robomath.Adept_2_Pose(xyzrpw)¶
Converts an Adept XYZRPW target to a pose (4x4 matrix)
See also
Mat,TxyzRxyz_2_Pose(),Pose_2_TxyzRxyz(),Pose_2_ABB(),Pose_2_Adept(),Pose_2_Comau(),Pose_2_Fanuc(),Pose_2_KUKA(),Pose_2_Motoman(),Pose_2_Nachi(),Pose_2_Staubli(),Pose_2_UR(),quaternion_2_pose()- Parameters
xyzrpw (
List[float]) –- Return type
- robodk.robomath.Pose_2_Adept(H)¶
Converts a pose to an Adept target
- Parameters
H (
Mat) – pose
See also
Mat,TxyzRxyz_2_Pose(),Pose_2_TxyzRxyz(),Pose_2_ABB(),Pose_2_Adept(),Pose_2_Comau(),Pose_2_Fanuc(),Pose_2_KUKA(),Pose_2_Motoman(),Pose_2_Nachi(),Pose_2_Staubli(),Pose_2_UR(),quaternion_2_pose()- Return type
List[float]
- robodk.robomath.Pose_2_Catia(H)¶
Converts a pose to Catia or Solidworks format, in mm and deg. It returns the values that correspond to the following operation: H = transl(x,y,z)*rotz(a)*rotx(b)*rotz(c).
- Parameters
H (
Mat) – pose
See also
Mat,TxyzRxyz_2_Pose(),Pose_2_TxyzRxyz(),Pose_2_ABB(),Pose_2_Adept(),Pose_2_Comau(),Pose_2_Fanuc(),Pose_2_KUKA(),Pose_2_Motoman(),Pose_2_Nachi(),Pose_2_Staubli(),Pose_2_UR(),quaternion_2_pose()- Return type
List[float]
- robodk.robomath.Comau_2_Pose(xyzrpw)¶
Converts a Comau XYZRPW target to a pose (4x4 matrix), the same representation required by PDL Comau programs.
See also
Mat,TxyzRxyz_2_Pose(),Pose_2_TxyzRxyz(),Pose_2_ABB(),Pose_2_Adept(),Pose_2_Comau(),Pose_2_Fanuc(),Pose_2_KUKA(),Pose_2_Motoman(),Pose_2_Nachi(),Pose_2_Staubli(),Pose_2_UR(),quaternion_2_pose()- Parameters
xyzrpw (
List[float]) –- Return type
- robodk.robomath.Pose_2_Comau(H)¶
Converts a pose to a Comau target, the same representation required by PDL Comau programs.
- Parameters
H (
Mat) – pose
See also
Mat,TxyzRxyz_2_Pose(),Pose_2_TxyzRxyz(),Pose_2_ABB(),Pose_2_Adept(),Pose_2_Comau(),Pose_2_Fanuc(),Pose_2_KUKA(),Pose_2_Motoman(),Pose_2_Nachi(),Pose_2_Staubli(),Pose_2_UR(),quaternion_2_pose()- Return type
List[float]
- robodk.robomath.Pose_2_Nachi(pose)¶
Converts a pose to a Nachi XYZRPW target
- Parameters
pose (
Mat) – pose
See also
Mat,TxyzRxyz_2_Pose(),Pose_2_TxyzRxyz(),Pose_2_ABB(),Pose_2_Adept(),Pose_2_Comau(),Pose_2_Fanuc(),Pose_2_KUKA(),Pose_2_Motoman(),Pose_2_Nachi(),Pose_2_Staubli(),Pose_2_UR(),quaternion_2_pose()- Return type
List[float]
- robodk.robomath.Nachi_2_Pose(xyzwpr)¶
Converts a Nachi XYZRPW target to a pose (4x4 matrix)
See also
Mat,TxyzRxyz_2_Pose(),Pose_2_TxyzRxyz(),Pose_2_ABB(),Pose_2_Adept(),Pose_2_Comau(),Pose_2_Fanuc(),Pose_2_KUKA(),Pose_2_Motoman(),Pose_2_Nachi(),Pose_2_Staubli(),Pose_2_UR(),quaternion_2_pose()- Parameters
xyzwpr (
List[float]) –- Return type
- robodk.robomath.pose_2_quaternion(Ti)¶
Returns the quaternion orientation vector of a pose (4x4 matrix)
- Parameters
Ti (
Mat) – pose
See also
Mat,TxyzRxyz_2_Pose(),Pose_2_TxyzRxyz(),Pose_2_ABB(),Pose_2_Adept(),Pose_2_Comau(),Pose_2_Fanuc(),Pose_2_KUKA(),Pose_2_Motoman(),Pose_2_Nachi(),Pose_2_Staubli(),Pose_2_UR(),quaternion_2_pose()- Return type
List[float]
- robodk.robomath.Pose_Split(pose1, pose2, delta_mm=1.0)¶
Create a sequence of poses that transitions from pose1 to pose2 by steps of delta_mm in mm (the first and last pose are not included in the list)
- robodk.robomath.quaternion_2_pose(qin)¶
Returns the pose orientation matrix (4x4 matrix) given a quaternion orientation vector
- Parameters
qin (list) – quaternions as 4 float values
See also
Mat,TxyzRxyz_2_Pose(),Pose_2_TxyzRxyz(),Pose_2_ABB(),Pose_2_Adept(),Pose_2_Comau(),Pose_2_Fanuc(),Pose_2_KUKA(),Pose_2_Motoman(),Pose_2_Nachi(),Pose_2_Staubli(),Pose_2_UR(),quaternion_2_pose()- Return type
- robodk.robomath.Pose_2_ABB(H)¶
Converts a pose to an ABB target (using quaternion representation).
- Parameters
H (
Mat) – pose
See also
Mat,TxyzRxyz_2_Pose(),Pose_2_TxyzRxyz(),Pose_2_ABB(),Pose_2_Adept(),Pose_2_Comau(),Pose_2_Fanuc(),Pose_2_KUKA(),Pose_2_Motoman(),Pose_2_Nachi(),Pose_2_Staubli(),Pose_2_UR(),quaternion_2_pose()- Return type
List[float]
- robodk.robomath.print_pose_ABB(pose)¶
Displays an ABB RAPID target (the same way it is displayed in IRC5 controllers).
- Parameters
pose (
Mat) – pose
- robodk.robomath.Pose_2_UR(pose)¶
Calculate the p[x,y,z,u,v,w] position with rotation vector for a pose target. This is the same format required by Universal Robot controllers.
See also
Mat,TxyzRxyz_2_Pose(),Pose_2_TxyzRxyz(),Pose_2_ABB(),Pose_2_Adept(),Pose_2_Comau(),Pose_2_Fanuc(),Pose_2_KUKA(),Pose_2_Motoman(),Pose_2_Nachi(),Pose_2_Staubli(),Pose_2_UR(),quaternion_2_pose()- Parameters
pose (
Mat) –- Return type
List[float]
- robodk.robomath.UR_2_Pose(xyzwpr)¶
Calculate the pose target given a p[x,y,z,u,v,w] cartesian target with rotation vector. This is the same format required by Universal Robot controllers.
