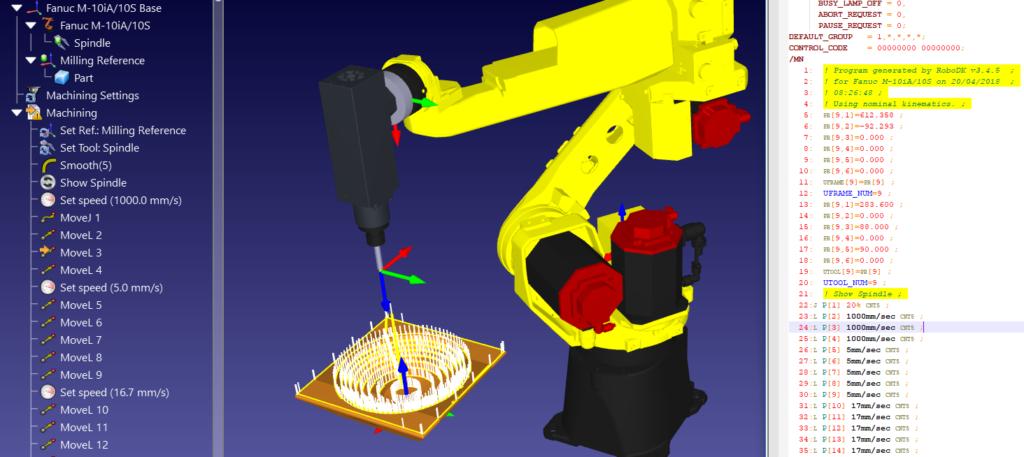
You want to layout your production plant in the right way. But how do you do that? Good plant layout design will help you get the most from your robotic investment.
Do robots have an impact on your plant layout?
You probably know that you need to optimize your plant layout so your products move efficiently from one production stage to another. But, it’s sometimes not so clear how to design a good layout.
Robots can help to improve the efficiency of your entire operations. But it matters where you place them in your plant.
Here is a quick guide on how to think about incorporating a robot into a production process.
What is Plant Layout Design? And Do You Need It?
Plant layout design is the process of optimizing the physical layout of components and processes within a production facility. It is a discipline with extensive research, software tools, and algorithms. The goal of this discipline is to improve the flow and efficiency of production processes.
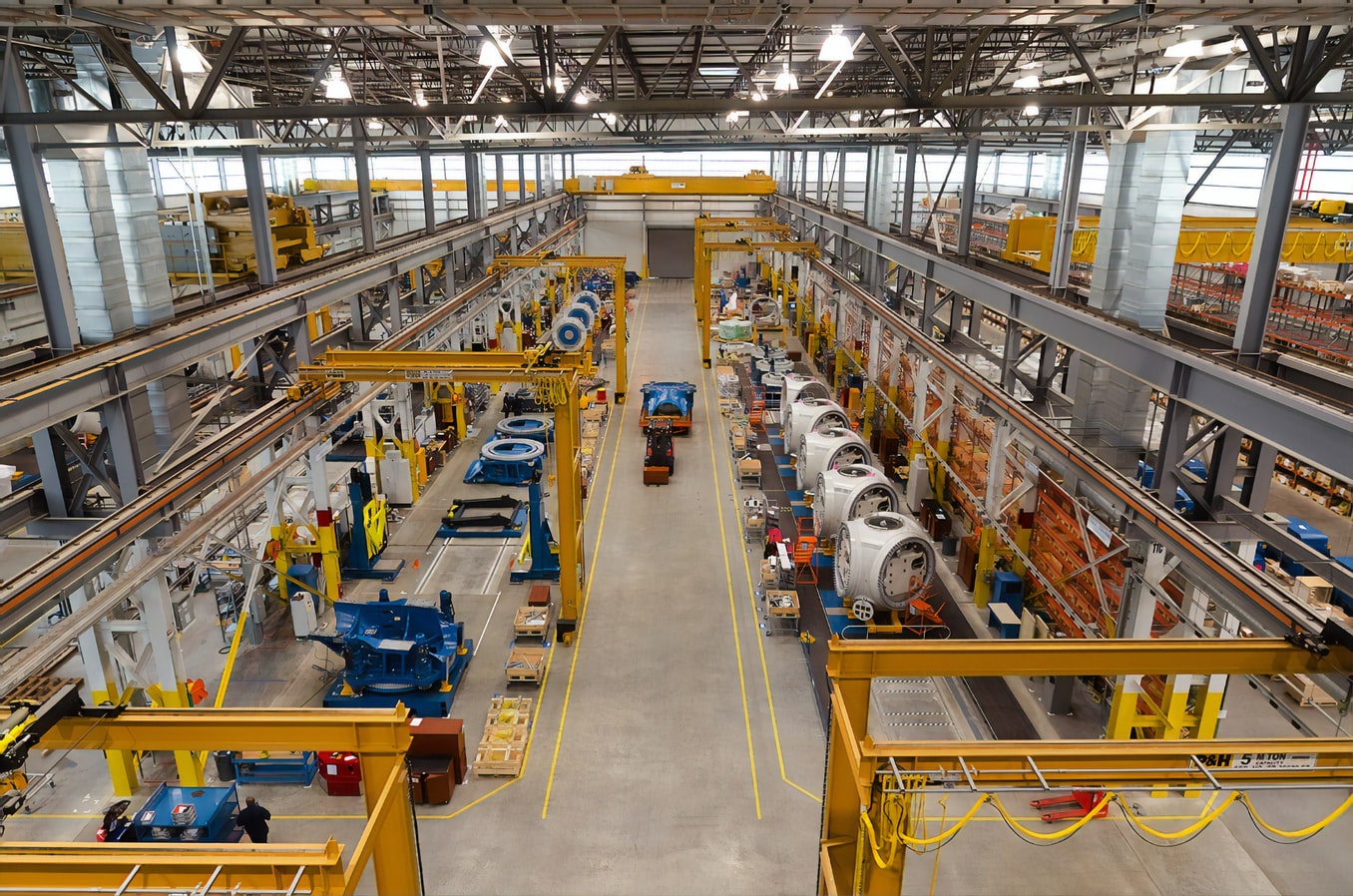

Why would you need to perform plant layout design on your facility? One reason is that it helps you to see how productive your plant could be and identify areas for improvement.
As plant design researchers explain “The layout design problem is a strategic issue and has a significant impact on the efficiency of a manufacturing system.”
When you get the layout design right, everything in your facility will move more efficiently. As a result, the whole factory will likely be more productive and produce less waste.
How to Improve Your Production Floor Layout
Whether you are using robots or not, the core goal of plant layout design is to improve your overall efficiency. You want to reduce the distances between the stages of your process, the number of physical touches of the workpieces, and unnecessary inventory.
Some people wrongly assume that you should only design your production floor layout when you are first designing your facility. While this is clearly an important moment in the life of a manufacturing plant, it’s only the beginning.
There are many opportunities for you to further optimize your plant layout over time.
One great moment to reassess your plant layout is when you add robotic automation. A robot can either subtly or drastically change the flow of your production. You want to ensure that you position it in the optimal place in your facility to make the most of its capabilities.
5 Tips for Designing a Process Layout for Robotics
Imagine you were to simply place your robot in the first available space in your facility. Perhaps it is in an empty corner, far away from most of the other processes. The robot’s positioning would soon become a problem. Soon, your team would be spending almost all their time moving items to and from the robot.
Here are 5 tips for incorporating a robot into your plant layout the right way:
1. Start With Your Manual Layout
You have probably performed the robot’s task manually for some time. There is no need to completely reinvent the operation when you automate it with a robot.
Look at your existing manual process and use it as a starting point. This will help make the transition to a robotic operation much smoother.

