The Item class represents an item in RoboDK station. An item can be a robot, a frame, a tool, an object, a target, ... any item visible in the station tree. An item can also be seen as a node where other items can be attached to (child items). Every item has one parent item/node and can have one or more child items/nodes. More...
#include <robodk_api.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| Item (RoboDK *rdk=nullptr, quint64 ptr=0, qint32 type=-1) | |
| Item (const Item &other) | |
| Item & | operator= (const Item &x)=default |
| QString | ToString () const |
| RoboDK * | RDK () |
| Returns the RoboDK link Robolink(). | |
| void | NewLink () |
| Create a new communication link for RoboDK. Use this for robots if you use a multithread application running multiple robots at the same time. | |
| int | Type () const |
| Item type (object, robot, tool, reference, robot machining project, ...) | |
| void | Save (const QString &filename) |
| Save a station, a robot, a tool or an object to a file. | |
| void | Delete () |
| Deletes an item and its childs from the station. | |
| bool | Valid (bool check_pointer=false) const |
| Check if an item is valid (not null and available in the open station) | |
| void | setParent (Item parent) |
| Attaches the item to a new parent while maintaining the relative position with its parent. The absolute position is changed. | |
| void | setParentStatic (Item parent) |
| Attaches the item to another parent while maintaining the current absolute position in the station. The relationship between this item and its parent is changed to maintain the abosolute position. | |
| Item | AttachClosest () |
| Attach the closest object to the tool. Returns the item that was attached. | |
| Item | DetachClosest (Item parent) |
| Detach the closest object attached to the tool (see also setParentStatic). | |
| void | DetachAll (Item parent) |
| Detach any object attached to a tool. | |
| Item | Parent () const |
| Return the parent item of this item. | |
| QList< Item > | Childs () const |
| Returns a list of the item childs that are attached to the provided item. | |
| bool | Visible () const |
| Returns 1 if the item is visible, otherwise, returns 0. | |
| void | setVisible (bool visible, int visible_frame=-1) |
| Sets the item visiblity status. | |
| QString | Name () const |
| Returns the name of an item. The name of the item is always displayed in the RoboDK station tree. | |
| void | setName (const QString &name) |
| Set the name of a RoboDK item. | |
| void | setPose (const Mat pose) |
| Sets the local position (pose) of an object, target or reference frame. For example, the position of an object/frame/target with respect to its parent. If a robot is provided, it will set the pose of the end efector. | |
| Mat | Pose () const |
| Returns the local position (pose) of an object, target or reference frame. For example, the position of an object/frame/target with respect to its parent. If a robot is provided, it will get the pose of the end efector. | |
| void | setGeometryPose (const Mat pose) |
| Sets the position (pose) the object geometry with respect to its own reference frame. This procedure works for tools and objects. | |
| Mat | GeometryPose () |
| Returns the position (pose) the object geometry with respect to its own reference frame. This procedure works for tools and objects. | |
| Mat | PoseTool () |
| Returns the tool pose of an item. If a robot is provided it will get the tool pose of the active tool held by the robot. | |
| Mat | PoseFrame () |
| Returns the reference frame pose of an item. If a robot is provided it will get the tool pose of the active reference frame used by the robot. | |
| void | setPoseFrame (const Mat frame_pose) |
| Sets the reference frame of a robot(user frame). The frame can be either an item or a pose. If "frame" is an item, it links the robot to the frame item. If frame is a pose, it updates the linked pose of the robot frame (with respect to the robot reference frame). | |
| void | setPoseFrame (const Item frame_item) |
| Sets the tool of a robot or a tool object (Tool Center Point, or TCP). The tool pose can be either an item or a 4x4 Matrix. If the item is a tool, it links the robot to the tool item.If tool is a pose, it updates the current robot TCP. | |
| void | setPoseTool (const Mat tool_pose) |
| Sets the tool of a robot or a tool object (Tool Center Point, or TCP). The tool pose can be either an item or a 4x4 Matrix. If the item is a tool, it links the robot to the tool item.If tool is a pose, it updates the current robot TCP. | |
| void | setPoseTool (const Item tool_item) |
| Sets the tool of a robot or a tool object (Tool Center Point, or TCP). The tool pose can be either an item or a 4x4 Matrix. If the item is a tool, it links the robot to the tool item.If tool is a pose, it updates the current robot TCP. | |
| void | setPoseAbs (const Mat pose) |
| Sets the global position (pose) of an item. For example, the position of an object/frame/target with respect to the station origin. | |
| Mat | PoseAbs () |
| Returns the global position (pose) of an item. For example, the position of an object/frame/target with respect to the station origin. | |
| void | setColor (double colorRGBA[4]) |
| Changes the color of a robot/object/tool. A color must must in the format COLOR=[R,G,B,(A=1)] where all values range from 0 to 1. Alpha (A) defaults to 1 (100% opaque). Set A to 0 to make an object transparent. | |
| void | Scale (double scale) |
| Apply a scale to an object to make it bigger or smaller. The scale can be uniform (if scale is a float value) or per axis (if scale is a vector). | |
| void | Scale (double scale_xyz[3]) |
| Apply a per-axis scale to an object to make it bigger or smaller. The scale can be uniform (if scale is a float value) or per axis (if scale is a vector). | |
| GetPointsResult | GetPoints (int featureType=RoboDK::FEATURE_SURFACE, int featureId=0) |
| Retrieves the point under the mouse cursor, a curve or the 3D points of an object. The points are provided in [XYZijk] format in relative coordinates. The XYZ are the local point coordinate and ijk is the normal of the surface. | |
| bool | SelectedFeature (int &featureType, int &featureId) |
| Retrieve the currently selected feature for this object. | |
| Item | setMachiningParameters (QString ncfile="", Item part_obj=nullptr, QString options="") |
| Update the robot milling path input and parameters. Parameter input can be an NC file (G-code or APT file) or an object item in RoboDK. A curve or a point follow project will be automatically set up for a robot manufacturing project. Tip: Use getLink() and setLink() to get/set the robot tool, reference frame, robot and program linked to the project. Tip: Use setPose() and setJoints() to update the path to tool orientation or the preferred start joints. Tip: Use setPoseTool() and setPoseFrame() to link to the corresponding tool and reference frames. | |
| void | setAsCartesianTarget () |
| Sets a target as a cartesian target. A cartesian target moves to cartesian coordinates. | |
| void | setAsJointTarget () |
| Sets a target as a joint target. A joint target moves to a joints position without regarding the cartesian coordinates. | |
