Introduction
The ISO standard “ISO9283: Manipulating industrial robots - Performance criteria and related test methods” describes tests to evaluate the performance of industrial robots. Among other things, it provides procedures to properly measure robot position accuracy, repeatability and path accuracy.
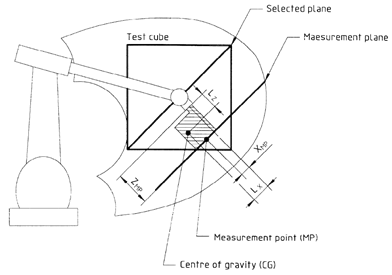
According to the ISO9283 norm, all the testing should be performed inside the so-called ISO test cube. The ISO test cube is supposed to be the largest cube that can fit inside the robot workspace. Furthermore, position accuracy and repeatability should be measured at five different configurations 30 times. It is well known that 5 configurations are not enough to provide an appropriate measurement of accuracy for modern robots.
Most robot manufacturers only provide robot positional accuracy if the robot has been calibrated, furthermore, they use at least 100 different configurations to provide appropriate position accuracy statistics. Industrial robots are highly repeatable but not accurate; therefore, the accuracy of an industrial robot can be improved through calibration.
Typical robot workspace in the 80s Typical robot workspace of a modern robot
However, the ISO9283 norm is often used for repeatability and path accuracy tests even if the robot has not been calibrated.
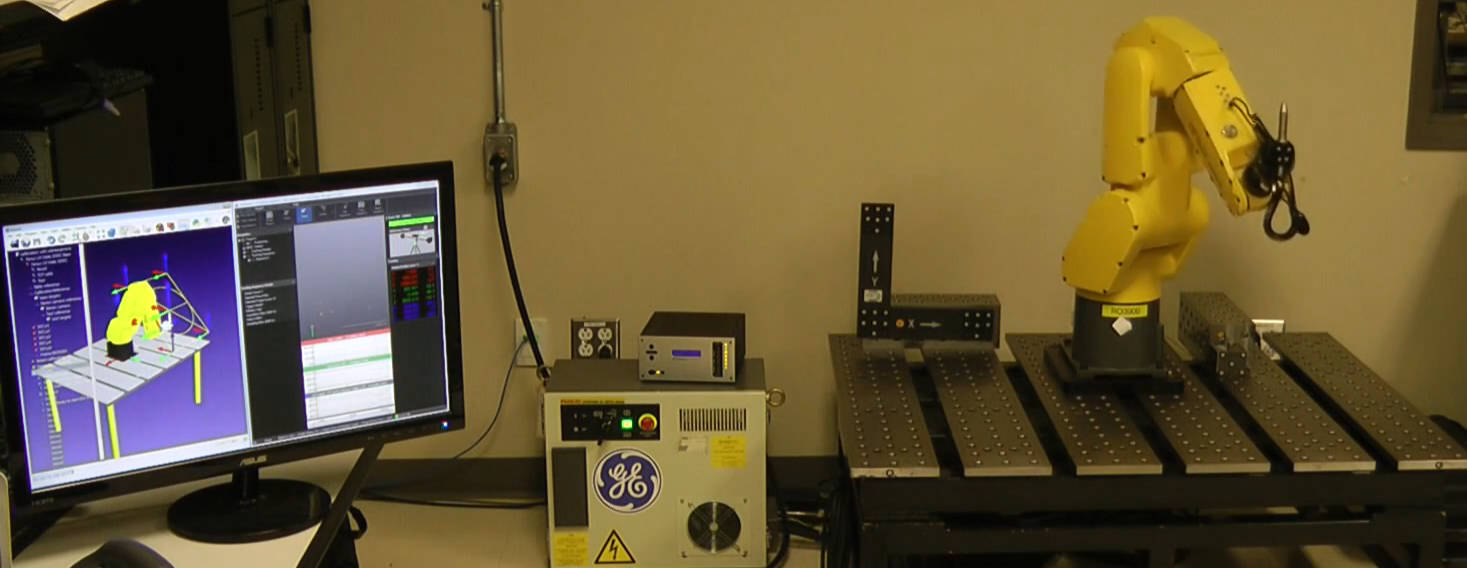

It is recommended to watch the following video showing path accuracy tests with RoboDK: https://youtu.be/yMQjqAQY1iE.
RoboDK can also be used to calibrate the robots as well as to test their performance before and after calibration. Finally, RoboDK can also be used to test the accuracy of the robot before and after calibration through ballbar testing.