As one of the world’s most powerful numerical computing platforms, MATLAB® is used by millions of engineers and scientists worldwide. Sitting at the forefront of research and innovation, this software from MathWorks offers unparalleled features for advanced robotics.
RoboDK has a strong integration with the MathWorks platform. Compared to alternatives, this pairing provides a more robust and practical way to introduce advanced algorithms into your industrial robotic deployments.
In this article, we show some examples of real-world applications and explain how you can use RoboDK and MATLAB software in your own projects.
Introducing… MathWorks, MATLAB, and Simulink®
MathWorks is the company behind the widely popular software platform, MATLAB and Simulink. Used extensively in research, education, and industry, these tools are the birthplace of many of the world’s most pioneering developments.
Simulink — Simulink is a block diagram environment for multidomain simulation and Model-Based Design. It supports system-level design, simulation, automatic code generation, and continuous test and verification of embedded systems. Simulink provides a graphical editor, customizable block libraries, and solvers for modeling and simulating dynamic systems.
MATLAB — MATLAB is a high-level language and interactive environment for numerical computation, visualization, and programming. It enables you to analyze data, develop algorithms, and create models and applications. With MATLAB, you can perform tasks ranging from quick calculations to large-scale simulations. With Robotics System Toolbox™ available in MATLAB, engineers gain ready-to-use algorithms and simulations for motion planning, control, and testing of robotic systems. Widely adopted across research, education, and industry, MATLAB powers applications from signal and imaging processing to AI, robotics, and advanced system design.
What’s Missing? How RoboDK Adds Robust Industrial Support
While MATLAB excels in modeling, simulation, and algorithm design, it doesn’t natively provide integration with the broad ecosystem of industrial robots used in factories worldwide. This creates a gap in direct deployment workflows – particularly around hardware connectivity and rapid implementation in some industrial environments.
That’s where the RoboDK integration comes in…
RoboDK bridges this gap by offering extensive support for over 1000 industrial robot models from many robot brands. With our dedicated plugins, it is quick and straightforward to send MATLAB and Simulink programs to your robotic hardware and work in tandem with these powerful software tools. Together, these two platforms create a comprehensive solution for both research and industrial applications. This reliable integration enables users to leverage MATLAB and Simulink for advanced tasks. Like AI, computer vision, and state machine design while ensuring compatibility with industrial-grade robotics hardware.
3 Real-World Applications with RoboDK and MATLAB
The power of RoboDK and MATLAB comes when you can see how you can apply them to real-world applications.
Here are 3 examples of real-world applications where the platforms combine for advanced robotics:
1. Smarter QA Testing with Vision-Guided Robots
One promising application is using MATLAB for quality assurance (QA) testing and inspection.
In this case, the vision system captures product data. The visual information is then processed with MATLAB’s powerful processing algorithms, identifying tasks or areas to inspect. These tasks are then dynamically sent to RoboDK. Which commands the robot to move precisely between inspection points.To learn more about the use of MATLAB and deep learning for automated inspection, see here.
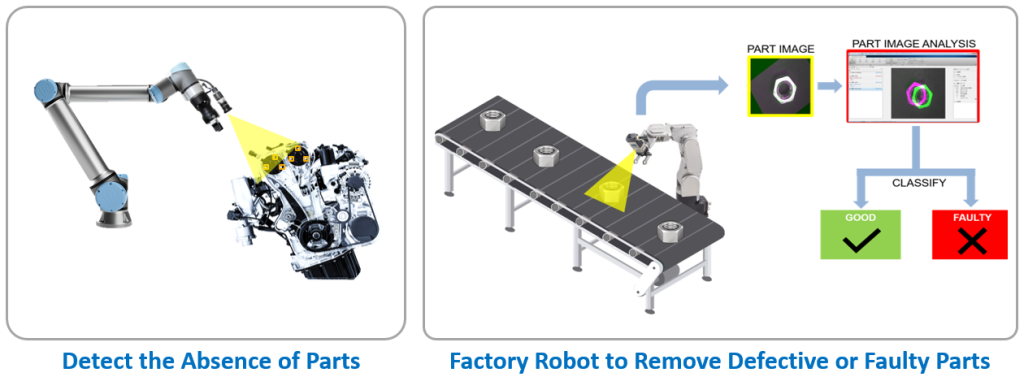
Using MATLAB and deep learning to perform visual inspection.
2. Optimal & Collision-Free Motion in Industrial Tasks
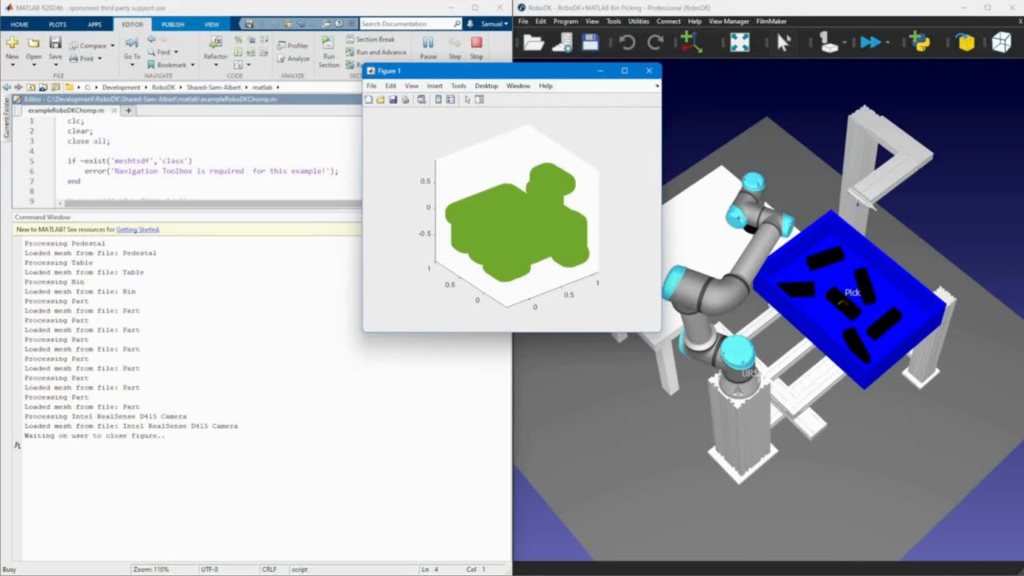
At the recent International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2025), an application was demonstrated using RoboDK and MATLAB for an advanced bin-picking application.