| bool | isJointTarget () const |
| Returns True if a target is a joint target (green icon). Otherwise, the target is a Cartesian target (red icon). | |
| tJoints | Joints () const |
| Returns the current joints of a robot or the joints of a target. If the item is a cartesian target, it returns the preferred joints (configuration) to go to that cartesian position. | |
| tJoints | JointsHome () const |
| Returns the home joints of a robot. These joints can be manually set in the robot "Parameters" menu, then select "Set home position". | |
| void | setJointsHome (const tJoints &jnts) |
| Set robot joints for the home position. | |
| Item | ObjectLink (int link_id=0) |
| Returns an item pointer to the geometry of a robot link. This is useful to show/hide certain robot links or alter their geometry. | |
| Item | getLink (int type_linked=RoboDK::ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT) |
| Returns an item linked to a robot, object, tool, program or robot machining project. This is useful to retrieve the relationship between programs, robots, tools and other specific projects. | |
| void | setJoints (const tJoints &jnts) |
| Set robot joints or the joints of a target. | |
| void | JointLimits (tJoints *lower_limits, tJoints *upper_limits) |
| Retrieve the joint limits of a robot. | |
| void | setJointLimits (const tJoints &lower_limits, const tJoints &upper_limits) |
| Set the joint limits of a robot. | |
| void | setRobot (const Item &robot) |
| Sets the robot of a program or a target. You must set the robot linked to a program or a target every time you copy paste these objects. If the robot is not provided, the first available robot will be chosen automatically. | |
| Item | AddTool (const Mat &tool_pose, const QString &tool_name="New TCP") |
| Adds an empty tool to the robot provided the tool pose (4x4 Matrix) and the tool name. | |
| Mat | SolveFK (const tJoints &joints, const Mat *tool=nullptr, const Mat *ref=nullptr) |
| Computes the forward kinematics of the robot for the provided joints. The tool and the reference frame are not taken into account. | |
| void | JointsConfig (const tJoints &joints, tConfig config) |
| Returns the robot configuration state for a set of robot joints. | |
| tJoints | SolveIK (const Mat &pose, const Mat *tool=nullptr, const Mat *ref=nullptr) |
| Computes the inverse kinematics for the specified robot and pose. The joints returned are the closest to the current robot configuration (see SolveIK_All()) | |
| tJoints | SolveIK (const Mat pose, tJoints joints_approx, const Mat *tool=nullptr, const Mat *ref=nullptr) |
| Computes the inverse kinematics for the specified robot and pose. The joints returned are the closest to the current robot configuration (see SolveIK_All()) | |
| tMatrix2D * | SolveIK_All_Mat2D (const Mat &pose, const Mat *tool=nullptr, const Mat *ref=nullptr) |
| Computes the inverse kinematics for the specified robot and pose. The function returns all available joint solutions as a 2D matrix. | |
| QList< tJoints > | SolveIK_All (const Mat &pose, const Mat *tool=nullptr, const Mat *ref=nullptr) |
| Computes the inverse kinematics for the specified robot and pose. The function returns all available joint solutions as a 2D matrix. | |
| bool | Connect (const QString &robot_ip="") |
| Connect to a real robot using the corresponding robot driver. | |
| bool | Disconnect () |
| Disconnect from a real robot (when the robot driver is used) | |
| void | MoveJ (const Item &itemtarget, bool blocking=true) |
| Moves a robot to a specific target ("Move Joint" mode). By default, this function blocks until the robot finishes its movements. Given a target item, MoveJ can also be applied to programs and a new movement instruction will be added. | |
| void | MoveJ (const tJoints &joints, bool blocking=true) |
| Moves a robot to a specific target ("Move Joint" mode). By default, this function blocks until the robot finishes its movements. | |
| void | MoveJ (const Mat &target, bool blocking=true) |
| Moves a robot to a specific target ("Move Joint" mode). By default, this function blocks until the robot finishes its movements. | |
| void | MoveL (const Item &itemtarget, bool blocking=true) |
| Moves a robot to a specific target ("Move Linear" mode). By default, this function blocks until the robot finishes its movements. Given a target item, MoveL can also be applied to programs and a new movement instruction will be added. | |
| void | MoveL (const tJoints &joints, bool blocking=true) |
| Moves a robot to a specific target ("Move Linear" mode). By default, this function blocks until the robot finishes its movements. | |
| void | MoveL (const Mat &target, bool blocking=true) |
| Moves a robot to a specific target ("Move Linear" mode). By default, this function blocks until the robot finishes its movements. | |
| void | MoveC (const Item &itemtarget1, const Item &itemtarget2, bool blocking=true) |
| Moves a robot to a specific target ("Move Circular" mode). By default, this function blocks until the robot finishes its movements. | |
| void | MoveC (const tJoints &joints1, const tJoints &joints2, bool blocking=true) |
| Moves a robot to a specific target ("Move Circular" mode). By default, this function blocks until the robot finishes its movements. | |
| void | MoveC (const Mat &target1, const Mat &target2, bool blocking=true) |
| Moves a robot to a specific target ("Move Circular" mode). By default, this function blocks until the robot finishes its movements. | |
| int | MoveJ_Test (const tJoints &j1, const tJoints &j2, double minstep_deg=-1) |
| Checks if a joint movement is possible and, optionally, free of collisions. | |
| int | MoveL_Test (const tJoints &joints1, const Mat &pose2, double minstep_mm=-1) |
| Checks if a linear movement is free of issues and, optionally, collisions. | |
| void | setSpeed (double speed_linear, double accel_linear=-1, double speed_joints=-1, double accel_joints=-1) |
| Sets the speed and/or the acceleration of a robot. | |
| void | setRounding (double zonedata) |
| Sets the robot movement smoothing accuracy (also known as zone data value). | |
| void | ShowSequence (tMatrix2D *sequence) |
| Displays a sequence of joints. | |
| bool | Busy () |
| Checks if a robot or program is currently running (busy or moving) | |
| void | Stop () |
| Stops a program or a robot. | |
| void | WaitMove (double timeout_sec=300) const |
| Waits (blocks) until the robot finishes its movement. | |
| void | setAccuracyActive (int accurate=1) |
| Sets the accuracy of the robot active or inactive. A robot must have been calibrated to properly use this option. | |
| bool | MakeProgram (const QString &filename) |
| Saves a program to a file. | |
| void | setRunType (int program_run_type) |
| Sets if the program will be run in simulation mode or on the real robot. Use: "PROGRAM_RUN_ON_SIMULATOR" to set the program to run on the simulator only or "PROGRAM_RUN_ON_ROBOT" to force the program to run on the robot. | |
| int | RunProgram () |
