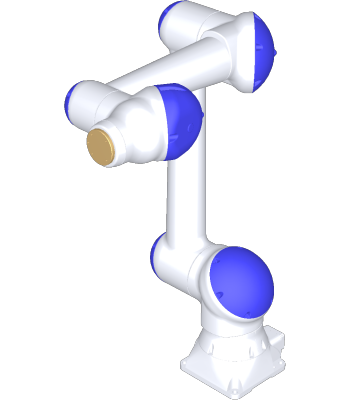
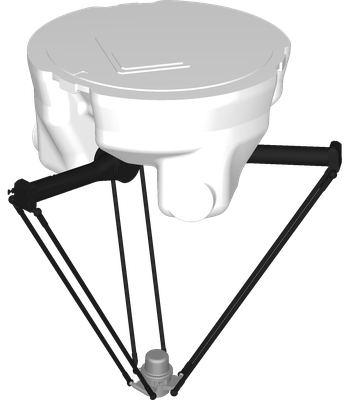
Yaskawa, one of the biggest Japanese manufacturers of robotic hardware, has securely made its name in the global worldwide robotics landscape.
Established in 1915, Yaskawa has continually marked itself as an innovator through its Motoman series of industrial robots. The company has been constantly innovating in large and small ways, from introducing the L10WA in 1983 (the first 6-axis robot to feature an extra wrist) to the new MotoMini, one of the smallest and lightest 6-axis robot in the industry.
In this spotlight on Yaskawa, we’ll look at how you can program Yaskawa robots easily for your chosen application.
The Yaskawa Story: What Sets Yaskawa Robots Apart
Yaskawa has passed some momentous milestones in recent years. In 2015, it celebrated its 100th anniversary and in 2021 they sold their 500,000th robot. With this rising popularity, many more people are using Yaskawa robots for a wide range of applications.
Founded by Daigorou Yasukawa, the company’s story began in 1915 when it began manufacturing three-phase induction motors. Yaskawa’s robotic journey began in the 1960s with the introduction of various robotic products, including MOTO fingers and arms. Their first full electric robot, MOTOMAN-L10, was completed in 1977.
Yaskawa’s core brand values revolve around the principles of quality, profitability, and market satisfaction. The company is committed to using its technologies to improve management efficiency and contribute to social development and human welfare.

What Industries are Yaskawa Robots Used In?
Yaskawa’s industrial robots have found widespread adoption across various sectors, solidifying its position as a global leader.
Within the electrical and electronic manufacturing industry, companies utilize Yaskawa robots throughout the entire production process, from upstream production to downstream testing and shipping. Their smaller robots prove particularly advantageous for manufacturers operating within limited space.
For industries like biomedical and semiconductor manufacturing, Yaskawa provides specific robot solutions that can operate under hygiene control requirements.
Other industries include food production, logistics, and automotive manufacturing.
3 Example Applications for Yaskawa Robots
Whatever application you are looking to deploy, it’s likely a Yaskawa robot exists to help you to achieve it.
Here are 3 example applications from different industries that people are already achieving with Yaskawa robots:
1. Electronics mounting, welding, and painting
In the “3C” industry (Communication, Computer, and Consumer Electronics), robots are involved at almost all stages.
Yaskawa robots are often used in the construction and finishing of circuit boards. This includes assembly of the casings, welding and soldering of metal pieces, and painting of the final product.
A particular challenge for such applications is often space restrictions, which Yaskawa has addressed with a range of small, light robots.
2. Experiment preparation and analysis
In the biomedical manufacturing industry, Yaskawa robotic solutions that operate under strict hygiene controls with high precision.
One type of application in this industry includes the preparation of biological specimens for testing and running of the tests.
By using such robots, the skilled biological researchers can focus on more high-level tasks like analyzing the data gathered during the tests.
3. Flat Panel Display Glass Transporting
Many applications in the semiconductor manufacturing industry are suitable for robotic automation.
One such task involves manufacturing Flat Panel Display (FPD) glass, which companies use to produce computer monitors, smartphones, and televisions.
Robots are an ideal solution for handling and processing of this glass as even small amounts of dust can jeopardize the product quality.

Options for Programming Yaskawa Robots
Whatever application you choose for your Yaskawa robot, it’s important to find a method of programming that helps you to deploy the robot easily and efficiently.
There are 3 main options for programming a Yaskawa robot:
- Brand Programming Langauge: Inform II — the primary language for programming is Inform II, though Yaskawa also supports some PLC-integrated options. This is the most labor-intensive method.
- Teach Pendant — A very common method of teaching Yaskawa robots is to use the teach pendant, which involves manually guiding the robot through movements. It is a time-consuming approach.
- RoboDK — For a more intuitive and graphical approach to programming, supported by a powerful API if you need it, you can also program your Yaskawa robots offline using RoboDK.
Spotlight on 3 Models in the RoboDK Library
The robot library includes an extensive collection of Yaskawa robots models.
At the time of writing, it includes over 90 Yaskawa models, of various types, including 5 and 6 DoF arms, Delta, Scara, and palletizing robots, as well as external axes.
Here are 3 models that you can find in the library:
Robot 1: Yaskawa HC10
The Yaskawa HC10 is a 6-axis robot that is commonly used for arc welding applications. It offers a 10 kg payload, 1.2 m of reach, and a repeatability of 0.1 mm.
This collaborative robot is designed to enhance current production by adding collaborative welding capabilities.
Robot 2: Motoman MPP3
The Motoman MPP3 is a 4-axis Delta robot that balances compact design and operational reach. It has a 1 kg payload, 650 mm of reach, and repeatability of 0.1 mm. It is also on the heavy side at 115 kg weight.
Optimized for primary packaging this robot is ideal for the food industry as it uses an NSF-H1 certified food-grade lubricants and anti-corrosive coating.
Robot 3: Motoman MPL800II
The Motoman MPL800II is a 4-axis palletizing robot arm offering an impressive 800 kg of payload and 3.2 m of reach. The repeatability is 0.5 mm and its weight is 2550 kg.
With its large payload, this is the largest palletizing robot that Yaskawa manufactures.
How to Program Yaskawa Robots Easily with RoboDK
If you want to streamline the deployment process for your Yaskawa industrial robot, it’s worth looking at using RoboDK for your programming.
RoboDK’s rich simulation environment makes it easy to quickly design robot programs and test them before you put the robot into production. The intuitive graphical interface allows you to quickly create robust programs while the API allows you to incorporate any advanced features you want.
To start, download a trial copy of RoboDK from our download page and load up your favorite robot model.
Which Yaskawa model do you use and for which applications? Tell us in the comments below or join the discussion on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, or in the RoboDK Forum.. Also, check out our extensive video collection and subscribe to the RoboDK YouTube Channel