See also
- Parameters
xyzwpr (
List[float]) –- Return type
- robodk.robomath.dh(rz, tx=None, tz=None, rx=None)¶
Returns the Denavit-Hartenberg 4x4 matrix for a robot link. calling dh(rz,tx,tz,rx) is the same as using rotz(rz)*transl(tx,0,tz)*rotx(rx) calling dh(rz,tx,tz,rx) is the same as calling dh([rz,tx,tz,rx])
- Parameters
rz (
float) –tx (
Optional[float], default:None) –tz (
Optional[float], default:None) –rx (
Optional[float], default:None) –
- Return type
- robodk.robomath.dhm(rx, tx=None, tz=None, rz=None)¶
Returns the Denavit-Hartenberg Modified 4x4 matrix for a robot link (Craig 1986).
calling dhm(rx,tx,tz,rz) is the same as using rotx(rx)*transl(tx,0,tz)*rotz(rz)
calling dhm(rx,tx,tz,rz) is the same as calling dhm([rx,tx,tz,rz])
- Parameters
rx (
float) –tx (
Optional[float], default:None) –tz (
Optional[float], default:None) –rz (
Optional[float], default:None) –
- Return type
- robodk.robomath.joints_2_angles(jin, type)¶
Converts the robot encoders into angles between links depending on the type of the robot.
- Parameters
jin (
List[float]) –type (
int) –
- Return type
List[float]
- robodk.robomath.angles_2_joints(jin, type)¶
Converts the angles between links into the robot motor space depending on the type of the robot.
- Parameters
jin (
List[float]) –type (
int) –
- Return type
List[float]
- robodk.robomath.norm(p)¶
Returns the norm of a 3D vector
- Parameters
p (
List[float]) –- Return type
float
- robodk.robomath.normalize3(a)¶
Returns the unitary vector
- Parameters
a (
List[float]) –- Return type
List[float]
- robodk.robomath.cross(a, b)¶
Returns the cross product of two 3D vectors
- Parameters
a (
List[float]) –b (
List[float]) –
- Return type
List[float]
- robodk.robomath.dot(a, b)¶
Returns the dot product of two 3D vectors
- Parameters
a (
List[float]) –b (
List[float]) –
- Return type
List[float]
- robodk.robomath.angle3(a, b)¶
Returns the angle in radians of two 3D vectors
- Parameters
a (
List[float]) –b (
List[float]) –
- Return type
float
- robodk.robomath.pose_angle(pose)¶
Returns the angle in radians of a 4x4 matrix pose
- Parameters
pose (
Mat) – pose- Return type
float
- robodk.robomath.pose_angle_between(pose1, pose2)¶
Returns the angle in radians between two poses (4x4 matrix pose)
- robodk.robomath.mult3(v, d)¶
Multiplies a 3D vector to a scalar
- Parameters
v (
List[float]) –d (
List[float]) –
- Return type
List[float]
- robodk.robomath.subs3(a, b)¶
Subtracts two 3D vectors c=a-b
- Parameters
a (
List[float]) –b (
List[float]) –
- Return type
List[float]
- robodk.robomath.add3(a, b)¶
Adds two 3D vectors c=a+b
- Parameters
a (
List[float]) –b (
List[float]) –
- Return type
List[float]
- robodk.robomath.distance(a, b)¶
Calculates the distance between two points
- Parameters
a (
List[float]) –b (
List[float]) –
- Return type
float
- robodk.robomath.pose_is_similar(a, b, tolerance=0.1)¶
Check if the pose is similar. Returns True if both poses are less than 0.1 mm or 0.1 deg appart. Optionally provide the tolerance in mm+deg
- Parameters
a (
List[float]) –b (
List[float]) –tolerance (
float, default:0.1) –
- Return type
bool
- robodk.robomath.intersect_line_2_plane(pline, vline, pplane, vplane)¶
Calculates the intersection betweeen a line and a plane
- Parameters
pline (
List[float]) –vline (
List[float]) –pplane (
List[float]) –vplane (
List[float]) –
- Return type
List[float]
- robodk.robomath.proj_pt_2_plane(point, planepoint, planeABC)¶
Projects a point to a plane
- Parameters
point (
List[float]) –planepoint (
List[float]) –planeABC (
List[float]) –
- Return type
List[float]
- robodk.robomath.proj_pt_2_line(point, paxe, vaxe)¶
Projects a point to a line
- Parameters
point (
List[float]) –paxe (
List[float]) –vaxe (
List[float]) –
- Return type
List[float]
- robodk.robomath.fitPlane(points)¶
Returns the equation and normal for a best fit plane to a cloud of points.
Uses singular value decomposition to produce a least squares fit to a plane. Points must have centroid at [0, 0, 0]. Must provide at least 4 points.
- Parameters
points (array-like) – a 3xN array of points. Each column represents one point.
- Returns
pplane: the equation of the best-fit plane, in the form b(1)*X + b(2)*Y +b(3)*Z + b(4) = 0.
- Return type
array_like
- Returns
vplane: the normal vector of the best-fit plane.
- Return type
list of floats
- exception robodk.robomath.MatrixError¶
An exception class for Matrix
- class robodk.robomath.Mat(rows=None, ncols=None)¶
Mat is a matrix object. The main purpose of this object is to represent a pose in the 3D space (position and orientation).
A pose is a 4x4 matrix that represents the position and orientation of one reference frame with respect to another one, in the 3D space.
Poses are commonly used in robotics to place objects, reference frames and targets with respect to each other.
See also
TxyzRxyz_2_Pose(),Pose_2_TxyzRxyz(),Pose_2_ABB(),Pose_2_Adept(),Adept_2_Pose(),Pose_2_Comau(),Pose_2_Fanuc(),Pose_2_KUKA(),KUKA_2_Pose(),Pose_2_Motoman(),Pose_2_Nachi(),Pose_2_Staubli(),Pose_2_UR(),quaternion_2_pose()Example:
from robodk.robolink import * # import the robolink library from robodk.robomath import * # import the robomath library RDK = Robolink() # connect to the RoboDK API robot = RDK.Item('', ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT) # Retrieve a robot available in RoboDK #target = RDK.Item('Target 1') # Retrieve a target (example) pose = robot.Pose() # retrieve the current robot position as a pose (position of the active tool with respect to the active reference frame) # target = target.Pose() # the same can be applied to targets (taught position) # Read the 4x4 pose matrix as [X,Y,Z , A,B,C] Euler representation (mm and deg): same representation as KUKA robots XYZABC = Pose_2_KUKA(pose) print(XYZABC) # Read the 4x4 pose matrix as [X,Y,Z, q1,q2,q3,q4] quaternion representation (position in mm and orientation in quaternion): same representation as ABB robots (RAPID programming) xyzq1234 = Pose_2_ABB(pose) print(xyzq1234) # Read the 4x4 pose matrix as [X,Y,Z, u,v,w] representation (position in mm and orientation vector in radians): same representation as Universal Robots xyzuvw = Pose_2_UR(pose) print(xyzuvw) x,y,z,a,b,c = XYZABC # Use the KUKA representation (for example) and calculate a new pose based on the previous pose XYZABC2 = [x,y,z+50,a,b,c+45] pose2 = KUKA_2_Pose(XYZABC2) # Convert the XYZABC array to a pose (4x4 matrix) robot.MoveJ(pose2) # Make a joint move to the new position # target.setPose(pose2) # We can also update the pose to targets, tools, reference frames, objects, ...