2. Break Your Task Into Steps
Break down your manual task into discrete steps.
This serves two purposes:
- It gives you a clear understanding of the task and how it feeds into your other processes.
- It gives you a map of the steps that the robot will have to perform. These form the blueprint of the robot deployment.
3. Use Simulation to Improve Your Design
Drawing out your layout on a piece of paper is a good start. However, you will gain a much deeper understanding of your cell layout when you use simulation software.
A good robot simulator will allow you to model the various aspects of your robot application. It will clearly show you how the components will interact with each other, helping you to optimize your application.
4. Minimize Movement Waste
One of the major wastes in any manufacturing process is unnecessary movement. If you can reduce the distance that products move through your process, you will start to see many ways to remove this waste.
Often, multiple processes feed into and out of a robot cell. Use your simulation software to identify ways to minimize movement waste.
5. Be Aware of Space Restrictions
Look at the space that your robot cell will require. Remember to include additional aspects like the size of conveyors, the robot’s various accessories, and the required safety distances around the robot.
Then identify where in your facility you have enough space to fit the robot.
Where would be the optimal position for the robot? And how can you move operations to make that positioning possible?
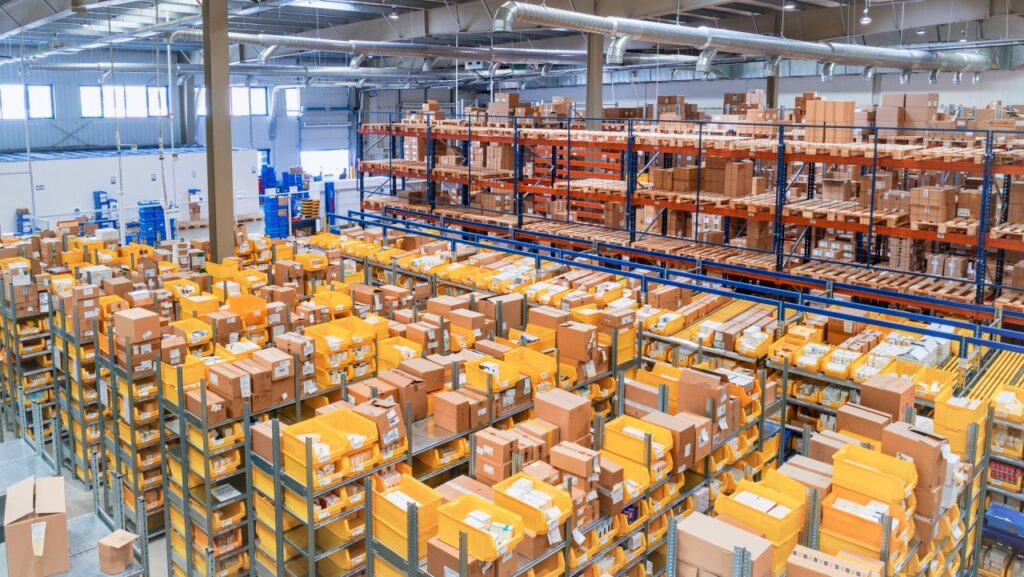

What Does a Good Factory Floor Plan Look Like?
A well-designed factory is clear, simple, and uncluttered.
One sign that you have designed your factory floor plan effectively is that people aren’t running around all the time to solve problems. There are no “spaghetti networks” of conveyors feeding into the robot.
Each step of your process effortlessly feeds into the next step. Actions are obvious and well-planned.
Achieving a well-designed manufacturing facility isn’t only about the layout of your components. It’s also about having an efficient process flow.
If you are using robots, one of the best actions you can take to improve this process flow is to model your robotic application in a good robot simulator. This helps you to see all of the steps in action so that you can easily identify areas for improvement.
What aspects of plant layout design do you currently struggle with? Tell us in the comments below or join the discussion on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, or in the RoboDK Forum.. Also, check out our extensive video collection and subscribe to the RoboDK YouTube Channel.