| Runs a program. It returns the number of instructions that can be executed successfully (a quick program check is performed before the program starts) This is a non-blocking call. Use IsBusy() to check if the program execution finished. Notes: if setRunMode(RUNMODE_SIMULATE) is used -> the program will be simulated (default run mode) if setRunMode(RUNMODE_RUN_ROBOT) is used -> the program will run on the robot (default when RUNMODE_RUN_ROBOT is used) if setRunMode(RUNMODE_RUN_ROBOT) is used together with program.setRunType(PROGRAM_RUN_ON_ROBOT) -> the program will run sequentially on the robot the same way as if we right clicked the program and selected "Run on robot" in the RoboDK GUI. | |
| int | RunCode (const QString ¶meters) |
| Runs a program. It returns the number of instructions that can be executed successfully (a quick program check is performed before the program starts) Program parameters can be provided for Python calls. This is a non-blocking call.Use IsBusy() to check if the program execution finished. Notes: if setRunMode(RUNMODE_SIMULATE) is used -> the program will be simulated (default run mode) if setRunMode(RUNMODE_RUN_ROBOT) is used ->the program will run on the robot(default when RUNMODE_RUN_ROBOT is used) if setRunMode(RUNMODE_RUN_ROBOT) is used together with program.setRunType(PROGRAM_RUN_ON_ROBOT) -> the program will run sequentially on the robot the same way as if we right clicked the program and selected "Run on robot" in the RoboDK GUI. | |
| int | RunInstruction (const QString &code, int run_type=RoboDK::INSTRUCTION_CALL_PROGRAM) |
| Adds a program call, code, message or comment inside a program. | |
| void | Pause (double time_ms=-1) |
| Generates a pause instruction for a robot or a program when generating code. Set it to -1 (default) if you want the robot to stop and let the user resume the program anytime. | |
| void | setDO (const QString &io_var, const QString &io_value) |
| Sets a variable (output) to a given value. This can also be used to set any variables to a desired value. | |
| void | setAO (const QString &io_var, const QString &io_value) |
| Set an analog Output. | |
| QString | getDI (const QString &io_var) |
| Get a Digital Input (DI). This function is only useful when connected to a real robot using the robot driver. It returns a string related to the state of the Digital Input (1=True, 0=False). This function returns an empty string if the script is not executed on the robot. | |
| QString | getAI (const QString &io_var) |
| Get an Analog Input (AI). This function is only useful when connected to a real robot using the robot driver. It returns a string related to the state of the Digital Input (0-1 or other range depending on the robot driver). This function returns an empty string if the script is not executed on the robot. | |
| void | waitDI (const QString &io_var, const QString &io_value, double timeout_ms=-1) |
| Waits for an input io_id to attain a given value io_value. Optionally, a timeout can be provided. | |
| void | customInstruction (const QString &name, const QString &path_run, const QString &path_icon="", bool blocking=true, const QString &cmd_run_on_robot="") |
| Add a custom instruction. This instruction will execute a Python file or an executable file. | |
| void | ShowInstructions (bool visible=true) |
| Show or hide instruction items of a program in the RoboDK tree. | |
| void | ShowTargets (bool visible=true) |
| Show or hide targets of a program in the RoboDK tree. | |
| int | InstructionCount () |
| Returns the number of instructions of a program. | |
| void | Instruction (int ins_id, QString &name, int &instype, int &movetype, bool &isjointtarget, Mat &target, tJoints &joints) |
| Returns the program instruction at position id. | |
| void | setInstruction (int ins_id, const QString &name, int instype, int movetype, bool isjointtarget, const Mat &target, const tJoints &joints) |
| Sets the program instruction at position id. | |
| int | InstructionList (tMatrix2D *instructions) |
| Returns the list of program instructions as an MxN matrix, where N is the number of instructions and M equals to 1 plus the number of robot axes. | |
| double | Update (int collision_check=RoboDK::COLLISION_OFF, int timeout_sec=3600, double *out_nins_time_dist=nullptr, double mm_step=-1, double deg_step=-1) |
| Updates a program and returns the estimated time and the number of valid instructions. An update can also be applied to a robot machining project. The update is performed on the generated program. | |
| int | InstructionListJoints (QString &error_msg, tMatrix2D **joint_list, double mm_step=10.0, double deg_step=5.0, const QString &save_to_file="", bool collision_check=false, int flags=0, double time_step_s=0.1) |
| Returns a list of joints an MxN matrix, where M is the number of robot axes plus 4 columns. Linear moves are rounded according to the smoothing parameter set inside the program. | |
| QString | setParam (const QString ¶m, const QString &value) |
| Set a specific item parameter. Select Tools-Run Script-Show Commands to see all available commands for items and the station. Note: For parameters (commands) that require a JSON string value you can also provide a dict. | |
| void | setParam (const QString ¶m, const QByteArray &value) |
| Set a specific binary item parameter. | |
| QByteArray | getParam (const QString ¶m) |
| Get a specific binary item parameter. | |
| bool | Finish () |
| Disconnect from the RoboDK API. This flushes any pending program generation. | |
| quint64 | GetID () |
| Get the item pointer. | |
Private Attributes | |
| RoboDK * | _RDK |
| Pointer to RoboDK link object. | |
| quint64 | _PTR |
| Pointer to the item inside RoboDK. | |
| qint32 | _TYPE |
| Item type. | |
Friends | |
| class | RoboDK_API::RoboDK |
The Item class represents an item in RoboDK station. An item can be a robot, a frame, a tool, an object, a target, ... any item visible in the station tree. An item can also be seen as a node where other items can be attached to (child items). Every item has one parent item/node and can have one or more child items/nodes.
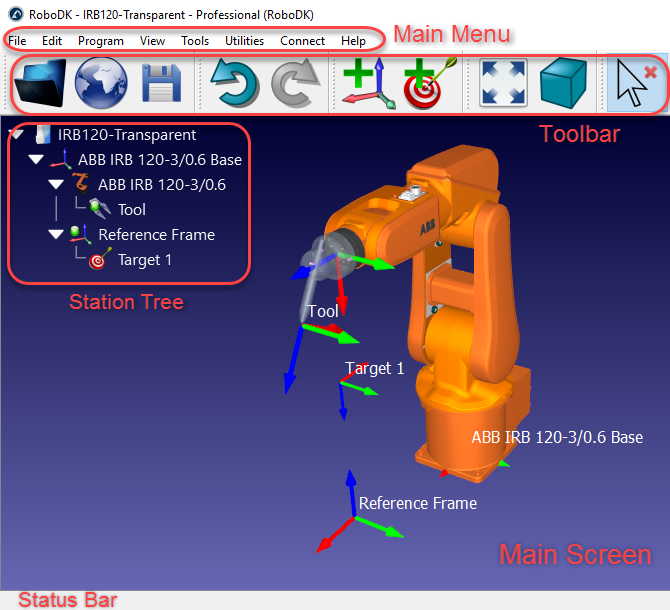
Definition at line 1777 of file robodk_api.h.
Definition at line 560 of file robodk_api.cpp.
Definition at line 565 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| ~Item | ( | ) |
Definition at line 570 of file robodk_api.cpp.
Adds an empty tool to the robot provided the tool pose (4x4 Matrix) and the tool name.
| tool_pose | TCP as a 4x4 Matrix (pose of the tool frame) |
| tool_name | New tool name |
| tool_pose | pose -> TCP as a 4x4 Matrix (pose of the tool frame) |
| tool_name | New tool name |
Definition at line 1257 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| Item AttachClosest | ( | ) |
Attach the closest object to the tool. Returns the item that was attached.
Definition at line 672 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| bool Busy | ( | ) |
Checks if a robot or program is currently running (busy or moving)
Definition at line 1618 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| QList< Item > Childs | ( | ) | const |
Returns a list of the item childs that are attached to the provided item.
add more methods
Definition at line 726 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| bool Connect | ( | const QString & | robot_ip = "" | ) |
Connect to a real robot using the corresponding robot driver.