- Parameters
rows (
Union[int,List[List[float]],Mat,None], default:None) –ncols (
Optional[int], default:None) –
- __init__(rows=None, ncols=None)¶
Initializes a new instance of the Mat class.
- Parameters
rows (int or List[List[float]] or Mat) – Number of rows, a 2D list representing the matrix, or another Mat instance to clone.
ncols (int) – Number of columns (required if rows is an integer).
- copy()¶
Creates a deep copy of the matrix.
- Returns
A new instance of Mat that is a copy of this instance.
- Return type
- toNumpy()¶
Return a copy of the Mat matrix as a numpy array
- ColsCount()¶
Return the number of coumns. Same as len().
See also
- Return type
int
- RowsCount()¶
Return the number of rows
See also
- Return type
int
- Cols()¶
Retrieve the matrix as a list of columns (list of list of float).
See also
Example:
>>> transl(10,20,30).Rows() [[1, 0, 0, 10], [0, 1, 0, 20], [0, 0, 1, 30], [0, 0, 0, 1]] >>> transl(10,20,30).Cols() [[1, 0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1, 0], [10, 20, 30, 1]]
- Return type
List[List[float]]
- Rows()¶
Get the matrix as a list of lists
See also
- Return type
List[List[float]]
- Col(n)¶
“Get the Column n from the matrix
- Parameters
n (
int) –- Return type
List[float]
- Row(n)¶
“Get the Row n from the matrix
- Parameters
n (
int) –- Return type
List[float]
- size(dim=None)¶
Returns the size of the matrix.
- Parameters
dim (int) – Optional. If specified, returns the size of the specified dimension (0 for rows, 1 for columns).
- Return type
Union[int,Tuple[int,int]]- Returns
The size of the matrix as a tuple (rows, columns), or the size of the specified dimension.
- catV(mat2)¶
Concatenate with another matrix (vertical concatenation)
- catH(mat2)¶
Concatenate with another matrix (horizontal concatenation)
- isHomogeneous()¶
Checks if the matrix is a homogeneous transformation matrix (4x4).
- Returns
True if the matrix is homogeneous, False otherwise.
- Return type
bool
- RelTool(x, y, z, rx=0, ry=0, rz=0)¶
Calculates a relative target with respect to the tool coordinates. This procedure has exactly the same behavior as ABB’s RelTool instruction. X,Y,Z are in mm, RX,RY,RZ are in degrees.
- Parameters
x (float) – translation along the Tool X axis (mm)
y (float) – translation along the Tool Y axis (mm)
z (float) – translation along the Tool Z axis (mm)
rx (float) – rotation around the Tool X axis (deg) (optional)
ry (float) – rotation around the Tool Y axis (deg) (optional)
rz (float) – rotation around the Tool Z axis (deg) (optional)
See also
- Return type
- Offset(x, y, z, rx=0, ry=0, rz=0)¶
Calculates a relative target with respect to this pose. X,Y,Z are in mm, RX,RY,RZ are in degrees.
- Parameters
x (float) – translation along the Reference X axis (mm)
y (float) – translation along the Reference Y axis (mm)
z (float) – translation along the Reference Z axis (mm)
rx (float) – rotation around the Reference X axis (deg) (optional)
ry (float) – rotation around the Reference Y axis (deg) (optional)
rz (float) – rotation around the Reference Z axis (deg) (optional)
See also
- Return type
- invH()¶
Returns the inverse of the matrix. Assumes the matrix is homogeneous.
- Returns
The inverse of the matrix.
- Return type
- Raises
MatrixError – If the matrix is not homogeneous.
- inv()¶
Returns the inverse of the matrix. Assumes the matrix is homogeneous.
- Returns
The inverse of the matrix.
- Return type
- tolist()¶
Returns the first column of the matrix as a list
- Return type
List[float]
- list()¶
Returns the first column of the matrix as a list
- Return type
List[float]
- Pos()¶
Extracts the translation part of a homogeneous transformation matrix.
- Returns
The translation vector [X, Y, Z].
- Return type
List[float]
- VX()¶
Extracts the X-axis vector from a homogeneous transformation matrix.
- Returns
The X-axis vector [Xx, Xy, Xz].
- Return type
List[float]
- VY()¶
Extracts the Y-axis vector from a homogeneous transformation matrix.
- Returns
The Y-axis vector [Yx, Yy, Yz].
- Return type
List[float]
- VZ()¶
Extracts the Z-axis vector from a homogeneous transformation matrix.
- Returns
The Z-axis vector [Zx, Zy, Zz].
- Return type
List[float]
- Rot33()¶
Returns the sub 3x3 rotation matrix
- setPos(newpos)¶
Sets the translation part of a homogeneous transformation matrix.
- setVX(v_xyz)¶
Sets the X-axis vector of a homogeneous transformation matrix.
- setVY(v_xyz)¶
Sets the Y-axis vector of a homogeneous transformation matrix.
- setVZ(v_xyz)¶
Sets the Z-axis vector of a homogeneous transformation matrix.
- translationPose()¶
Return the translation pose of this matrix. The rotation returned is set to identity (assumes that a 4x4 homogeneous matrix is being used)
- Return type
- rotationPose()¶
Return the rotation pose of this matrix. The position returned is set to [0,0,0] (assumes that a 4x4 homogeneous matrix is being used)
- Return type
2.3. robodialogs.py¶
The robodialogs sub-module is a dialogs toolbox. It contains, open and save file dialogs, message prompts, input dialogs etc.
This module is a dialog toolbox for the RoboDK API and RoboDK Add-ins. This toolbox includes user prompts, open file dialogs, messages, etc.