By applying the CHOMP algorithm for rigid body motion planning, the team optimized robot trajectories to be both collision-avoiding and smooth, ensuring efficient and reliable performance in a bin-picking task. This highlights how the integration of RoboDK and MATLAB enables the design of an optimal path that balances safety, precision, and execution speed.
3. From Algorithm to Real Robot: Real-Time Deployment Powered by MATLAB + RoboDK
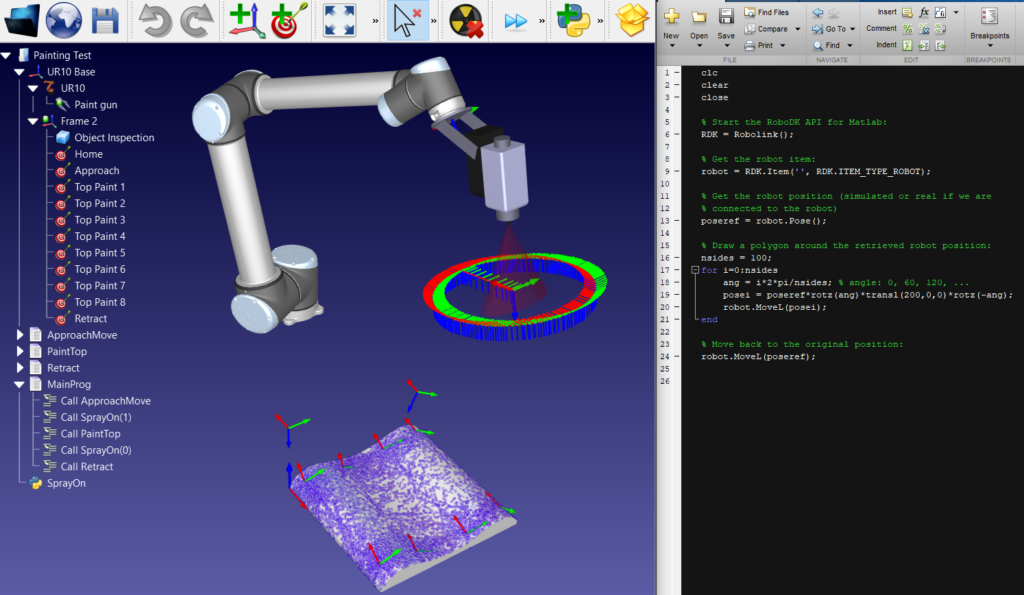
A key advantage of the MATLAB–RoboDK workflow is the ability to take algorithms that were designed, simulated, and verified in MATLAB. And use RoboDK to deploy them directly to industrial robot hardware.
A recent example used a Mecademic MECA500 robot to demonstrate this end-to-end workflow. The development team first used MATLAB to generate a complex polygon-drawing algorithm and validated the motion virtually using MATLAB’. Once the algorithm behaved as intended, the same trajectory was passed through RoboDK, which handled communication with the robot and executed the commands in real time—both in the RoboDK simulator and on the physical MECA500.
Algorithm designed and simulated in MATLAB, deployed in real time to the MECA500 through RoboDK
Preparing the Next Generation of Robotics Engineers
With MATLAB’s proven impact across industry and education, the collaboration with RoboDK opens even more doors for educational robotics.
The combination of these powerful software tools allows students and teachers to design and test algorithms in MATLAB/Simulink and then immediately validate those in an accurate robot simulation. This combination is more robust than alternatives, such as ROS, which can have limitations in stability, real-time performance, and technical support.
With RoboDK’s extensive Robot Library, the students gain access to the same robotic hardware used in industry. From industry-leading brands like KUKA and ABB to education-compatible platforms like Dobot, this will give students skills that will directly apply to careers beyond educational settings.
RoboDK is already a go-to platform for many educational and research projects. With the MATLAB integrations, this truly closes the gap with industrial robotics and the next generation of engineers.
Getting Started with RoboDK + MATLAB
Are you ready to bridge the gap between advanced programming and industrial robotics?
Whether you are an engineer, researcher, student, or something else, the RoboDK and MathWorks integration empowers you to take your robotic projects to the next level.
A good place to start is to familiarize yourself with RoboDK and its capabilities. You could start by creating a simple program with the MATLAB API to program your simulated robot from within the MATLAB environment. From there, you are limited only by your imagination!
By integrating the immense computing power of MATLAB/Simulink with RoboDK’s extensive robot compatibility, you can create robot applications that could even innovate the next generation of robotics.
What application will you create first with MATLAB and RoboDK? Join the discussion on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, or in the RoboDK Forum.. Also, check out our extensive video collection and subscribe to the RoboDK YouTube Channel.