Connect to a real robot using the robot driver.
| robot_ip | IP of the robot to connect. Leave empty to use the one defined in RoboDK |
| robot_ip | IP of the robot to connect. Leave empty to use the one defined in RoboDK |
Definition at line 1401 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void customInstruction | ( | const QString & | name, |
| const QString & | path_run, | ||
| const QString & | path_icon = "", | ||
| bool | blocking = true, | ||
| const QString & | cmd_run_on_robot = "" ) |
Add a custom instruction. This instruction will execute a Python file or an executable file.
| name | |
| path_run | path to run(relative to RoboDK/bin folder or absolute path) |
| path_icon | icon path(relative to RoboDK/bin folder or absolute path) |
| blocking | True if blocking, 0 if it is a non blocking executable trigger |
| cmd_run_on_robot | Command to run through the driver when connected to the robot |
:param name: digital input (string or number)
Definition at line 1861 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void Delete | ( | ) |
Deletes an item and its childs from the station.
Definition at line 624 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void DetachAll | ( | Item | parent | ) |
Detach any object attached to a tool.
Definition at line 698 of file robodk_api.cpp.
Detach the closest object attached to the tool (see also setParentStatic).
Definition at line 685 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| bool Disconnect | ( | ) |
Disconnect from a real robot (when the robot driver is used)
Definition at line 1415 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| bool Finish | ( | ) |
Disconnect from the RoboDK API. This flushes any pending program generation.
Definition at line 2129 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| Mat GeometryPose | ( | ) |
Returns the position (pose) the object geometry with respect to its own reference frame. This procedure works for tools and objects.
Definition at line 840 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| QString getAI | ( | const QString & | io_var | ) |
Get an Analog Input (AI). This function is only useful when connected to a real robot using the robot driver. It returns a string related to the state of the Digital Input (0-1 or other range depending on the robot driver). This function returns an empty string if the script is not executed on the robot.
| io_var | io_var -> analog input (string or number as a string) |
Definition at line 1825 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| QString getDI | ( | const QString & | io_var | ) |
Get a Digital Input (DI). This function is only useful when connected to a real robot using the robot driver. It returns a string related to the state of the Digital Input (1=True, 0=False). This function returns an empty string if the script is not executed on the robot.
| io_var | io_var -> digital input (string or number as a string) |
Definition at line 1811 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| quint64 GetID | ( | ) |
Get the item pointer.
Definition at line 2134 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| Item getLink | ( | int | type_linked = RoboDK::ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT | ) |
Returns an item linked to a robot, object, tool, program or robot machining project. This is useful to retrieve the relationship between programs, robots, tools and other specific projects.
Returns an item pointer (Item class) to a robot, object, tool or program. This is useful to retrieve the relationship between programs, robots, tools and other specific projects.
| type_linked | type of linked object to retrieve |
| type_linked | type of linked object to retrieve |
Definition at line 1184 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| QByteArray getParam | ( | const QString & | param | ) |
Get a specific binary item parameter.
| param | item parameter |
Definition at line 2115 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| GetPointsResult GetPoints | ( | int | featureType = RoboDK::FEATURE_SURFACE, |
| int | featureId = 0 ) |
Retrieves the point under the mouse cursor, a curve or the 3D points of an object. The points are provided in [XYZijk] format in relative coordinates. The XYZ are the local point coordinate and ijk is the normal of the surface.
| featureType | The type of geometry (FEATURE_SURFACE, FEATURE_POINT, ...). Set to FEATURE_SURFACE and if not point or curve was selected, the name of the geometry will be 'point on surface'. |
| featureId | The internal ID to retrieve the right geometry from the object (use SelectedFeature). |
Definition at line 1024 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void Instruction | ( | int | ins_id, |
| QString & | name, | ||
| int & | instype, | ||
| int & | movetype, | ||
| bool & | isjointtarget, | ||
| Mat & | target, | ||
| tJoints & | joints ) |
Returns the program instruction at position id.
| ins_id | |
| name | |
| instype | |
| movetype | |
| isjointtarget | |
| target | |
| joints |
Definition at line 1951 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| int InstructionCount | ( | ) |
Returns the number of instructions of a program.
ADD MORE METHODS
Definition at line 1932 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| int InstructionList | ( | tMatrix2D * | instructions | ) |
Returns the list of program instructions as an MxN matrix, where N is the number of instructions and M equals to 1 plus the number of robot axes.
| instructions | the matrix of instructions |
Definition at line 2004 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| int InstructionListJoints | ( | QString & | error_msg, |
| tMatrix2D ** | joint_list, | ||
| double | mm_step = 10.0, | ||
| double | deg_step = 5.0, | ||
| const QString & | save_to_file = "", | ||
| bool | collision_check = false, | ||
| int | result_flag = 0, | ||
| double | time_step_s = 0.1 ) |
Returns a list of joints an MxN matrix, where M is the number of robot axes plus 4 columns. Linear moves are rounded according to the smoothing parameter set inside the program.
| error_msg | Returns a human readable error message (if any) |
| joint_list | Returns the list of joints as [J1, J2, ..., Jn, ERROR, MM_STEP, DEG_STEP, MOVE_ID] if a file name is not specified |
If flags == LISTJOINTS_SPEED: [J1, J2, ..., Jn, ERROR, MM_STEP, DEG_STEP, MOVE_ID, TIME, X_TCP, Y_TCP, Z_TCP, Speed_J1, Speed_J2, ..., Speed_Jn] If flags == LISTJOINTS_ACCEL: [J1, J2, ..., Jn, ERROR, MM_STEP, DEG_STEP, MOVE_ID, TIME, X_TCP, Y_TCP, Z_TCP, Speed_J1, Speed_J2, ..., Speed_Jn, Accel_J1, Accel_J2, ..., Accel_Jn]
| mm_step | Maximum step in millimeters for linear movements (millimeters) |
| deg_step | Maximum step for joint movements (degrees) |
| save_to_file | Provide a file name to directly save the output to a file. If the file name is not provided it will return the matrix. If step values are very small, the returned matrix can be very large. |
| collision_check | Check for collisions |
| result_flag | set to 1 to include the timings between movements, set to 2 to also include the joint speeds (deg/s), set to 3 to also include the accelerations, set to 4 to include all previous information and make the splitting time-based. |
| time_step_s | (optional) set the time step in seconds for time based calculation. This value is only used when the result flag is set to 4 (time based). |
| error_msg | Returns a human readable error message (if any) |
| joint_list | Returns the list of joints as [J1, J2, ..., Jn, ERROR, MM_STEP, DEG_STEP, MOVE_ID] if a file name is not specified |
| mm_step | Maximum step in millimeters for linear movements (millimeters) |
| deg_step | Maximum step for joint movements (degrees) |
| save_to_file | Provide a file name to directly save the output to a file. If the file name is not provided it will return the matrix. If step values are very small, the returned matrix can be very large. |
| collision_check | Check for collisions |
| result_flag | set to 1 to include the timings between movements, set to 2 to also include the joint speeds (deg/s), set to 3 to also include the accelerations, set to 4 to include all previous information and make the splitting time-based. |
| time_step_s | (optional) set the time step in seconds for time based calculation. This value is only used when the result flag is set to 4 (time based). |
Definition at line 2065 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| bool isJointTarget | ( | ) | const |
Returns True if a target is a joint target (green icon). Otherwise, the target is a Cartesian target (red icon).