More information about the RoboDK API for Python here:
- robodk.robodialogs.FILE_TYPES_ALL = ('All Files', '.*')¶
File type filter for all files
- robodk.robodialogs.FILE_TYPES_ROBODK = ('RoboDK Files', '.sld .rdk .robot .tool .rdka .rdkbak .rdkp .py')¶
File type filter for RoboDK files
- robodk.robodialogs.FILE_TYPES_3D_OBJECT = ('3D Object Files', '.sld .stl .iges .igs .step .stp .obj .slp .3ds .dae .blend .wrl .wrml')¶
File type filter for 3D object files
- robodk.robodialogs.FILE_TYPES_TEXT = ('Text Files', '.txt .csv')¶
File type filter for text files
- robodk.robodialogs.FILE_TYPES_IMG = ('Image Files', '.png .jpg')¶
File type filter for image files
- robodk.robodialogs.FILE_TYPES_CAM = ('CAM Files', '.cnc .nc .apt .gcode .ngc .nci .anc .dxf .aptsource .cls .acl .cl .clt .ncl .knc')¶
File type filter for CAD/CAM files
- robodk.robodialogs.FILE_TYPES_ROBOT = ('Robot Files', '.mod .src .ls .jbi .prm .script .urp')¶
File type filter for robot files
- robodk.robodialogs.getOpenFile(path_preference='C:/RoboDK/Library/', strfile='', strtitle='Open File', defaultextension='.*', filetypes=[('All Files', '.*'), ('RoboDK Files', '.sld .rdk .robot .tool .rdka .rdkbak .rdkp .py'), ('3D Object Files', '.sld .stl .iges .igs .step .stp .obj .slp .3ds .dae .blend .wrl .wrml'), ('Text Files', '.txt .csv'), ('Image Files', '.png .jpg'), ('CAM Files', '.cnc .nc .apt .gcode .ngc .nci .anc .dxf .aptsource .cls .acl .cl .clt .ncl .knc'), ('Robot Files', '.mod .src .ls .jbi .prm .script .urp')])¶
Deprecated since version 5.5: Obsolete. Use
getOpenFileName()instead.Pop up a file dialog window to select a file to open. Returns a file object opened in read-only mode. Use returned value.name to retrieve the file path.
- Parameters
path_preference (str) – The initial folder path, optional
strfile (str) – The initial file name (with extension), optional
strtitle (str) – The dialog title, optional
defaultextension (str) – The initial file extension filter, e.g. ‘.*’
filetypes (list of tuples of str) – The available file type filters, e.g. ‘[(‘All Files’, ‘.*’), (‘Text Files’, ‘.txt .csv’)]’
- Returns
An read-only handle to the file, or None if the user cancels
- Return type
TextIOWrapper
See also
- robodk.robodialogs.getSaveFile(path_preference='C:/RoboDK/Library/', strfile='', strtitle='Save As', defaultextension='.*', filetypes=[('All Files', '.*'), ('RoboDK Files', '.sld .rdk .robot .tool .rdka .rdkbak .rdkp .py'), ('3D Object Files', '.sld .stl .iges .igs .step .stp .obj .slp .3ds .dae .blend .wrl .wrml'), ('Text Files', '.txt .csv'), ('Image Files', '.png .jpg'), ('CAM Files', '.cnc .nc .apt .gcode .ngc .nci .anc .dxf .aptsource .cls .acl .cl .clt .ncl .knc'), ('Robot Files', '.mod .src .ls .jbi .prm .script .urp')])¶
Deprecated since version 5.5: Obsolete. Use
getSaveFileName()instead.Pop up a file dialog window to select a file to save. Returns a file object opened in write-only mode. Use returned value.name to retrieve the file path.
- Parameters
path_preference (str) – The initial folder path, optional
strfile (str) – The initial file name (with extension), optional
strtitle (str) – The dialog title, optional
defaultextension (str) – The initial file extension filter, e.g. ‘.*’
filetypes (list of tuples of str) – The available file type filters, e.g. ‘[(‘All Files’, ‘.*’), (‘Text Files’, ‘.txt .csv’)]’
- Returns
An write-only handle to the file, or None if the user cancels
- Return type
TextIOWrapper
See also
- robodk.robodialogs.getOpenFileName(path_preference='C:/RoboDK/Library/', strfile='', strtitle='Open File', defaultextension='.*', filetypes=[('All Files', '.*'), ('RoboDK Files', '.sld .rdk .robot .tool .rdka .rdkbak .rdkp .py'), ('3D Object Files', '.sld .stl .iges .igs .step .stp .obj .slp .3ds .dae .blend .wrl .wrml'), ('Text Files', '.txt .csv'), ('Image Files', '.png .jpg'), ('CAM Files', '.cnc .nc .apt .gcode .ngc .nci .anc .dxf .aptsource .cls .acl .cl .clt .ncl .knc'), ('Robot Files', '.mod .src .ls .jbi .prm .script .urp')])¶
Pop up a file dialog window to select a file to open. Returns the file path as a string.
- Parameters
path_preference (str) – The initial folder path, optional
strfile (str) – The initial file name (with extension), optional
strtitle (str) – The dialog title, optional
defaultextension (str) – The initial file extension filter, e.g. ‘.*’
filetypes (list of tuples of str) – The available file type filters, e.g. ‘[(‘All Files’, ‘.*’), (‘Text Files’, ‘.txt .csv’)]’
- Returns
The file path, or None if the user cancels
- Return type
str
See also
- robodk.robodialogs.getOpenFileNames(path_preference='C:/RoboDK/Library/', strfile='', strtitle='Open File(s)', defaultextension='.*', filetypes=[('All Files', '.*'), ('RoboDK Files', '.sld .rdk .robot .tool .rdka .rdkbak .rdkp .py'), ('3D Object Files', '.sld .stl .iges .igs .step .stp .obj .slp .3ds .dae .blend .wrl .wrml'), ('Text Files', '.txt .csv'), ('Image Files', '.png .jpg'), ('CAM Files', '.cnc .nc .apt .gcode .ngc .nci .anc .dxf .aptsource .cls .acl .cl .clt .ncl .knc'), ('Robot Files', '.mod .src .ls .jbi .prm .script .urp')])¶
Pop up a file dialog window to select one or more file to open. Returns the file path as a list of string.
- Parameters
path_preference (str) – The initial folder path, optional
strfile (str) – The initial file name (with extension), optional
strtitle (str) – The dialog title, optional
defaultextension (str) – The initial file extension filter, e.g. ‘.*’
filetypes (list of tuples of str) – The available file type filters, e.g. ‘[(‘All Files’, ‘.*’), (‘Text Files’, ‘.txt .csv’)]’
- Returns
A list of file path(s), or None if the user cancels
- Return type
list of str
See also
- robodk.robodialogs.getSaveFileName(path_preference='C:/RoboDK/Library/', strfile='', strtitle='Save As', defaultextension='.*', filetypes=[('All Files', '.*'), ('RoboDK Files', '.sld .rdk .robot .tool .rdka .rdkbak .rdkp .py'), ('3D Object Files', '.sld .stl .iges .igs .step .stp .obj .slp .3ds .dae .blend .wrl .wrml'), ('Text Files', '.txt .csv'), ('Image Files', '.png .jpg'), ('CAM Files', '.cnc .nc .apt .gcode .ngc .nci .anc .dxf .aptsource .cls .acl .cl .clt .ncl .knc'), ('Robot Files', '.mod .src .ls .jbi .prm .script .urp')])¶
Pop up a file dialog window to select a file to save. Returns the file path as a string.