Definition at line 1110 of file robodk_api.cpp.
Retrieve the joint limits of a robot.
Returns the joint limits of a robot.
| lower_limits | |
| upper_limits |
Definition at line 1212 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| tJoints Joints | ( | ) | const |
Returns the current joints of a robot or the joints of a target. If the item is a cartesian target, it returns the preferred joints (configuration) to go to that cartesian position.
Definition at line 1125 of file robodk_api.cpp.
Returns the robot configuration state for a set of robot joints.
| joints | array of joints |
| config | configuration status as [REAR, LOWERARM, FLIP] |
| joints | array of joints |
Definition at line 1295 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| tJoints JointsHome | ( | ) | const |
Returns the home joints of a robot. These joints can be manually set in the robot "Parameters" menu, then select "Set home position".
Definition at line 1141 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| bool MakeProgram | ( | const QString & | filename | ) |
Saves a program to a file.
| filename | File path of the program |
| run_mode | RUNMODE_MAKE_ROBOTPROG to generate the program file.Alternatively, Use RUNMODE_MAKE_ROBOTPROG_AND_UPLOAD or RUNMODE_MAKE_ROBOTPROG_AND_START to transfer the program through FTP and execute the program. |
| filename | File path of the program |
Definition at line 1680 of file robodk_api.cpp.
Moves a robot to a specific target ("Move Circular" mode). By default, this function blocks until the robot finishes its movements.
| itemtarget1 | Intermediate target to move to as a target item (RoboDK target item) |
| itemtarget2 | Final target to move to as a target item (RoboDK target item) |
| itemtarget1 | target -> intermediate target to move to as a target item (RoboDK target item) |
| itemtarget2 | target -> final target to move to as a target item (RoboDK target item) |
| blocking | blocking -> True if we want the instruction to block until the robot finished the movement (default=true) |
Definition at line 1502 of file robodk_api.cpp.
Moves a robot to a specific target ("Move Circular" mode). By default, this function blocks until the robot finishes its movements.
| target1 | Intermediate pose target to move to. It must be a 4x4 Homogeneous matrix |
| target2 | Final pose target to move to. It must be a 4x4 Homogeneous matrix |
| target1 | pose -> intermediate pose target to move to. It must be a 4x4 Homogeneous matrix |
| target2 | pose -> final pose target to move to. It must be a 4x4 Homogeneous matrix |
| blocking | blocking -> True if we want the instruction to block until the robot finished the movement (default=true) |
Definition at line 1522 of file robodk_api.cpp.
Moves a robot to a specific target ("Move Circular" mode). By default, this function blocks until the robot finishes its movements.
| joints1 | Intermediate joint target to move to. |
| joints2 | Final joint target to move to. |
| joints1 | joints -> intermediate joint target to move to. |
| joints2 | joints -> final joint target to move to. |
| blocking | blocking -> True if we want the instruction to block until the robot finished the movement (default=true) |
Definition at line 1512 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void MoveJ | ( | const Item & | itemtarget, |
| bool | blocking = true ) |
Moves a robot to a specific target ("Move Joint" mode). By default, this function blocks until the robot finishes its movements. Given a target item, MoveJ can also be applied to programs and a new movement instruction will be added.
Moves a robot to a specific target ("Move Joint" mode). By default, this function blocks until the robot finishes its movements.
| target | Target to move to as a target item (RoboDK target item) |
| target | target -> target to move to as a target item (RoboDK target item) |
| blocking | blocking -> True if we want the instruction to block until the robot finished the movement (default=true) |
Definition at line 1429 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void MoveJ | ( | const Mat & | target, |
| bool | blocking = true ) |
Moves a robot to a specific target ("Move Joint" mode). By default, this function blocks until the robot finishes its movements.
| target | Pose target to move to. It must be a 4x4 Homogeneous matrix |
| target | pose -> pose target to move to. It must be a 4x4 Homogeneous matrix |
| blocking | blocking -> True if we want the instruction to block until the robot finished the movement (default=true) |
Definition at line 1456 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void MoveJ | ( | const tJoints & | joints, |
| bool | blocking = true ) |
Moves a robot to a specific target ("Move Joint" mode). By default, this function blocks until the robot finishes its movements.
| target | Robot joints to move to |
| target | joints -> joint target to move to. |
| blocking | blocking -> True if we want the instruction to block until the robot finished the movement (default=true) |
Definition at line 1447 of file robodk_api.cpp.
Checks if a joint movement is possible and, optionally, free of collisions.
Checks if a joint movement is free of collision.
| j1 | Start joints |
| j2 | Destination joints |
| minstep_deg | Maximum joint step in degrees. If this value is not provided it will use the path step defined in Tools-Options-Motion (degrees). |
| j1 | joints -> start joints |
| j2 | joints -> destination joints |
| minstep_deg | (optional): maximum joint step in degrees |
Definition at line 1533 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void MoveL | ( | const Item & | itemtarget, |
| bool | blocking = true ) |
Moves a robot to a specific target ("Move Linear" mode). By default, this function blocks until the robot finishes its movements. Given a target item, MoveL can also be applied to programs and a new movement instruction will be added.
Moves a robot to a specific target ("Move Linear" mode). By default, this function blocks until the robot finishes its movements.
| itemtarget | Target to move to as a target item (RoboDK target item) |
| itemtarget | target -> target to move to as a target item (RoboDK target item) |
| blocking | blocking -> True if we want the instruction to block until the robot finished the movement (default=true) |
Definition at line 1465 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void MoveL | ( | const Mat & | target, |
| bool | blocking = true ) |
Moves a robot to a specific target ("Move Linear" mode). By default, this function blocks until the robot finishes its movements.
| target | Pose target to move to. It must be a 4x4 Homogeneous matrix |
| target | pose -> pose target to move to. It must be a 4x4 Homogeneous matrix |
| blocking | blocking -> True if we want the instruction to block until the robot finished the movement (default=true) |
Definition at line 1492 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void MoveL | ( | const tJoints & | joints, |
| bool | blocking = true ) |
Moves a robot to a specific target ("Move Linear" mode). By default, this function blocks until the robot finishes its movements.
| joints | Robot joints to move to |
| joints | joints -> joint target to move to. |
| blocking | blocking -> True if we want the instruction to block until the robot finished the movement (default=true) |
Definition at line 1483 of file robodk_api.cpp.
Checks if a linear movement is free of issues and, optionally, collisions.