- Parameters
path_preference (str) – The initial folder path, optional
strfile (str) – The initial file name (with extension), optional
strtitle (str) – The dialog title, optional
defaultextension (str) – The initial file extension filter, e.g. ‘.*’
filetypes (list of tuples of str) – The available file type filters, e.g. ‘[(‘All Files’, ‘.*’), (‘Text Files’, ‘.txt .csv’)]’
- Returns
The file path, or None if the user cancels
- Return type
str
See also
- robodk.robodialogs.getOpenFolder(path_preference='C:/RoboDK/Library/', strtitle='Open Folder')¶
Pop up a folder dialog window to select a folder to open. Returns the path of the folder as a string.
- Parameters
path_preference (str) – The initial folder path, optional
strtitle (str) – The dialog title, optional
- Returns
The folder path, or None if the user cancels
- Return type
str
See also
- robodk.robodialogs.getSaveFolder(path_preference='C:/RoboDK/Library/', strtitle='Save to Folder', **kwargs)¶
Pop up a folder dialog window to select a folder to save into. Returns the path of the folder as a string.
- Parameters
path_preference (str) – The initial folder path, optional
strtitle (str) – The dialog title, optional
- Returns
The folder path, or None if the user cancels
- Return type
str
See also
- robodk.robodialogs.ShowMessage(msg, title=None)¶
Show a blocking message, with an ‘OK’ button.
- Parameters
msg (str) – The message to be displayed
title (str) – The window title, optional
- Returns
True
- Return type
bool
See also
- robodk.robodialogs.ShowMessageOkCancel(msg, title=None)¶
Show a blocking message, with ‘OK’ and ‘Cancel’ buttons.
- Parameters
msg (str) – The message to be displayed
title (str) – The window title, optional
- Returns
True if the user clicked ‘OK’, false for everything else
- Return type
bool
See also
- robodk.robodialogs.ShowMessageYesNo(msg, title=None)¶
Show a blocking message, with ‘Yes’ and ‘No’ buttons.
- Parameters
msg (str) – The message to be displayed
title (str) – The window title, optional
- Returns
True if the user clicked ‘Yes’, false for everything else
- Return type
bool
- robodk.robodialogs.ShowMessageYesNoCancel(msg, title=None)¶
Show a blocking message, with ‘Yes’, ‘No’ and ‘Cancel’ buttons.
- Parameters
msg (str) – The message to be displayed
title (str) – The window title, optional
- Returns
True for ‘Yes’, false for ‘No’, and None for ‘Cancel’
- Return type
bool
See also
- robodk.robodialogs.mbox(msg, b1='OK', b2='Cancel', frame=True, t=False, entry=None, *args, **kwargs)¶
Deprecated since version 5.5: Obsolete. Use
InputDialog()instead.Create an instance of MessageBox, and get data back from the user.
- Parameters
msg (str) – string to be displayed
b1 (str, tuple) – left button text, or a tuple (<text for button>, <to return on press>)
b2 (str, tuple) – right button text, or a tuple (<text for button>, <to return on press>)
frame (bool) – include a standard outerframe: True or False
t (int, float) – time in seconds (int or float) until the msgbox automatically closes
entry (None, bool, str) – include an entry widget that will provide its contents returned. Provide text to fill the box
See also
- Return type
Any
- robodk.robodialogs.InputDialog(msg, value, title=None, default_button=False, default_value=None, embed=False, actions=None, *args, **kwargs)¶
Show a blocking input dialog, with ‘OK’ and ‘Cancel’ buttons.
- The input field is automatically created for supported types:
Base types: bool, int, float, str
list or tuple of base types
dropdown formatted as [int, [str, str, …]]. e.g. [1, [‘Option #1’, ‘Option #2’]] where 1 means the default selected option is Option #2.
dictionary of supported types, where the key is the field’s label. e.g. {‘This is a bool!’ : True}.
- Parameters
msg (str) – Message to the user (describes what to enter)
value (
Any) – Initial value of the input (see supported types)title (embed) – Window title, optional
default_button (
bool, default:False) – Show a button to reinitialize the input to default, defaults to falsedefault_value (
Optional[Any], default:None) – Default values to restore. If not provided, the original values will be usedtitle – Embed the window inside RoboDK, defaults to false
actions (list of tuples of str, callable) – List of optional action callbacks to add as buttons, formatted as [(str, callable), …]. e.g. [(“Button #1”, action_1), (“Button #2”, action_2)]
- Returns
The user input if the user clicked ‘OK’, None for everything else
- Return type
See supported types
Example:
print(InputDialog('This is as input dialog.\n\nEnter an integer:', 0)) print(InputDialog('This is as input dialog.\n\nEnter a float:', 0.0)) print(InputDialog('This is as input dialog.\n\nEnter text:', '')) print(InputDialog('This is as input dialog.\n\nSet a boolean:', False)) print(InputDialog('This is as input dialog.\n\nSelect from a dropdown:', [0, ['RoboDK is the best', 'I love RoboDK!', "Can't hate it, can I?"]])) print(InputDialog('This is as input dialog.\n\nSet multiple entries:', { 'Enter an integer:': 0, 'Enter a float:': 0.0, 'Set a boolean:': False, 'Enter text:': '', 'Select from a dropdown:': [0, ['RoboDK is the best!', 'I love RoboDK!', "Can't hate it, can I?"]], 'Edit int list:': [0, 0, 0], 'Edit float list:': [0., 0.], }))
- Parameters
embed (
bool, default:False) –
2.4. robofileio.py¶
The robofileio sub-module is a file operation toolbox. It contains file properties, CSV exporter, FTP, etc.
This module provides file operations utilities for the RoboDK API. This toolbox includes FTP transfer functions, CSV import/export, file operations, etc.
More information about the RoboDK API for Python here:
- robodk.robofileio.searchfiles(pattern='C:\\\\RoboDK\\\\Library\\\\*.rdk')¶
List the files in a directory with a given extension
- Parameters
pattern (
str, default:'C:\\\\RoboDK\\\\Library\\\\*.rdk') –- Return type
List[str]
- robodk.robofileio.getFileDir(filepath)¶
Returns the directory of a file path
- Parameters
filepath (
str) –- Return type
str
- robodk.robofileio.getBaseName(filepath)¶
Returns the file name and extension of a file path
- Parameters
filepath (
str) –- Return type
str
- robodk.robofileio.getFileName(filepath)¶
Returns the file name (with no extension) of a file path
- Parameters
filepath (
str) –- Return type
str
- robodk.robofileio.DateModified(filepath, stringformat=False)¶
Returns the time that a file was modified
- Parameters
filepath (
str) –stringformat (
bool, default:False) –
- Return type
Union[float,str]
- robodk.robofileio.DateCreated(filepath, stringformat=False)¶
Returns the time that a file was created
- Parameters
filepath (
str) –stringformat (
bool, default:False) –
- Return type
Union[float,str]
- robodk.robofileio.DirExists(folder)¶
Returns true if the folder exists
- Parameters
folder (
str) –- Return type
bool
- robodk.robofileio.FileExists(file)¶
Returns true if the file exists
- Parameters
file (
str) –- Return type
bool
- robodk.robofileio.FilterName(namefilter, safechar='P', reserved_names=None, max_len=- 1, space_to_underscore=False, invalid_chars=' .-[]/\\\\;,><&*:%=+@!#^|?^')¶
Get a safe program or variable name that can be used for robot programming. Removes invalid characters (such as .-[]/;,><&*:%=+@!#^|?), remove non-english characters, etc.
- Parameters
namefilter (str) – The name to filter
safechar (str, optional) – Safe character to start a name with, in case the first character is a digit. Defaults to ‘P’
reserved_names (list of str, optional) – List of reserved names. A number is appended at the end if it already exists. The new name is added to the list. Defaults to None
max_len (int, optional) – Maximum length of the name (number of characters), -1 means no maximum. Defaults to -1
space_to_underscore (bool, optional) – Replace whitespaces with underscores
invalid_chars (str, optional) – string containing all invalid character to remove. Defaults to r’ .-[]/;,><&*:%=+@!#^|?^’
- Returns
The filtered name
- Return type
str
- robodk.robofileio.FilterNumber(number, fixed_points=6, strip_zeros=True, round_number=True)¶
Get a formatted numerical number (float or int) as a string.
- Parameters
number (float or int) – The number
fixed_points (int, optional) – Maximum number of decimals, defaults to 6
strip_zeros (bool, optional) – Remove trailing zeros, including the decimal point. Defaults to True
round_number (bool, optional) – Round the number instead of cropping it. Defaults to True
- Returns
The formatted number
- Return type
str
- robodk.robofileio.RobotPostFunction(r, data_json, err_msg='Unable to process this function. Please contact us at info@robodk.com.')¶
Post processor callback for custom functions.
- Parameters
r (RobotPost) – The robot post processor instance
data_json (dict) – The function callback name is specified by the ‘fcn’ key. The dictionary is passed as an argument to the callback function.
err_msg (str, optional) – The error message to display to the user, defaults to “Unable to process this function. Please contact us at info@robodk.com.”
- robodk.robofileio.LoadList(strfile, separator=',', codec='utf-8')¶
Load data from a CSV file or a TXT file to a Python list (list of list of numbers)
See also
Example:
csvdata = LoadList(strfile, ',') values = [] for i in range(len(csvdata)): print(csvdata[i]) values.append(csvdata[i]) # We can also save the list back to a CSV file # SaveList(csvdata, strfile, ',')
- Parameters
strfile (
str) –separator (
str, default:',') –codec (
str, default:'utf-8') –
- Return type
List
- robodk.robofileio.SaveList(list_variable, strfile, separator=',')¶
Save a list or a list of lists as a CSV or TXT file.
See also
- Parameters
list_variable (
List) –strfile (
str) –separator (
str, default:',') –
- robodk.robofileio.LoadMat(strfile, separator=',')¶
Load data from a CSV file or a TXT file to a
MatMatrixSee also
- Parameters
strfile (
str) –separator (
str, default:',') –
- Return type
- robodk.robofileio.RemoveFileFTP(ftp, filepath)¶
Delete a file on a remote server.
- Parameters
ftp (ftplib.FTP) –
filepath (
str) –
- robodk.robofileio.RemoveDirFTP(ftp, path)¶
Recursively delete a directory tree on a remote server.
- Parameters
ftp (ftplib.FTP) –
path (
str) –
- robodk.robofileio.UploadDirFTP(localpath, server_ip, remote_path, username, password)¶
Upload a folder to a robot through FTP recursively
- Parameters
localpath (
str) –server_ip (
str) –remote_path (
str) –username (
str) –password (
str) –
- Return type
bool
- robodk.robofileio.UploadFileFTP(file_path_name, server_ip, remote_path, username, password)¶
Upload a file to a robot through FTP
- Parameters
file_path_name (
str) –server_ip (
str) –remote_path (
str) –username (
str) –password (
str) –
- Return type
bool
- robodk.robofileio.UploadFTP(program, robot_ip, remote_path, ftp_user, ftp_pass, pause_sec=2)¶
Upload a program or a list of programs to the robot through FTP provided the connection parameters
- Parameters
program (
Union[str,List[str]]) –robot_ip (
str) –remote_path (
str) –ftp_user (
str) –ftp_pass (
str) –pause_sec (
float, default:2) –
2.5. roboapps.py¶
The roboapps sub-module is a RoboDK Apps toolbox. More info here: https://github.com/RoboDK/Plug-In-Interface/tree/master/PluginAppLoader
Warning
The roboapps sub-module is specific to the Python API.
This module is a toolbox for RoboDK Add-ins and the RoboDK API for Python. This toolbox helps create checkable actions in RoboDK Add-ins, automatic Add-in settings UI, etc.
More information about the RoboDK API for Python here:
- class robodk.roboapps.RunApplication(rdk=None)¶
Class to detect when the terminate signal is emitted to stop an action.
RUN = RunApplication() while RUN.Run(): # your main loop to run until the terminate signal is detected ...
- Parameters
rdk (
Optional[Robolink], default:None) –
- RDK = None¶
- time_last = -1¶
- param_name = None¶
- Run()¶
Run callback.
- Returns
True as long as the App is permitted to run.
- Return type
bool
- robodk.roboapps.Unchecked()¶
Verify if the command “Unchecked” is present. In this case it means the action was just unchecked from RoboDK (applicable to checkable actions only).
Example for a ‘Checkable Action’:
def runmain(): if roboapps.Unchecked(): ActionUnchecked() else: roboapps.SkipKill() # Optional, prevents RoboDK from force-killing the action after 2 seconds ActionChecked()
See also
- Return type
bool
- robodk.roboapps.Checked()¶
Verify if the command “Checked” is present. In this case it means the action was just checked from RoboDK (applicable to checkable actions only).
Example for a ‘Checkable Action’:
def runmain(): if roboapps.Checked(): ActionChecked()
See also
- Return type
bool
- robodk.roboapps.KeepChecked()¶
Keep an action checked even if the execution of the script completed (applicable to checkable actions only).
Example for a ‘Checkable Option’:
def runmain(): if roboapps.Unchecked(): ActionUnchecked() else: roboapps.KeepChecked() # Important, prevents RoboDK from unchecking the action after it has completed ActionChecked()
See also
- robodk.roboapps.SkipKill()¶
For Checkable actions, this setting will tell RoboDK App loader to not kill the process a few seconds after the terminate function is called. This is needed if we want the user input to save the file. For example: The Record action from the Record App.