Checks if a linear movement is free of collision.
| joints1 | Start joints |
| pose2 | Destination pose (active tool with respect to the active reference frame) |
| minstep_mm | Maximum joint step in mm. If this value is not provided it will use the path step defined in Tools-Options-Motion (mm). |
| j1 | joints -> start joints |
| pose2 | joints -> destination pose (active tool with respect to the active reference frame) |
| minstep_mm | (optional): maximum joint step in degrees |
Definition at line 1554 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| QString Name | ( | ) | const |
Returns the name of an item. The name of the item is always displayed in the RoboDK station tree.
Definition at line 774 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void NewLink | ( | ) |
Create a new communication link for RoboDK. Use this for robots if you use a multithread application running multiple robots at the same time.
Definition at line 593 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| Item ObjectLink | ( | int | link_id = 0 | ) |
Returns an item pointer to the geometry of a robot link. This is useful to show/hide certain robot links or alter their geometry.
Returns an item pointer (:class:.Item) to a robot link. This is useful to show/hide certain robot links or alter their geometry.
| link_id | link index(0 for the robot base, 1 for the first link, ...) |
| link_id | link index(0 for the robot base, 1 for the first link, ...) |
Definition at line 1169 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| Item Parent | ( | ) | const |
Return the parent item of this item.
Definition at line 711 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void Pause | ( | double | time_ms = -1 | ) |
Generates a pause instruction for a robot or a program when generating code. Set it to -1 (default) if you want the robot to stop and let the user resume the program anytime.
| time_ms | Time in milliseconds |
Definition at line 1771 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| Mat Pose | ( | ) | const |
Returns the local position (pose) of an object, target or reference frame. For example, the position of an object/frame/target with respect to its parent. If a robot is provided, it will get the pose of the end efector.
Definition at line 815 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| Mat PoseAbs | ( | ) |
Returns the global position (pose) of an item. For example, the position of an object/frame/target with respect to the station origin.
Definition at line 970 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| Mat PoseFrame | ( | ) |
Returns the reference frame pose of an item. If a robot is provided it will get the tool pose of the active reference frame used by the robot.
Definition at line 892 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| Mat PoseTool | ( | ) |
Returns the tool pose of an item. If a robot is provided it will get the tool pose of the active tool held by the robot.
Definition at line 879 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| RoboDK * RDK | ( | ) |
| int RunCode | ( | const QString & | parameters | ) |
Runs a program. It returns the number of instructions that can be executed successfully (a quick program check is performed before the program starts) Program parameters can be provided for Python calls. This is a non-blocking call.Use IsBusy() to check if the program execution finished. Notes: if setRunMode(RUNMODE_SIMULATE) is used -> the program will be simulated (default run mode) if setRunMode(RUNMODE_RUN_ROBOT) is used ->the program will run on the robot(default when RUNMODE_RUN_ROBOT is used) if setRunMode(RUNMODE_RUN_ROBOT) is used together with program.setRunType(PROGRAM_RUN_ON_ROBOT) -> the program will run sequentially on the robot the same way as if we right clicked the program and selected "Run on robot" in the RoboDK GUI.
| parameters | Number of instructions that can be executed |
Definition at line 1736 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| int RunInstruction | ( | const QString & | code, |
| int | run_type = RoboDK::INSTRUCTION_CALL_PROGRAM ) |
Adds a program call, code, message or comment inside a program.
| code | <string of the code or program to run/param>
|
Definition at line 1756 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| int RunProgram | ( | ) |
Runs a program. It returns the number of instructions that can be executed successfully (a quick program check is performed before the program starts) This is a non-blocking call. Use IsBusy() to check if the program execution finished. Notes: if setRunMode(RUNMODE_SIMULATE) is used -> the program will be simulated (default run mode) if setRunMode(RUNMODE_RUN_ROBOT) is used -> the program will run on the robot (default when RUNMODE_RUN_ROBOT is used) if setRunMode(RUNMODE_RUN_ROBOT) is used together with program.setRunType(PROGRAM_RUN_ON_ROBOT) -> the program will run sequentially on the robot the same way as if we right clicked the program and selected "Run on robot" in the RoboDK GUI.
Definition at line 1717 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void Save | ( | const QString & | filename | ) |
Save a station, a robot, a tool or an object to a file.
Save a station or object to a file.
| filename | path and file name |
| filename |
Definition at line 617 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void Scale | ( | double | scale | ) |
Apply a scale to an object to make it bigger or smaller. The scale can be uniform (if scale is a float value) or per axis (if scale is a vector).
------------------------------— add curve, scale, recolor, ...
| scale | scale to apply as scale or [scale_x, scale_y, scale_z] |
Definition at line 1003 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void Scale | ( | double | scale_xyz[3] | ) |
Apply a per-axis scale to an object to make it bigger or smaller. The scale can be uniform (if scale is a float value) or per axis (if scale is a vector).
| scale | scale to apply as [scale_x, scale_y, scale_z] |
Definition at line 1016 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| bool SelectedFeature | ( | int & | featureType, |
| int & | featureId ) |
Retrieve the currently selected feature for this object.
| featureType | The type of geometry, FEATURE_SURFACE, FEATURE_POINT, ... |
| featureId | The internal ID to retrieve the raw geometry (use GetPoints) |
Definition at line 1047 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void setAccuracyActive | ( | int | accurate = 1 | ) |
Sets the accuracy of the robot active or inactive. A robot must have been calibrated to properly use this option.
| accurate | set to 1 to use the accurate model or 0 to use the nominal model |
Definition at line 1662 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void setAO | ( | const QString & | io_var, |
| const QString & | io_value ) |
Set an analog Output.
| io_var | Analog Output |
| io_value | Value as a string |
Definition at line 1798 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void setAsCartesianTarget | ( | ) |
Sets a target as a cartesian target. A cartesian target moves to cartesian coordinates.
Definition at line 1090 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void setAsJointTarget | ( | ) |
Sets a target as a joint target. A joint target moves to a joints position without regarding the cartesian coordinates.
Definition at line 1100 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void setColor | ( | double | colorRGBA[4] | ) |
Changes the color of a robot/object/tool. A color must must in the format COLOR=[R,G,B,(A=1)] where all values range from 0 to 1. Alpha (A) defaults to 1 (100% opaque). Set A to 0 to make an object transparent.
Set the color of an object, tool or robot. A color must in the format COLOR=[R,G,B,(A=1)] where all values range from 0 to 1.
| tocolor | color to change to |
| fromcolor | filter by this color |
| tolerance | optional tolerance to use if a color filter is used (defaults to 0.1) |
Definition at line 983 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void setDO | ( | const QString & | io_var, |
| const QString & | io_value ) |
Sets a variable (output) to a given value. This can also be used to set any variables to a desired value.
| io_var | io_var -> digital output (string or number) |
| io_value | io_value -> value (string or number) |
Definition at line 1785 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void setGeometryPose | ( | const Mat | pose | ) |
Sets the position (pose) the object geometry with respect to its own reference frame. This procedure works for tools and objects.
| pose | 4x4 homogeneous matrix |
| apply_movement | Apply the movement to the inner geometry and not as a pose shift |
| pose | 4x4 homogeneous matrix |
Definition at line 828 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void setInstruction | ( | int | ins_id, |
| const QString & | name, | ||
| int | instype, | ||
| int | movetype, | ||
| bool | isjointtarget, | ||
| const Mat & | target, | ||
| const tJoints & | joints ) |
Sets the program instruction at position id.
| ins_id | |
| name | |
| instype | |
| movetype | |
| isjointtarget | |
| target | |
| joints |
Definition at line 1981 of file robodk_api.cpp.