Example for a ‘Momentary Action’:
def runmain(): if roboapps.Unchecked(): roboapps.Exit() # or sys.exit() else: roboapps.SkipKill() # Optional, prevents RoboDK from force-killing the action after 2 seconds ActionChecked()
See also
- robodk.roboapps.Exit(exit_code=0)¶
Exit/close the action gracefully. If an error code is provided, RoboDK will display a trace to the user.
- Parameters
exit_code (
int, default:0) –
- robodk.roboapps.Str2FloatList(str_values, expected_nvalues=3)¶
Convert a string into a list of floats. It returns None if the array is smaller than the expected size.
- Parameters
str_values (list of str) – The string containing a list of floats
expected_nvalues (int, optional) – Expected number of values in the string list, defaults to 3
- Returns
The list of floats
- Return type
list of float
- robodk.roboapps.Registry(varname, setvalue=None)¶
Read value from the registry or set a value. It will do so at HKEY_CURRENT_USER so no admin rights required.
- Parameters
varname (
str) –setvalue (
Optional[str], default:None) –
- robodk.roboapps.value_to_widget(value, parent)¶
Convert a value to a widget (Tkinter or Qt).
The widget is automatically created for supported types: - Base types: bool, int, float, str - list or tuple of base types - dropdown formatted as [int, [str, str, …]]. e.g. [1, [‘Option #1’, ‘Option #2’]] where 1 means the default selected option is Option #2. - dictionary of supported types, where the key is the field’s label. e.g. {‘This is a bool!’ : True}.
- Parameters
value (see supported types) – The value to convert as a widget, and the initial value of the widget
parent (
Any) – Parent of the widget (Qt/Tkinter)
- Returns
(widget, funcs) the widget, and a list of ‘get’ functions to retrieve the value of the widget
- Return type
tuple of widget (Qt/Tkinter), callable
See also
- robodk.roboapps.widget_to_value(funcs, original_value)¶
Retrieve the value from a widget’s list of get functions. The original value is required to recreate the original format.
- Parameters
funcs (list of callable) – list of get functions, see
value_to_widget()original_value (
Any) – The original value, seevalue_to_widget()
- Return type
Any- Returns
The value
See also
- robodk.roboapps.get_robodk_theme(RDK=None)¶
Get RoboDK’s active theme (Options->General->Theme)
- Parameters
RDK (
Optional[Robolink], default:None) –- Return type
str
- robodk.roboapps.get_qt_app(robodk_icon=True, robodk_theme=True, RDK=None)¶
Get the QApplication instance.
Note: If RoboDK is not running, The RoboDK theme is not applied.
- Parameters
robodk_icon (bool) – Applies the RoboDK logo, defaults to True
robodk_theme (bool) – Applies the current RoboDK theme, defaults to True
RDK (Robolink) – Link to the running RoboDK instance for the theme, defaults to None
- Returns
The QApplication instance
- Return type
PySide2.QtWidgets.QApplication
- robodk.roboapps.set_qt_theme(app, RDK=None)¶
Set a Qt application theme to match RoboDK’s theme.
- Parameters
app (
PySide2.QtWidgets.QApplication) – The QApplicationRDK (
Optional[Robolink], default:None) –
- robodk.roboapps.get_qt_robodk_icon(icon_name, RDK=None)¶
Retrieve a RoboDK icon by name, such as robot, tool and frame icons (requires Qt module).
- Parameters
icon_name (str) – The name of the icon
- Returns
a QImage of the icon if it succeeds, else None
- Return type
PySide2.QtGui.QImage
See also
- Parameters
RDK (
Optional[Robolink], default:None) –
- robodk.roboapps.get_qt_robodk_icons(RDK=None)¶
Retrieve a dictionary of available RoboDK icons, such as robot, tool and frame icons (requires Qt module).
- Returns
a dictionary of QImage of available icons
- Return type
dict of
PySide2.QtGui.QImage
See also
- Parameters
RDK (
Optional[Robolink], default:None) –
- robodk.roboapps.value_to_qt_widget(value, parent=None)¶
Convert a value to a widget. For instance, a float into a QDoubleSpinBox, a bool into a QCheckBox.
The widget is automatically created for supported types: - bool, int, float, str (base types) - list or tuple of base types - dropdown formatted as [int, [str, str, …]] i.e. [1, [‘Option #1’, ‘Option #2’]] where 1 means the default selected option is Option #2. - dictionary of supported values, formatted as {label:value}
- Return type
Tuple[QWidget,List]- Returns
(widget, funcs) the widget, and a list of get functions to retrieve the value of the widget
- Parameters
value (
Any) –parent (
Optional[QWidget], default:None) –
- robodk.roboapps.get_tk_app(robodk_icon=True, robodk_theme=True, RDK=None)¶
Get the QApplication instance.
- Parameters
robodk_icon (bool) – Applies the RoboDK logo, defaults to True
robodk_theme (bool) – Applies the current RoboDK theme, defaults to True
RDK (Robolink) – Link to the running RoboDK instance for the theme, defaults to None
- Returns
The QApplication instance
- Return type
PySide2.QtWidgets.QApplication
- robodk.roboapps.value_to_tk_widget(value, frame)¶
Convert a value to a widget. For instance, a float into a Spinbox, a bool into a Checkbutton.
The widget is automatically created for supported types: - bool, int, float, str (base types) - list or tuple of base types - dropdown formatted as [int, [str, str, …]] i.e. [1, [‘Option #1’, ‘Option #2’]] where 1 means the default selected option is Option #2. - dictionary of supported values, formatted as {label:value}
- Return type
Widget- Returns
(widget, funcs) the widget, and a list of get functions to retrieve the value of the widget
- Parameters
value (
Any) –frame (
Widget) –
- class robodk.roboapps.AppSettings(settings_param='App-Settings')¶
Generic application settings class to save and load settings to a RoboDK station with a built-in UI.
- Parameters
settings_param (str) – RoboDK parameter used to store this app settings. It should be unique if you have more than one App setting.