Set the joint limits of a robot.
| lower_limits | |
| upper_limits |
Definition at line 1227 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void setJoints | ( | const tJoints & | jnts | ) |
Set robot joints or the joints of a target.
Sets the current joints of a robot or the joints of a target. It the item is a cartesian target, it returns the preferred joints (configuration) to go to that cartesian position.
| joints |
Definition at line 1199 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void setJointsHome | ( | const tJoints & | jnts | ) |
Set robot joints for the home position.
Sets the joint position of the "home" joints for a robot.
| joints |
Definition at line 1156 of file robodk_api.cpp.
Update the robot milling path input and parameters. Parameter input can be an NC file (G-code or APT file) or an object item in RoboDK. A curve or a point follow project will be automatically set up for a robot manufacturing project.
Tip: Use getLink() and setLink() to get/set the robot tool, reference frame, robot and program linked to the project.
Tip: Use setPose() and setJoints() to update the path to tool orientation or the preferred start joints.
Tip: Use setPoseTool() and setPoseFrame() to link to the corresponding tool and reference frames.
Update the robot milling path input and parameters. Parameter input can be an NC file (G-code or APT file) or an object item in RoboDK. A curve or a point follow project will be automatically set up for a robot manufacturing project. Tip: Use getLink() and setLink() to get/set the robot tool, reference frame, robot and program linked to the project. Tip: Use setPose() and setJoints() to update the path to tool orientation or the preferred start joints.
| ncfile | path to the NC (G-code/APT/Point cloud) file to load (optional) |
| part_obj | object holding curves or points to automatically set up a curve/point follow project (optional) |
| options | Additional options (optional) |
| ncfile | path to the NC (G-code/APT/Point cloud) file to load (optional) |
| part_obj | object holding curves or points to automatically set up a curve/point follow project (optional) |
| options | Additional options (optional) |
Definition at line 1071 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void setName | ( | const QString & | name | ) |
| void setParam | ( | const QString & | param, |
| const QByteArray & | value ) |
Set a specific binary item parameter.
| param | item parameter |
| value | binary data |
Definition at line 2106 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| QString setParam | ( | const QString & | param, |
| const QString & | value ) |
Set a specific item parameter. Select Tools-Run Script-Show Commands to see all available commands for items and the station. Note: For parameters (commands) that require a JSON string value you can also provide a dict.
| param | item parameter |
| value | value |
Definition at line 2095 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void setParent | ( | Item | parent | ) |
Attaches the item to a new parent while maintaining the relative position with its parent. The absolute position is changed.
| parent |
Definition at line 647 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void setParentStatic | ( | Item | parent | ) |
Attaches the item to another parent while maintaining the current absolute position in the station. The relationship between this item and its parent is changed to maintain the abosolute position.
| parent | parent item to attach this item to |
| parent | parent item to attach this item |
Definition at line 660 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void setPose | ( | const Mat | pose | ) |
Sets the local position (pose) of an object, target or reference frame. For example, the position of an object/frame/target with respect to its parent. If a robot is provided, it will set the pose of the end efector.
| pose | 4x4 homogeneous matrix |
Definition at line 802 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void setPoseAbs | ( | const Mat | pose | ) |
Sets the global position (pose) of an item. For example, the position of an object/frame/target with respect to the station origin.
| pose | 4x4 homogeneous matrix (pose) |
Definition at line 957 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void setPoseFrame | ( | const Item | frame_item | ) |
Sets the tool of a robot or a tool object (Tool Center Point, or TCP). The tool pose can be either an item or a 4x4 Matrix. If the item is a tool, it links the robot to the tool item.If tool is a pose, it updates the current robot TCP.
| pose | 4x4 homogeneous matrix (pose) |
Definition at line 919 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void setPoseFrame | ( | const Mat | frame_pose | ) |
Sets the reference frame of a robot(user frame). The frame can be either an item or a pose. If "frame" is an item, it links the robot to the frame item. If frame is a pose, it updates the linked pose of the robot frame (with respect to the robot reference frame).
| frame_pose | 4x4 homogeneous matrix (pose) |
Definition at line 906 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void setPoseTool | ( | const Item | tool_item | ) |
Sets the tool of a robot or a tool object (Tool Center Point, or TCP). The tool pose can be either an item or a 4x4 Matrix. If the item is a tool, it links the robot to the tool item.If tool is a pose, it updates the current robot TCP.
| tool_item | Tool item |
Definition at line 945 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void setPoseTool | ( | const Mat | tool_pose | ) |
Sets the tool of a robot or a tool object (Tool Center Point, or TCP). The tool pose can be either an item or a 4x4 Matrix. If the item is a tool, it links the robot to the tool item.If tool is a pose, it updates the current robot TCP.
| tool_pose | 4x4 homogeneous matrix (pose) |
Definition at line 932 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void setRobot | ( | const Item & | robot | ) |
Sets the robot of a program or a target. You must set the robot linked to a program or a target every time you copy paste these objects. If the robot is not provided, the first available robot will be chosen automatically.
| robot | Robot item |
Definition at line 1242 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void setRounding | ( | double | zonedata | ) |
Sets the robot movement smoothing accuracy (also known as zone data value).
| rounding_mm | Rounding value (double) (robot dependent, set to -1 for accurate/fine movements) |
| zonedata | zonedata value (int) (robot dependent, set to -1 for fine movements) |
Definition at line 1593 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void setRunType | ( | int | program_run_type | ) |
Sets if the program will be run in simulation mode or on the real robot. Use: "PROGRAM_RUN_ON_SIMULATOR" to set the program to run on the simulator only or "PROGRAM_RUN_ON_ROBOT" to force the program to run on the robot.
Definition at line 1700 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void setSpeed | ( | double | speed_linear, |
| double | speed_joints = -1, | ||
| double | accel_linear = -1, | ||
| double | accel_joints = -1 ) |
Sets the speed and/or the acceleration of a robot.
| speed_linear | linear speed in mm/s (-1 = no change) |
| accel_linear | linear acceleration in mm/s2 (-1 = no change) |
| speed_joints | joint speed in deg/s (-1 = no change) |
| accel_joints | joint acceleration in deg/s2 (-1 = no change) |
| speed_linear | linear speed in mm/s (-1 = no change) |
| speed_joints | joint speed in deg/s (-1 = no change) |
| accel_linear | linear acceleration in mm/s2 (-1 = no change) |
| accel_joints | joint acceleration in deg/s2 (-1 = no change) |
Definition at line 1576 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void setVisible | ( | bool | visible, |
| int | visible_frame = -1 ) |
Sets the item visiblity status.
| visible | |
| visible_reference | set the visible reference frame (1) or not visible (0) |
| visible | |
| visible_frame | srt the visible reference frame (1) or not visible (0) |
Definition at line 757 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void ShowInstructions | ( | bool | visible = true | ) |
Show or hide instruction items of a program in the RoboDK tree.
| show |
Definition at line 1906 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void ShowSequence | ( | tMatrix2D * | sequence | ) |
Displays a sequence of joints.
| sequence | joint sequence as a 6xN matrix or instruction sequence as a 7xN matrix |
Definition at line 1605 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void ShowTargets | ( | bool | visible = true | ) |
Show or hide targets of a program in the RoboDK tree.
| show |
Definition at line 1918 of file robodk_api.cpp.
Computes the forward kinematics of the robot for the provided joints. The tool and the reference frame are not taken into account.
| joints |
Definition at line 1273 of file robodk_api.cpp.
Computes the inverse kinematics for the specified robot and pose. The joints returned are the closest to the current robot configuration (see SolveIK_All())
| pose | 4x4 matrix -> pose of the robot flange with respect to the robot base frame |
| joints_close | Aproximate joints solution to choose among the possible solutions. Leave this value empty to return the closest match to the current robot position. |
| tool_pose | Optionally provide a tool pose, otherwise, the robot flange is used. Tip: use robot.PoseTool() to retrieve the active robot tool. |
| reference_pose | Optionally provide a reference pose, otherwise, the robot base is used. Tip: use robot.PoseFrame() to retrieve the active robot reference frame. |
| pose | 4x4 matrix -> pose of the robot flange with respect to the robot base frame |
| tool | 4x4 matrix -> Optionally provide a tool, otherwise, the robot flange is used. Tip: use robot.PoseTool() to retrieve the active robot tool. |
| reference | 4x4 matrix -> Optionally provide a reference, otherwise, the robot base is used. Tip: use robot.PoseFrame() to retrieve the active robot reference frame. |
Definition at line 1313 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| tJoints SolveIK | ( | const Mat | pose, |
| tJoints | joints_approx, | ||
| const Mat * | tool = nullptr, | ||
| const Mat * | ref = nullptr ) |
Computes the inverse kinematics for the specified robot and pose. The joints returned are the closest to the current robot configuration (see SolveIK_All())
| pose | 4x4 matrix -> pose of the robot flange with respect to the robot base frame |
| joints_approx | Aproximate solution. Leave empty to return the closest match to the current robot position. |
| tool | 4x4 matrix -> Optionally provide a tool, otherwise, the robot flange is used. Tip: use robot.PoseTool() to retrieve the active robot tool. |
| reference | 4x4 matrix -> Optionally provide a reference, otherwise, the robot base is used. Tip: use robot.PoseFrame() to retrieve the active robot reference frame. |
Definition at line 1341 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| QList< tJoints > SolveIK_All | ( | const Mat & | pose, |
| const Mat * | tool = nullptr, | ||
| const Mat * | ref = nullptr ) |
Computes the inverse kinematics for the specified robot and pose. The function returns all available joint solutions as a 2D matrix.
| pose | 4x4 matrix -> pose of the robot tool with respect to the robot frame |
| tool_pose | Optionally provide a tool pose, otherwise, the robot flange is used. Tip: use robot.PoseTool() to retrieve the active robot tool. |
| reference_pose | Optionally provide a reference pose, otherwise, the robot base is used. Tip: use robot.PoseFrame() to retrieve the active robot reference frame. |
Definition at line 1383 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| tMatrix2D * SolveIK_All_Mat2D | ( | const Mat & | pose, |
| const Mat * | tool = nullptr, | ||
| const Mat * | ref = nullptr ) |
Computes the inverse kinematics for the specified robot and pose. The function returns all available joint solutions as a 2D matrix.
| pose | 4x4 matrix -> pose of the robot tool with respect to the robot frame |
| tool_pose | Optionally provide a tool pose, otherwise, the robot flange is used. Tip: use robot.PoseTool() to retrieve the active robot tool. |
| reference_pose | Optionally provide a reference pose, otherwise, the robot base is used. Tip: use robot.PoseFrame() to retrieve the active robot reference frame. |
| pose | 4x4 matrix -> pose of the robot tool with respect to the robot frame |
Definition at line 1366 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void Stop | ( | ) |
| QString ToString | ( | ) | const |
Definition at line 574 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| int Type | ( | ) | const |
Item type (object, robot, tool, reference, robot machining project, ...)
Returns the type of an item (robot, object, target, reference frame, ...)
GENERIC ITEM CALLS
Definition at line 602 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| double Update | ( | int | collision_check = RoboDK::COLLISION_OFF, |
| int | timeout_sec = 3600, | ||
| double * | out_nins_time_dist = nullptr, | ||
| double | mm_step = -1, | ||
| double | deg_step = -1 ) |
Updates a program and returns the estimated time and the number of valid instructions. An update can also be applied to a robot machining project. The update is performed on the generated program.
| collision_check | check_collisions: Check collisions (COLLISION_ON -yes- or COLLISION_OFF -no-) |
| timeout_sec | Maximum time to wait for the update to complete (in seconds) |
| out_nins_time_dist | optional double array [3] = [valid_instructions, program_time, program_distance] |
| mm_step | Maximum step in millimeters for linear movements (millimeters). Set to -1 to use the default, as specified in Tools-Options-Motion. |
| deg_step | Maximum step for joint movements (degrees). Set to -1 to use the default, as specified in Tools-Options-Motion. |
Definition at line 2026 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| bool Valid | ( | bool | check_deleted = false | ) | const |
Check if an item is valid (not null and available in the open station)
Checks if the item is valid. An invalid item will be returned by an unsuccessful function call.
| item_check | Item to check |
True if the item exists, false otherwise
true if valid, false if invalid
Definition at line 637 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| bool Visible | ( | ) | const |
Returns 1 if the item is visible, otherwise, returns 0.
Definition at line 744 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void waitDI | ( | const QString & | io_var, |
| const QString & | io_value, | ||
| double | timeout_ms = -1 ) |
Waits for an input io_id to attain a given value io_value. Optionally, a timeout can be provided.
| io_var | io_var -> digital output (string or number) |
| io_value | io_value -> value (string or number) |
| timeout_ms | int (optional) -> timeout in miliseconds |
Definition at line 1841 of file robodk_api.cpp.
| void WaitMove | ( | double | timeout_sec = 300 | ) | const |
Waits (blocks) until the robot finishes its movement.
| timeout_sec | timeout -> Max time to wait for robot to finish its movement (in seconds) |
Definition at line 1642 of file robodk_api.cpp.
|
friend |
Definition at line 1778 of file robodk_api.h.
|
private |
Pointer to the item inside RoboDK.
Definition at line 2545 of file robodk_api.h.
|
private |
Pointer to RoboDK link object.
Definition at line 2542 of file robodk_api.h.
|
private |
Item type.
Definition at line 2548 of file robodk_api.h.