Example:
class Settings(AppSettings): def __init__(self, settings_param='My-App-Settings'): super().__init__(settings_param=settings_param) # List the variable names you would like to save and their default values. # Variables that start with underscore (_) will not be saved. self.BOOL = True self.INT = 123456 self.FLOAT = 0.123456789 self.STRING = 'Text' self.INT_LIST = [1, 2, 3] self.FLOAT_LIST = [1.0, 2.0, 3.0] self.STRING_LIST = ['First line', 'Second line', 'Third line'] self.MIXED_LIST = [False, 1, '2'] self.INT_TUPLE = (1, 2, 3) self.DROPDOWN = [1, ['First line', 'Second line', 'Third line']] self.DICT = {'This is a string': 'Text', 'This is a float': 0.0} # Variable names when displayed on the user interface (detailed descriptions). # Create this dictionary in the same order that you want to display it. # If AppSettings._FIELDS_UI is not provided, all variables of this class will be used and displayed with their attribute name. # Fields within dollar signs (i.e. $abc$) are used as section headers. from collections import OrderedDict self._FIELDS_UI = OrderedDict() self._FIELDS_UI['SECTION_1'] = '$This is a section$' self._FIELDS_UI['BOOL'] = 'This is a bool' self._FIELDS_UI['INT'] = 'This is an int' self._FIELDS_UI['FLOAT'] = 'This is a float' self._FIELDS_UI['STRING'] = 'This is a string' self._FIELDS_UI['INT_LIST'] = 'This is an int list' self._FIELDS_UI['FLOAT_LIST'] = 'This is a float list' self._FIELDS_UI['STRING_LIST'] = 'This is a string list' self._FIELDS_UI['MIXED_LIST'] = 'This is a mixed list' self._FIELDS_UI['INT_TUPLE'] = 'This is an int tuple' self._FIELDS_UI['SECTION_2'] = '$This is another section$' self._FIELDS_UI['DROPDOWN'] = 'This is a dropdown' self._FIELDS_UI['DICT'] = 'This is a dictionary' S = Settings() S.Load() # Load previously saved settings from RoboDK S.ShowUI('Settings for my App') print(S.BOOL)
- __init__(settings_param='App-Settings')¶
- Parameters
settings_param (
str, default:'App-Settings') –
- CopyFrom(other)¶
Copy settings from another AppSettings instance.
- Parameters
other (AppSettings) – The other AppSettings instance
- SetDefaults()¶
Set defaults settings. Attributes in ‘AppSettings._ATTRIBS_SKIP_DEFAULT’, if defined, are ignored.
- GetDefaults()¶
Get the default settings.
- Return type
Dict
- getAttribs()¶
Get the list of all attributes (settings). Attributes that starts with ‘_’ are ignored.
- Returns
all attributes
- Return type
list of str
- get(attrib, default_value=None)¶
Get attribute value by key, otherwise it returns None
- Parameters
attrib (
str) –default_value (
Optional[Any], default:None) –
- Return type
Any
- Save(rdk=None, autorecover=False)¶
Save the class attributes as a RoboDK binary parameter in the specified station. If the station is not provided, it uses the active station.
- Parameters
rdk (Robolink, optional) – Station to save to, defaults to None
autorecover (bool, optional) – Create a backup in the station, defaults to False
- Load(rdk=None)¶
Load the class attributes from a RoboDK binary parameter. If the station is not provided, it uses the active station.
- Parameters
rdk (Robolink, optional) – Station to load from, defaults to None
- Return type
bool- Returns
True if it succeeds, else false.
- Erase(rdk=None)¶
Completely erase the stored settings and its backup from RoboDK.
- Parameters
rdk (
Optional[Robolink], default:None) –
- ShowUI(windowtitle=None, embed=False, show_default_button=True, actions=None, *args, **kwargs)¶
Show the Apps Settings in a GUI.
- Parameters
windowtitle (str) – Window title, defaults to the Settings name
embed (bool) – Embed the settings window in RoboDK, defaults to False
show_default_button (bool) – Set to true to add a Default button to reset the fields, defaults to True
actions (list of tuples of str, callable) – List of optional action callbacks to add as buttons, formatted as [(str, callable), …]. e.g. [(“Button #1”, action_1), (“Button #2”, action_2)]
- Returns
False if the user cancelled, else True.
- robodk.roboapps.ShowExample()¶
2.6. robolinkutils.py¶
The robolinkutils sub-module provides utility functions using the Robolink module.
Warning
The robolinkutils sub-module is specific to the Python API.
This module defines general utility functions for Robolink and Items. These functions facilitate the usage of some RoboDK API functions and create RoboDK add-ins.
More information about the RoboDK API for Python and RoboDK Add-ins here:
- robodk.robolinkutils.getLinks(item, type_linked=2)¶
Get all the items of a specific type for which getLink() returns the specified item.
- robodk.robolinkutils.getAncestors(item, parent_types=None)¶
Get the list of parents of an Item up to the Station, with type filtering (i.e. [ITEM_TYPE_FRAME, ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT, ..]). By default, it will return all parents of an Item with no regard to their type, ordered from the Item’s parent to the Station.
- robodk.robolinkutils.getLowestCommonAncestor(item1, item2)¶
Finds the lowest common ancestor (LCA) between two Items in the Station’s tree.
- robodk.robolinkutils.getAncestorPose(item_child, item_parent)¶
Gets the pose between two Items that have a hierarchical relationship in the Station’s tree. There can be N Items between the two. This function will throw an error for synchronized axis.
- robodk.robolinkutils.getPoseWrt(item1, item2)¶
Gets the pose of an Item (item1) with respect to an another Item (item2).
child.PoseWrt(child.Parent()) # will return a forward pose from the parent to the child child.Parent().PoseWrt(child) # will return an inverse pose from the child to the parent tool.PoseWrt(tool.Parent()) # will return the PoseTool() of the tool tool.PoseWrt(station) # will return the absolute pose of the tool
- Parameters
item1 (
robolink.Item) – The source Itemitem2 (
robolink.Item) – The second Item
- Returns
The pose from the source Item to the second Item
- Return type
robomath.Mat
- robodk.robolinkutils.setPoseAbsIK(item, pose_abs)¶
Set the pose of the item with respect to the absolute reference frame, accounting for inverse kinematics. For instance, you can set the absolute pose of a ITEM_TYPE_TOOL directly without accounting for the robot kinematics. This function will throw an error for synchronized axis.
tool_item.setPoseAbs(eye(4)) # will SET the tool center point with respect to the station at [0,0,0,0,0,0] setPoseAbsIK(tool_item, eye(4)) # will MOVE the robot so that the tool center point with regard to the station is [0,0,0,0,0,0]
- Parameters
item (
robolink.Item) – The source Itempose_abs (
robomath.Mat) – pose of the item with respect to the station reference
- robodk.robolinkutils.SolveIK_Conf(robot, pose, toolpose=None, framepose=None, joint_config=[0, 1, 0])¶
Calculates the inverse kinematics for the specified robot and pose. The function returns only the preferred solutions from the joint configuration as a 2D matrix. Returns a list of joints as a 2D matrix [N x M], where N is the number of degrees of freedom (robot joints) and M is the number of solutions. For some 6-axis robots, SolveIK returns 2 additional values that can be ignored.
- Parameters
robot (
robolink.Item) – The robot Itempose (
Mat) – pose of the robot flange with respect to the robot base frametoolpose (
Mat) – Tool pose with respect to the robot flange (TCP)framepose (
Mat) – Reference pose (reference frame with respect to the robot base)joint_config (list of int) – desired joint configuration, as [Front(0)/Rear(1)/Any(-1), Elbow Up(0)/Elbow Down(1)/Any(-1), Non-flip(0)/Flip(1)/Any(-1)]
- Return type
List[Mat]